Introduction
The clinical picture triggered by the bite of a venomous snake is known as ophidiotoxicosis. 1 Every year, about 2.4 million people are bitten by venomous snakes around the world, causing between 94 000 and 125 000 deaths, as well as 400 000 secondary amputations and other complications such as infections, deformities, psychological sequelae and injuries derived from non-medical cultural practices to prevent the progression of poison. Such practices include the intake of hydrocarbons or alcohol, electrical burns, tourniquets, among others 2, which mostly have a negative impact on the work capacity of the people affected and, therefore, family and regional economy. 2,3
Colombia is a tropical country characterized by high biodiversity, where venomous snakes are found mainly in areas below 2 500 maml, especially those that generate the greatest risk to populations. For this reason, ophidic accidents occur more frequently in rural areas, being farmers the most affected population, with a higher incidence in young adults and in males. 4
According to statistics from the Instituto Nacional de Salud (National Health Institute) 1, between 2 000 and 3 000 ophidian accidents occur in Colombia every year, with an incidence of 6.2 cases per 100 000 inhabitants in less populated regions and 20 cases per 100 000 inhabitants in the most populated. 4 For the most part (90-95%), these accidents are caused by snakes of the Bothrops genus, and Antioquia and Chocó are the most affected departments. About 5-9% of the events in Colombia are fatal and 6-10% have sequelae. 4
Although the epidemiological potential of snake bites is not greater than that of diseases transmitted by vectors or other infectious diseases, it is important to note that the impact of mortality caused by ophidiotoxicosis is greater than that attributed to diseases that have been recognized as unattended in tropical regions, which include dengue, cholera, leishmaniasis, chagas, etc. 5, thus turning ophidic accidents into a major public health issue.
In Colombia, some factors that hinder rapid attention of these patients have been identified, namely, geographical features, poor infrastructure for transportation from rural areas to care centers, inadequate cultural practices and lack of thorough medical management of ophidic accidents by health professionals. 6-9
The treatment of ophidism should be comprehensive and timely, based mostly on the administration of polyvalent antivenin serum specific for the type of venom inoculated according to the genus of the snake. Clinical and paraclinical assessment performed by health personnel is highly important to correlate the semiology with the type and degree of poisoning and, thus, be able to administer sufficient antivenin vials in a timely manner. 5
The severity of poisoning and the type of venom are determined by factors such as the age of the victim, the size of the bite and sensitivity to the poison, the time elapsed since the bite until receiving medical attention, the location and depth of the bite, the number of bites, the size of the snake and the amount of poison inoculated. 9,10
Currently, Colombia has a Public Health Surveillance Protocol for Ophidic Accidents 1 and a Guide for the Management of Toxicological Emergencies 5, which establish the basic guidelines for hospital care. However, there is still a high mortality rate and disability secondary to inadequate prehospital treatment.
Therefore, the objective of this study is to perform a clinical characterization of snake bite cases treated in a tertiary hospital in Bogotá between 2004 and 2014, making a comparison with the treatment recommended in national and international management guidelines and review articles, in order to analyze the factors that can provide a continuous improvement in the care of patients with this diagnosis.
Materials and methods
A descriptive, retrospective, cross-sectional study was carried out, with sampling at convenience and evaluation of secondary data sources. The evaluation was made on 42 clinical charts of patients diagnosed with poisonous and non-poisonous snake bites during the aforementioned period, and attended at Hospital Universitario de La Samaritana Empresa Social del Estado (HUS), located in Bogotá, Colombia. Clinical charts with pictures compatible with bites or stings by other animals, blunt trauma to the extremities and poisoning by chemical substances were excluded.
After receiving the authorization from the Ethics Committee, a format was used to collect information regarding the patient's sex, age, geographical area where the bite occurred, occupation, previous morbidities, bite history and use of antiophidic serum, treatment prior to hospital admission, anatomical location of the bite, time of evolution of the condition, time elapsed between the bite and the administration of the antivenin serum, requirement of hospitalization and admission to the intensive care unit, classification of the severity of the ophidic accident, number of days of antibiotic treatment, need for surgical management, complications, antivenin serum side effects, paraclinical evolution of the patient, and alarming signs and symptoms at admission and discharge, such as findings on vital signs, pain, hemorrhages, neurological symptoms and fever.
Once data were collected, information was entered into a spreadsheet in Microsoft Excel 2013. Absolute and relative frequencies of the variables of interest were estimated and grouped into tables. Variables regarding the use of antibiotics and frequency of infections were compared with data from another national hospital-based study using a proportion comparison test. If p<0.05, a statistically significant difference was considered.
Results
The most significant results were that the average age was 41.3 years, 76% of the population was male, 42.8% were farmers from the region and Cundinamarca was the main geographical area where ophidic accidents occurred (80.9%). Regarding the anatomical place of the bite, 53% of the patients were bitten in the lower limbs and the remaining patients in the upper limbs (Table 1).
Table 1 Characteristics of the studied population.

Source: Own elaboration based on the data obtained in the study.
With respect to severity, numerical and (1, 2, 3 and 4) and status records (mild, moderate and severe) were obtained. Taking into account the most used classification, 63.3% of patients were classified in moderate stage, 28% in severe and 7% in mild. The time elapsed from the bite until initiation of medical attention ranged between 1 and 5 hours in 45.2% of the patients, of which 28.5% were in a moderate stage of poisoning.
Regarding the time elapsed from the bite to the administration of antivenin, antivenin was administered between 6 and 11 hours after the bite in 30.9% of patients, of which 21.4% were found in moderate stage, while two patients, with moderate and severe classification, respectively, were not administered any. In relation to previous attention at the HUS, 71.4% of patients were attended first by a medicine men/women and the most frequent procedure (35%) was tourniquet. Of the total patients, 41 required some type of surgical procedure; however, it should be noted that 70% underwent fasciotomy (Table 2).
Table 2 Distribution of patients according to characteristics associated with the stage of severity.

Source: Own elaboration based on the data obtained in the study.
A prevalence of 90% in in-hospital infectious complications was found, which includes those associated with intradermal and musculoskeletal infectious processes, and of those, 9.5% of the patients without treatment were classified as moderate and mild).
When specifying the antibiotics used, 31 different schemes were observed. The most widely used drug was crystalline penicillin in 17 cases, followed by clindamycin in 16, ampicillin sulbactam in 14, and ciprofloxacin in 12. Additionally, records of patients who were administered piperacillin tazobactam, cefazolin, amikacin, meropenem, gentamicin, vancomycin, imipenem, among others were obtained.
76% of the patients presented some complications, being more frequent hematological and dermatological alterations (25%). The moderate stage included 42% of patients with complications, of which compartment syndrome was the most frequent, followed by dermatological, hematological and musculoskeletal alterations, while patients in severe stage presented multisystemic complications (hematologic, renal and pulmonary) by 33%. Table 3 shows the main complications observed by groups and those observed at least once in patients.
Table 3 Complications observed in patients.

Source: Own elaboration based on the data obtained in the study.
It was possible to establish that more than 97% of patients were bitten by snakes of the Viperidae family, with a mortality rate of 7%, while only one case of coral (Elapidae) bite was observed. The number of antivenin vials used per patient was quantified according to the severity of the ophidic accident. It is worth noting that 5 moderate-stage patients received less than 4 vials, while 3 in moderate stage received more than 15, and 3 in severe stage received 4 vials or less. In addition, it was found that the most frequent antivenin side effect was anaphylactic shock with 26.5% (Table 4).
Discussion
Results reveal a scenario in which diverse medical, sociocultural and economic factors converge and lead to an outcome. Epidemiological data obtained from the population studied are similar to those found by some researchers in Colombia 7 and those recorded in the national report of ophidian accidents. 11
Furthermore, similarities with other studies were found regarding cultural practices that are carried out in cases of ophidism, such as tourniquets, plasters, cuts, suction, burns and alcohol and petroleum intake.
With regard to in-hospital care, about 50% of the patients received antivenin in less than 6 hours after the accident, suggesting that the remaining 50% presented with advanced progression of systemic and local effects of the poison upon admission. 8 Based on the type of ophidian accident, management guidelines 5 and the consensus of the review articles 6, initiating early antivenin administration is highly recommended to reduce vital organ involvement and mortality.
Fibrinogen uptake and coagulation times were found in 30% of the patients treated, as well as patients with moderate and severe classification who did not receive antivenin. According to the recommendation, coagulation and fibrinogen times should be measured on hospital admission, since the latter is the most useful parameter for determining the severity of poisoning by the Viperidae family and the number of initial antivenin vials. 5-7,10
The most frequent side effect of the drug (antivenin serum) among the entire population was anaphylactic shock with 26.5%, followed by skin rash with 17% and hives in equal proportion. These data coincide with the findings of some researchers when comparing different types of antivenins. 12,13
Fasciotomy was performed in 70% of the patients; however, this procedure is contraindicated in ophidic accidents due to the absence of a true compartment syndrome and high risk of superinfection. 6,14,15 The most frequent complication in 90% of the patients was local or systemic infection, followed by multisystem failure (50%). Broad spectrum antibiotics were established within the treatment.
Given that current guidelines recommend initiating prophylactic treatment with crystalline penicillin/clindamycin 5 and adjusting antibiotics based on the culture obtained from the affected site 15,16, a comparison of antibiotic management was made against a descriptive study conducted in Hospital Pablo Tobón Uribe (HPTU) of Medellín between 2000 and 2006. 17 Eight HPTU patients who presented with infectious complications were identified out of a total of 52 snake bites; they underwent microbiological isolation of the affected site and prophylactic and in-hospital antibiotic treatment established prior to the culture was observed. This study shows that the most prevalent bacterium in those for whom antibiotic therapy previously indicated was not adequate and also generated resistance was Morganella Morgagni and other Gram-negative bacteria. 17,18
Additionally, a statistical comparison was made based on hospitals, taking into account the frequency of patients treated with penicillin or clindamycin prior to admission and, at in-hospital level, prior to culture (Table 5). Greater frequency was observed in the use of the recommendation at the HUS, but also greater infectious complications, at hospital level, were found with a statistically significant difference compared to the HPTU.
Table 5 Prophylactic antibiotic treatment used in the Hospital Pablo Tobón Uribe and the Hospital Universitario de La Samaritana Empresa Social del Estado.
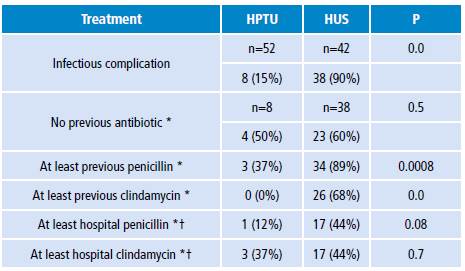
HPTU: Hospital Pablo Tobón Uribe; HUS: Hospital Universitario de La
Samaritana Empresa Social del Estado.
* In a patient with an infectious complication.
† Previous to sampling.
Source: Own elaboration based on López et al.17
Conclusions
Ophidic accidents continue to be an important cause of morbidity and disability in Colombia; therefore, this is a public health issue with consequences that generate disability and limitations in the economic development of the communities. Training the rural population and health personnel is important to avoid secondary complications due to empirical treatments. 9,19,20
Information regarding ophidian accidents reported in the 2004-2014 period at the HUS allowed to demonstrate variability in management, classification of severity, use of antivenin, examinations and antibiotic and surgical treatment in patients with respect to management guidelines and studies conducted in comparable hospitals.
Clinical management of poisoning by venomous animals should be personalized. 21 However, medical knowledge is part of a continuous updating process, based on studies with a high level of evidence from specialized centers, which promote the re-evaluation of medical practices within care centers for the sole purpose of reducing disability and mortality in patients.















