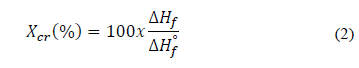1. Introduction
Worldwide polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) production continues to increase. In 2018, PHA production was about 29,000 tons, while it is expected to reach 37,000 tons by 2023 [1]. Microbial PHA are obtained through different strategies such as bioprocess (batch, fed-batch, and continuous) and by using cultures (pure and mixed) [2,3]. These strategies seek to increase yields in biomass and PHA production while reducing costs associated with the process. In this sense, economical substrates available from different industrial sectors are common alternatives for reducing the costs of PHA production.
PHAs have been synthesized by bacteria from a wide range of substrates, namely renewable sources (e.g., sucrose, cellulose, hemicellulose, starch, and triglycerides), industrial by-products (e.g., molasses, whey, and residual glycerol), organic acids (e.g., 4-hydroxybutyric acid and propionic acid), fossil resources (e.g., methane, mineral oil, and lignin), and water treatment residuals (e.g., residual water and activated sludge effluent) [4]. The physics and chemical characteristics of PHAs synthesized by bacteria depend on the carbon source, the enzymatic machinery present in the strain, and the fermentation strategies used in the biopolymer production process [5,6].
Pure glucose is usually used as a substrate in PHA production as this is the natural substrate for PHA-producing microorganisms. However, this is an expensive substrate. Nonetheless, some studies have reported the use of low-cost industrial by-products. In this sense, residual glycerol, obtained as a by-product in the biodiesel industry, has become an accessible and readily available carbon source for chemical and microbiological transformations, such as PHA production by microorganisms [7,8].
On the other hand, commercial PHA production is mainly focused on the use of Gram-negative bacteria (e.g., Cupriavidus, Pseudomonas, and E. coli) [9]. Nonetheless, these bacteria have endotoxins (lipopolysaccharides, LPS), which are released in the biopolymer extraction processes and affect their subsequent application in some areas of the industry (e.g., medical and pharmaceutical), thus requiring additional stages of purification [10]. In contrast, Gram-positive bacteria, specifically those belonging to the genus Bacillus, have been widely studied as PHA producers from different agro-industrial residuals, increasing interest in these at the industrial level [11]. One of their advantages is the lack of LPS, which makes purification stages after the production process of these biopolymers unnecessary. The absence of these steps reduces production costs, which is one of the main challenges facing the PHA industry’s petroleum-derived plastics.
About 150 different monomers have been identified within this type of biopolymer [12]. The chemical structure of each type of PHA, and therefore its industrial application, depends on the type of microorganism, its enzymatic capabilities, and the carbon sources [13]. Consequently, the characterization of PHA synthesized by microorganisms is one of the fundamental parts of the production process.
In this study, polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) production by B. megaterium LVN01 was evaluated under different operating conditions (C/N ratio, temperature, and incubation time) and different operation modes (batch and fed-batch). Residual glycerol obtained as a by-product of biodiesel production was implemented as the substrate. The PHB characterization was performed by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry (FTIR), and some physical properties were determined by Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA), and Differential Thermogravimetric Analysis (DTG).
2. Methods
2.1. Bacterial strain and inoculum preparation
All experiments were performed with B. megaterium LVN01 (GenBank: QJGY00000000.1), which was isolated from soil samples in Guarne (06°16′50″N, and 75°26′37″W, Antioquia, Colombia) [14]. Lysogeny broth (LB - 1.0% tryptone, 0.5% yeast extract, 1.0% NaCl) was used in this study, and it was supplemented with 1.4% agar as a solid medium. Cells were cultivated on LB agar plates at 37 °C for 24 h. One colony of B. megaterium LVN01 was used to inoculate 10 mL of LB. The culture flasks were placed on a rotary shaker and incubated overnight at 37 °C and 200 rpm. After incubation, 1 mL of culture broth was inoculated in 100 mL Erlenmeyer flasks containing 9 mL of fresh LB and incubated on a rotatory shaker at 37 °C and 200 rpm for 2 h (or until the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) was 0.5 - 0.6). This culture broth was used as inoculum for the following steps.
2.2. Carbon source
All experiments were performed using residual glycerol kindly provided by a Colombian biodiesel company (Bio D S.A Company). Donated samples corresponded to batch number GC00555TK452 and contained 83.1% (w/w) glycerol (Table S1).
2.3. Batch Process. Effect of the C/N ratio, temperature,and fermentation time on DWC and PHB productivity
Batch cultures were carried out using residual glycerol synthetic medium (WGM) that contained, 1.0 g L-1 yeast extract, 1.5 g L-1 KH2PO4, 3.6 g L-1 Na2HPO4, 0.2 g L-1 MgSO4·7H2O, and 1 mL of trace element solution (TES). TES contained: 10.0 g L-1 FeSO4·7H2O, 2.25 g L-1 ZnSO4·7H2O, 1.0 g L-1 CuSO4·5H2O, 0.5 g L-1 MgSO4·5H2O, 2.0 g L-1 CaCl2·2H2O, 0.23 g L-1 Na2B4O7·10H2O, 0.1 g L-1 (NH4)6Mo7O24, and 10 mL L-1 of HCl 35%, supplemented with residual glycerol as a carbon source and ammonium sulfate as a nitrogen source at different molar ratios (Table 1). An inoculum of 3 mL of B. megaterium LVN01 was added to 300 mL of WGM in a 1 L Erlenmeyer flask, which was incubated for 8 h at different temperatures, according to the test conditions. Finally, this pre-culture was used to inoculate 2.7 L of WGM culture broth at OD600 of 0.1. B. megaterium LVN01 was incubated in a 5 L bioreactor (Centricol, stirred tank series 01240) at 400 rpm, with aeration controlled by extra dry oxygen pulses to maintain aerobic conditions and with an initial pH value of 7.0. At the beginning of each batch, drops of 10% (v/v) antifoam solution (silicone oil) were added to the medium.
Table 1 conditions to determine the effect of the C/N ratio, temperature, and fermentation time on DCW and PHB productivity
| Factors | Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| C/N ratio (mol mol-1) | 21.6 | 33.2 | 44.9 |
| Time (h) | 36 | 48 | 72 |
| Temperature (°C) | 30 | 32.5 | 35 |
C: residual glycerol (20, 25 y 30 g L-1); N: (NH4)2SO4 (0.8, 1.4 y 2.5 g L-1)
Source: The Authors.
Growth was monitored spectrophotometrically by estimating the OD600 in a spectrophotometer (Shimadzu UV-1800) and with the determination of dry weight cell (DWC).To determine the effect of the variables (C/N ratio, temperature, and incubation time) on DWC and PHB productivity, a central composite design was implemented and analyzed using response surface methodologies. The operating conditions for obtaining higher PHB yields by B. megaterium strains reported in the literature were considered as the starting point in this study.
2.4. Fed-batch process
Fed-batch experiments were performed in 2 bioreactors, one of 5 L (Centricol, stirred tank series 01240) with a working volume of 3 L, and another of 14 L (New Brunswick BioFlo® / CelliGen® 115) with a working volume of 6 L. The parameters obtained in the batch and fed-batch approaches using the 5 L bioreactor were implemented in the 14 L bioreactor in the final scale-up stage. The bioreactors were operated at a stirring speed of 400 rpm. The dissolved oxygen was set at 100% saturation, using extra-dry industrial oxygen at the beginning of the processes. The initial pH value was set at 7.0. Drops of 10% (v/v) antifoam solution (silicone oil) were added when necessary. Bacterial growth was monitored spectrophotometrically by estimating the OD600 and by determining the DCW.
Initial working volumes for the 5 L and 14 L bioreactor were 2.5 L and 5.5 L, respectively. Residual glycerol (200 g L-1) was added 12 h and 24 h after inoculation, until a total workload of 3 L and 6 L was completed for the 5 L and 14 L bioreactors, respectively. The microorganism was incubated over 84 h. Triplicate independent samples were taken at each stage of the process.
2.5. PHB quantification and productivity
PHB quantification was performed using the crotonic acid method [15], with some modifications. The PHB was isolated from cells by extraction with NaClO 15 % (v/v):CHCl3 dispersion at 40 °C for 3 h in screw-cap tubes. Afterwards, the mixture was centrifuged at 8000 xg for 15 min at 20 °C, and the organic phase containing the PHB was filtered. An aliquot of 0.1 mL of the filtered solution was dissolved in 0.9 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4 95-97%). The solution was heated at 100 °C for 10 min, and then the mixture was cooled on ice. Finally, absorbance at 235 nm was measured in a UV-VIS spectrophotometer. The calibration curve was constructed by preparing solutions of known concentrations of crotonic acid in concentrated H2SO4 (Fig. S1). The solutions tested were compared against a concentrated H2SO4 blank.
PHB productivity was calculated as shown in eq. (1) and should be understood as the PHB concentration obtained using the methodology described above, which was produced in the WGM culture per unit of time. Triplicate independent samples were taken at each stage of the experiment.
2.6. Ammonium quantification
Residual ammonium quantification was determined following the methodology described by Solórzano [16], which quantifies a type of dye (indophenol blue), a molecule obtained from the reaction between phenol, sodium hypochlorite and ammonium, and catalyzed by sodium nitroprusside, at 640 nm through spectrophotometry. The calibration curve was constructed using (NH4)2SO4 solutions of known concentration.
2.7. PHB characterization
2.7.1. Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)
Material extracted from B. megaterium LVN01 cells and commercial PHB (Sigma-Aldrich, poly(3-hydroxybutyric acid)) were analyzed using FTIR. Spectra were recorded using a PerkinElmer Spectrum Two FTIR spectrometer. For each measurement, 32 scans were acquired and averaged in the range of 4000 cm−1 to 400 cm−1 with a spectral resolution of 4 cm−1.
2.7.2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
1H and 13C NMR spectra of material obtained from B. megaterium LVN01 and commercial PHB (Sigma-Aldrich), were recorded using a Bruker UltraShield Fourier 300 NMR spectrometer at 300 MHz, using tetramethylsilane as the internal standard. For each measurement, between 5 and 15 mg of biopolymer was dissolved in 0.5 mL of CDCl3.
2.7.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
Melting temperature (T m ) analyses were performed on a Mettler Toledo DSC 1 STARe System Calorimeter. Approximately 6 mg of the material extracted from B. megaterium LVN01 cells was subjected to a heating curve from 25°C to 200°C, with a heating ramp of 10°C min-1, under an inert nitrogen atmosphere.
2.7.4. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential thermogravimetric analysis (DTG)
Decomposition temperature (T d ) was determined in a NETZSCH Thermogravimetric Analyzer TG 209 F1 Libra. Samples were processed at a speed of 10 °C min-1 from 25 °C to 600 °C, under an inert nitrogen atmosphere. For this study, 2.5 mg of the extracted material was taken for each test. A DTG plot was obtained by calculating the first derivative of the data obtained for TGA.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Batch process
A preliminary approach used shake flasks in the process, in order to understand the microorganism’s behavior [17]. This section shows the results obtained for the scale-up of the B. megaterium LVN01: residual glycerol system in a 5 L bioreactor. Initially, the performance of the microorganism-substrate system was evaluated in a 5 L bioreactor with a working volume of 3 L under different C/N ratio, temperature, and incubation time conditions. The configuration of the independent variables for different assays was established by a central composite design. The expected values of DCW and PHB production, which is expressed in terms of PHB productivity, were fitted by complete second-order models, using the response surface methodology (Table 2).
Table 2 Evaluation of different batch culture operating conditions for the B. megaterium LVN01 system:residual glycerol.
| Ratio C/N (mol mol-1) | Temperature (°C) | Time (h) | DWC (g L-1) | Productivity (mg PHB L-1 h-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 33.2 | 32.5 | 48 | 0.50 | 7.6 |
| 44.9 | 30 | 36 | 0.70 | 13.8 |
| 21.6 | 35 | 36 | 0.48 | 7.9 |
| 44.9 | 32.5 | 48 | 0.92 | 11.2 |
| 21.6 | 35 | 72 | 1.26 | 8.8 |
| 44.9 | 35 | 36 | 0.51 | 10.3 |
| 33.2 | 30 | 48 | 0.62 | 7.3 |
| 21.6 | 35 | 72 | 0.76 | 3.2 |
| 33.2 | 32.5 | 72 | 0.50 | 1.8 |
| 44.9 | 30 | 72 | 0.49 | 5.4 |
| 21.6 | 30 | 72 | 1.03 | 6.7 |
| 33.2 | 35 | 48 | 1.00 | 12.8 |
| 33.2 | 32.5 | 48 | 0.59 | 8.9 |
| 33.2 | 32.5 | 36 | 0.48 | 12.3 |
| 21.6 | 30 | 36 | 0.50 | 10.8 |
| 21.6 | 32.5 | 48 | 2.10 | 15.5 |
Source: The Authors.
The quadratic effect of incubation time on the DCW (Table 3) and incubation time on PHB productivity (Table 4) were found to be significant (p <0.05). The fitted models explain 70% of the variability in DCW and 64% for PHB productivity. Likewise, the values that optimize the system for DCW (C/N ratio 21.6 mol mol-1, 32.8 °C and 58.9 h) and PHB productivity (C/N ratio 44.9 mol mol-1, 30.8 °C and 39.9 h) were established by analyzing the response surfaces (Fig. 1). These values are within the highest ranges reported for PHB production from glycerol by different strains of B. megaterium [18,19].
Table 3 ANOVA for DCW of the B. megaterium LVN01:residual glycerol system.
| Source | Sum of squares | Df | Mean square | F-ratio | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A: C/N ratio | 0.2790 | 1 | 0.2790 | 1.97 | 0.2096 |
| B: Temperature | 0.0017 | 1 | 0.0017 | 0.01 | 0.9154 |
| C: Time | 0.0458 | 1 | 0.0458 | 0.32 | 0.5896 |
| AA | 0.6053 | 1 | 0.6053 | 4.28 | 0.0839 |
| AB | 0.0094 | 1 | 0.0094 | 0.07 | 0.8050 |
| AC | 0.2294 | 1 | 0.2294 | 1.62 | 0.2497 |
| BB | 0.0272 | 1 | 0.0272 | 0.19 | 0.6763 |
| BC | 0.0017 | 1 | 0.0017 | 0.01 | 0.9173 |
| CC | 0.8759 | 1 | 0.8759 | 6.20 | 0.0472 |
| Total error | 0.8479 | 6 | 0.1413 | ||
| Total (corr.) | 2.8219 | 15 | |||
| Adj R2= 70% |
Source: The Authors.
Table 4 ANOVA for PHB productivity of the B. megaterium LVN01: residual glycerol system.
| Source | Sum of squares | Df | Mean square | F-ratio | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A: C/N ratio | 1.3213 | 1 | 1.3213 | 0.11 | 0.7536 |
| B:Temperature | 1.3383 | 1 | 1.3383 | 0.11 | 0.7520 |
| C:Time | 73.716 | 1 | 73.716 | 6.03 | 0.0494 |
| AA | 14.742 | 1 | 14.742 | 1.21 | 0.3143 |
| AB | 0.2932 | 1 | 0.2932 | 0.02 | 0.8820 |
| AC | 5.4283 | 1 | 5.4283 | 0.44 | 0.5300 |
| BB | 0.9201 | 1 | 0.9201 | 0.08 | 0.7931 |
| BC | 0.0889 | 1 | 0.0889 | 0.01 | 0.9348 |
| CC | 16.127 | 1 | 16.127 | 1.32 | 0.2945 |
| Total error | 73.377 | 6 | 12.229 | ||
| Total (corr.) | 206.00 | 15 | 1.3213 | ||
| Adj R2 = 64% |
Source: The Authors.
3.2. Fed-Batch process (5 L bioreactor)
Based on the above results, a 5 L bioreactor was used in fed-batch mode. Fig. 2 plots the values of the response variables obtained in the experiments carried out in a 5 L bioreactor for 84 h at 30.8°C with a C/N ratio of 44.9 mol mol-1.

Source: The Authors.
Figure 2 Fed-batch system in a 5 L bioreactor. ( ) PHB Productivity (mg L-1 h-1); ( ) ammonia nitrogen (g L-1); ( ) DCW (g L-1); A1 (12 h) and A2 (24 h) represent glycerol feed times.
Results in the 5 L bioreactor show that the DCW in fed-batch mode increased compared to using the same reactor under the same operating conditions but in batch mode. As shown in Fig. 2, DCW and PHB productivity reached 16.6 mg L-1 h-1 and 1.96 g L-1 respectively in the fed-batch system, after 48 h of incubation. However, the highest productivity was observed at 12 h (29.5 mg L-1 h-1) with a DCW of 0.97 g L-1. This indicates that B. megaterium LVN01 accumulates PHB faster during the first 12 h of incubation. These results are slightly higher than those previously reported for B. megaterium MTCC10086, with DCW values of 1.54 g L-1 and a PHB productivity of 13.5 mg L-1 h-1 [20].
Meanwhile, the concentration of ammonium throughout the experiment remained almost constant (Fig. S2). Since B. megaterium LVN01 requires yeast extract in the culture medium to be able to grow in the residual glycerol, it is evident that ammonium sulfate is not involved in its metabolism (Fig. S3). This strain displays better acceptance of yeast extract as the nitrogen source, instead of ammonium sulfate, which means that the concentration of ammonium sulfate remains constant. Similarly, it has been observed that yeast extract directly affects the growth of B. megaterium strains that use glycerol as a carbon source, whereas increased concentration of yeast extract in the medium leads to a decrease in both DCW and PHA productivity [19].
3.3. Fed-Batch process (14 L bioreactor)
Experiments in a 14 L bioreactor were performed with a working volume of 6 L. Fig. 3 illustrates the results obtained in the 14 L bioreactor operating in fed-batch mode for 84 h, under the same operating conditions used in the 5 L bioreactor (i.e., 30.8 ºC and C/N ratio of 44.9 mol mol-1).

Source: The Authors.
Figure 3 Fed-batch system in a 14 L bioreactor. ( ) PHB Productivity (mg L-1 h-1); ( ) ammonia nitrogen (g L-1). ( ) DCW (g L-1); A1 (12 h) and A2 (24 h) represent glycerol feed times.
As can be seen in Fig. 3, the trends in the data are similar to the data obtained in the 5 L bioreactor. However, it was observed that the highest DCW (1.91 g L-1) occurs at 36 h, slightly higher than the 1.74 g L-1 obtained in the 5 L bioreactor at the same point. This can be explained by the long stationary phase of the system under study. Thus, it can be seen that the system is in a stationary phase between 36 and 48 h for both study scales (5 L and 14 L) and that the system is at its maximum biomass production.
On the other hand, the higher productivity of PHB (35.6 mg L-1 h-1) is again evidenced at 12 h (slightly higher than the 29.5 mg L-1 h-1 obtained with a culture volume of 5 L). These results are similar to PHB productivities reported with Bacillus strains using glycerol as a carbon source [21,22].
Likewise, the same behavior with the nitrogen source was observed, which, as mentioned above, has also been reported elsewhere. This evidence confirms that yeast extract serves as the main nitrogen source for B. megaterium LVN01, and the acceptance of residual glycerol as a carbon source is possible only in the presence of yeast extract. It should be noted that other studies have also reported poor assimilation of ammonia nitrogen by strains of B. megaterium [23].
3.4. Functional groups identified by FTIR
The identification of the biopolymer’s functional groups was carried out using FTIR. The bands in the spectrum at 2976 cm-1 and 2932 cm-1 correspond to the stretching of CH groups. The signal at 1720 cm-1 corresponds to the stretching of the carbonyl group (C=O). 1280 cm-1 corresponds to the stretching of the ester group (C-O). The bands at 1380 cm-1, 1228 cm-1, and 1180 cm-1 correspond to groups CH3, CH2, and C-O-C, respectively. Based on these results, it was determined that the spectrum corresponds to the characteristic signals of the PHB (Fig. S4) [24,25].
3.5. Chemical structure elucidation by NMR
The chemical structure of the biopolymer produced was elucidated by 1H and 13C NMR. The signals at δ 1H : 1.30 ppm indicate the presence of the methyl group (CH3), 2.50 - 2.64 ppm for the methylene group (CH2), 5.28 ppm for the (CH) group (Fig. S5), and δ 13C : 169.20, 67.65, 40.81, and 19.80 ppm, which represent C=O, CH, CH2 and CH3, respectively (Fig. S6) [26,27].
The comparison of the NMR spectrum of commercial PHB with the spectrum of the PHA produced by B. megaterium LVN01 confirms that this microorganism produces PHB (Fig. S5 and S6).
3.6. Determination of the melting temperature by DSC
The melting temperature (T m ) and the melting enthalpy (ΔH f ) of the PHB synthesized by B. megaterium LVN01 from residual glycerol was analyzed by DSC (Fig. S7). Thus, the degree of crystallinity (X cr ) could be calculated using eq. (2).
Where:
ΔH f : Enthalpy of fusion of PHB produced by B. megaterium LVN01
ΔH f ° : Enthalpy of fusion of pure PHB, equivalent to 146 J g-1 [28].
For PHB, typical T m values are 130-180 °C [26,28], and X cr values are 30-60% [20,30]. In this study, the T m was equal to 168.9 °C. The ΔH f for the PHB was calculated as the area under the T m curve. Finally, X cr was calculated to be equal to 35.7%. These results correspond to the typical reported values for PHB synthesized by B. megaterium [18,31].
3.7. Thermal stability by TGA and DTG analyses
The PHB produced by B. megaterium LVN01 was analyzed through TGA and DTG to assess its thermal stability. The degradation of the PHB occurs in a simple process and starts around 230 °C, reaching its maximum decomposition temperature at 266.2 °C. The evaluation of the sample’s weight loss indicates that between 230 and 300 °C, 97.7% of the mass was lost (Fig. S8). As was expected, the values obtained in this study are similar to those reported for PHB elsewhere [18,26,27].
4. Conclusions
In a preliminary approach, batch cultures were used to establish optimal growth conditions for B. megaterium LVN01: residual glycerol system. It was determined that the best operating conditions were 30.8 °C, 39.9 h of incubation and a C/N ratio of 44.9 mol mol-1. In the case of the C/N ratio, the importance of the concentration of glycerol (substrate) instead of ammonium sulfate (nitrogen source) was established, as the ammonium remains almost constant throughout the processes.
The studies in 5 L and 14 L quantities established that 12 h of incubation displayed the highest PHB productivity (29.5 and 35.6 mg L-1 h-1, respectively). It was also determined that there is a stationary phase of at least 12 h when B. megaterium LVN01 presents the highest DCW, with values greater than 1.9 g L-1 in both bioreactors operating in fed-batch mode.
On the other hand, the significant effect of the presence/absence of yeast extract on the growth of B. megaterium LVN01 in residual glycerol was determined, leading to the conclusion that without this supplement, this strain is not capable of assimilating residual glycerol as a carbon source (data not shown).
Finally, the physical and chemical characterizations of the PHA synthesized by the B. megaterium LVN01 strain from residual glycerol were performed. FTIR, 1H-NMR, and 13C-NMR spectra allowed the chemical structure of the synthesized compound to be elucidated, and it was found that the monomer is 3-hydroxybutyrate (3HB). The biopolymer was therefore concluded to be PHB. The study of some physical and chemical properties of PHB established its melting (T m ) and decomposition temperatures (T d ), as well as its degree of crystallinity (X cr ). These values are within the reported ranges for PHB synthesized by strains of B. megaterium.