Introduction
The emergence of the COVID-19, belonging to the Betacorona virus genus and responsible for the SARS-CoV-2, has expanded worldwide since December 20191. According to the report 185 of the World Health Organization as of July 23, 2020, there have been 15012731 cases and 619 150 deaths worldwide2.
The incubation period for COVID-19 infection occurs in an ap proximate range of 2 to 14 days, however, incubation periods of 21, 22, or 27 days have been reported3. Most of the patients present a clinical picture with fever and cough, as well as al terations in the results of the chest tomography4-6. To a lesser extent, patients present symptoms such as muscle pain, fatigue, diarrhea, hemoptysis, headache and/or throat, chest tightness, and difficulty breathing, runny nose, nausea, vomiting5,6. The disease lasts approximately up to 2 weeks, or from 3 to 6 weeks if it becomes critical, it has been possible to describe that from the onset of symptoms to death, taking between 2 to 8 weeks1,7.
Globally, COVID-19 infection has been associated with high morbidity with the preexistence of chronic medical condi tions such as hypertension, cardiovascular disease, diabe tes, and chronic respiratory disease. Likewise, advanced age was associated with an increased risk of developing acute respiratory distress syndrome8 and death, probably due to a less vigorous immune response9, or due to both factors, being an older adult and presenting some comorbidity10.
Survival analyzes allow evaluating the statistics in the time that elapses between an initial event and a final event (death or recovery from the disease), deducing the event rates ba sed on the time necessary for the event to occur11. Survival analysis can handle correct censorship, recurring events, competitive risks since we have representative sets of risks available at each time point to allow us to model and esti mate even rates11.
In Colombia, the first positive case for COVID-19 was repor ted on March 6, 202012, and subsequently, the first death at tributed to COVID-19 infection was reported on March 21, 202013, figures that increased to a total of 211,038 confirmed cases and 7,166 deaths attributed to COVID-19 infection as of July 23, 20202, with an estimated average of 6.8 people/ day admitted to an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) (14. In this sense, the purpose of this study was to analyze the risk factors as sociated with the mortality and survival of COVID-19 cases in a cohort that involved the cases of positive patients reported to the surveillance system during the first five months (March 6 to July 8 of 2020) of a pandemic in Colombia.
Materials and methods
Population and design
A retrospective cohort study was carried out in the Colom bian population diagnosed with COVID-19. All the cases no tified to the Epidemiological Surveillance System - SIVIGILA - were included with the code 346 between March 6 and July 8, 2020.
Data collection
Access was obtained to an anonymized database containing sociodemographic information, clinical data, and laboratory results on the molecular diagnostic tests SARS-CoV-2, con tained in the epidemiological notification sheet for respira tory viruses 346. The variable of the outcome of the patient recovered or diad. Patients without data information on the date of onset of symptoms or death were excluded. The data were censored by the end date of the cohort follow-up. The time was recorded from the onset of symptoms to the date of death or end of follow-up, with a loss of 11.6% (14,949 data) due to lack of dates.
Epidemiological and laboratory surveillance data
The data analyzed in the present study were reported to the National Surveillance System, and they presen ted a positive result for the molecular test for detection of the polymerase chain reaction with reverse transcrip tase over time (RT-PCR) from nasopharyngeal samples.
Statistics analysis
Survival was defined as the death outcome caused by the disease11, the time was calculated from the date of onset of symptoms to the date of death or until July 8. Survival was analyzed by the actuarial method15. Differences were iden tified with the Long-rank test15. Cox regression analysis was applied to control confusion and interaction. Pearson’s Chi-square test and Poisson regression were used for determining associated factors. Analyzes were performed using the SPSS® version 22 statistical package, licensed by the National Institu te of Health. The significance level for all tests was 0.05.
Results
The most frequent age with the infection was the <30 years of age (32.81%), the male sex was predominated (53.81%), it was more frequent not to be hospitalized (87.2%), concerning the department or municipality analysis, the highest number of cases was reported for Bogotá (31.67%), followed by Ba rranquilla (12.65%), Atlántico (10.34%) and Valle (99.9%) (Ta ble 1). Statistically significant differences were presented for mortality with age, sex, hospitalization, and region (p <0.001, Chi-square test). When controlling for the confusion of the variables, among the risk factors was found the age, with an increase of RR of 1.07 per year, male sex, being hospitalized, and the department or municipality of Barranquilla, Atlántico and Cartagena. Antioquia, Cundinamarca, Bogotá, and Valle were protectors against the rest of the country. It was obser ved that in the crude RR the department of Nariño was a pro tective factor compared to the rest of the country, but when adjusting the RR it became not significant, although hospita lization was significant in both the crude RR and the adjusted RR, under its magnitude, considerably in adjusting covariates from a crude RR of 43.43 to an adjusted RR 19.19 (Table 2).
Table 1 General characteristics of COVID-19 mortality in Colombia between March 6th and July 8th 2020.

Table 2 Mortality Risk Factors for COVID-19 in Colombia between March 6th and July 8th 2020.

RR, Relative Risk; CI, confidence interval.
RR were derived from a Poisson Regression adjusting for age, sex, hospitalization and department.
Survival
The study included 4626 cases and 114112 censored cases. When evaluating the survival function for days of symptom onset, a probability of 100%, 98%, 97%, and 95% was presen ted for days 1, 10, 20, and 30, respectively, and the mortality occurred on the fifth day. From day 30 the survival rate was approximately 95% (Figure 1). The survival density function, differences were observed from the group of 40 years on wards, but more marked from the 60 years onwards, decrea sing the probability of survival (p <0.0001), for day 30 survival was in the group from 0 to 29 years of 100%, for the group of 30 to 39 years of 99%, for the group of 40 to 49 years of 98%, for the group of 50 to 59 years of 95%, for the group from 60 to 69 years of 86%, for the group of 70 to 79 years of 74% and the group ≥ 80 years of 60% (Figure 2). Survival in the entire age group of ≥ 60 years was 92%, 85%, and 78% at 10, 20, and 30 days, respectively.

Figure 2 Function of survival in the Colombian population with Covid-19 by age groups of 10 year in Colombia, 2020.
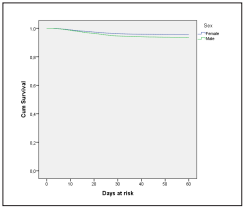
The comparison of the survival density function showed differences by sex, decreasing the probability of survi val in men (p <0.0001), survival in women at 30 days was 96%, and in men 95% (Figure 3). Concerning the survival by municipality or department, statistically, significant di fferences were found (p <0.0001), survival at 30 days was 99% in Antioquia, Cundinamarca and Nariño 97%, Carta gena and Bogotá 96%, Valle 95%, Atlántico and the rest of the country 94% and Barranquilla 93% (Figure 4). Regar ding hospitalization, differences were found (p <0.0001), the 30-day survival of those who were not hospitalized was 99%, and what had to be hospitalized was 68% (Figure 5).
The risk factors for survival were being a man, age, hospita lization, and region. The factors of the greatest magnitude were the age groups of 60 to 69 years, 70 to 79 years, and ≥80 years compared to the group <30 years, in addition to having been hospitalized. The municipalities or departments with the highest risk were Atlántico, Barranquilla, and Carta gena (Table 3).
Discussion
The present study analyzed the mortality trend attributable to COVID-19 in Colombia, from the identification of the first cases until July 8, 2020. The study provides the estimation of mortality for each age group, sex, hospitalization, and geo graphic region. In our study, from the onset of symptoms, it was observed that the survival rate was less than 96% for days 20 and 33. In studies it has been observed that death occurs approximately 6 to 41 days after the onset of symp toms, in a study of the southern region of Brazil, an average of 19 days was observed16. In China, COVID-19 course reports showed the median time from disease onset to dyspnea was similar in survivors and non-survivors, with a median dura tion of 13 days (9, 0-16, 5) for the survivors17.
The analysis for Colombia showed a lower probability of sur vival in adults older than 60 years. According to DANE, in Co lombia, the population over 60 years of age is approximately 13% (6,216,848/48’258,494)18 and is less than the estimated population in countries affected by high mortality attributed to Covid-19, like Italy, where it estimates 25% of the popu lation of adults over 65 years of age and where 8.6%, 35.6%, and 52.3% appeared in the groups from 60 to 69, 70 to 69 and> 80 years, respectively19. In China, there were cases of mortality of 8.0% and 14.8% for adults between 70 to 79 and over 80, respectively19. In Brazil, survival in patients ≥60 years was approximately 30 days> 60%, and in the minor group approximately 98%16.
It should be noted that the age group with the lowest survival in the studies is >60 years or older than 65 years, however, in this study, less survival was presented in the group ≥30 years, being more severe in groups ≥60 years, although with grea ter survival compared to Brazil, where a 78% to 60% survival was observed, respectively. Age also was associated with the hospitalization; in other reports of COVID-19 has associate the older age (≥65 years) associated with hospitalization19. In USA reports, 90% of hospitalized patients presented also one or more underlying conditions, being the most common the obesity, hypertension, chronic lung disease, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease20. In general, age and comorbidi ties has been found to be strong predictors of hospital and consequently associate to a critical illness and mortality21,22 .
The analysis of the disease by sex showed almost the same proportion of the disease between women (46.19%) and men (53.81%), this has been observed in several studies where no significant differences in frequency were found. of the disease in men and women16, (23)). However, in our study, higher mortality was observed in men than in women. This finding agrees with that reported regarding the difference in the susceptibility and response of viral infections in men and women, which is expressed in the incidence and severi ty of the disease23. Among the determinants associated with the immune response by sex, chromosomes, hormone pro duction, and the composition of the microbiome have been described, among others24; in COVID-19 infection, they have also made associations with factors such as mitochondria25. The analysis of sex and its dissimilarities helps to understand the dynamics of the infection and, above all, to direct the strategies for control, treatment, design, and efficacy of the vaccine, and in general health interventions26.
The analysis by region showed that the most impacted city was Bogotá, followed by the departments of Atlántico and Valle, even though the analysis included the months when the city instituted control strategies including personal care and strict confinement, which, draws attention and alarm to consider at the time of the intervention and the resumption of social production, this following what has been found in capital cities in the world, where the first findings have provi ded a scientific basis for local governments to make additio nal decisions on the resumption of work, it is recommended to focus attention mainly on densely populated cities, with the implementation of methods and strategies for the pre vention of outbreaks27.
The study had some limitations. Among these, the availabi lity and quality of the data, which are very important in any predictive regression model, although the study was based on information reported to the national reference center, the National Institute of Health, the data cannot be representa tive for all regions of the country, due to the underrepor ting or non-reporting of data to the surveillance system in various geographic regions, as well as, some regions have good coverage of health networks led by the departmen tal secretaries of health, which makes the report higher for some regions. During the pandemic, strengthening the vi rus detection capacity was established as a priority in most of the country; however, cases could remain unreported. Other limitations that may be affecting factors, the study did not consider the analysis of risk factors associated with comorbidities, already widely associated with the severity of infection, subsequent analysis of mortality should inclu de these additional variables. Also, the analysis establishes age, but this can present a confounding variable when it is not considered if it is associated with comorbidities, or with the persistence of symptoms since studies have shown that they can persist and prolong the disease in young adults between 18 and 34 years7. Finally, patients with negative nasopharyngeal swab results could have an active infection, and these were not followed or considered in the present study. However, despite the limitations, we consider that the results presented in the study are useful for the analysis of the variables associated with survival concerning COVID-19 infection in the first months of the pandemic in Colombia.
Comments
This study represents a preliminary analysis of survival on infec tion with the severe acute respiratory syndrome, SARS-CoV-2, which is carried out in the Colombian population. The analyzed data set allowed estimating both the impact and the trajectory of the pandemic, as well as understanding the SARS-CoV-2 disease in the Colombian population, which allows effective prioritiza tion of strategies for control, prevention, and intervention in the groups with a higher epidemiological risk for this new pathogen.