Introduction
Sepsis is defined as a potentially fatal organ dysfunction caused by the host's response to infection, whether in healthy or injured tissue, causing pathophysiological and biochemical disorders that cover a broad spectrum of clinical and laboratory manifestations ranging from bacteremia to septic shock 1. Early diagnosis and prompt, appropriate treatment are key for limiting damage and controlling the disease 2.
Considered to have one of the highest burdens of morbidity and mortality in the twenty-first century, sepsis very often affects older adults (OAs) in whom, despite advances in diagnosis and treatment, mortality continues to be high, causing more than 60% of hospital deaths in those over the age of 65 and up to 80% in those 80 years old or older 3-5.
Several factors predispose OAs to sepsis, resulting from typical aging changes such as oxidative stress, mitochondrial suppression, telomere shortening and DNA damage, which cause cellular disorders in cytokine regulation and the neuroendocrine response. These modify protein metabolism which, coupled with low food intake, leads to malnutrition and changes in the intestinal microbiota, potentiating a proinflammatory state and immunosenescence which may cause or worsen neurological conditions, triggering an impaired functional status with disuse atrophy, sarcopenia secondary to accelerated muscle loss, sluggishness and fatigue 6.
Furthermore, OAs often have multimorbidity, defined as the conjunction of several chronic conditions which require rehabilitation or a long period of health care 7, which is frequently advanced and a significant risk factor for developing infectious diseases, especially pneumonia, urinary tract infections and skin and soft tissue infections 8. These infections may begin with atypical symptoms such as delirium, functional decline, weight loss, fatigue, dizziness and falls, symptoms which are part of geriatric syndromes and cause special challenges in diagnosis and treatment. This population should be cared for by an interdisciplinary team 7,9, using the interdisciplinary team work model, caring for patients at various care levels (acute units, mid-stay units, day hospitals, and home care).
According to epidemiological reports in the United States, despite medical advances, greater access to health care and an improved quality of life, sepsis continues to cause up to 30% mortality in hospitalized patients 3, which may reach 50% if there is septic shock. These percentages are comparable to the mortality caused by cardiovascular disease 10. The vast majority of survivors develop medical, mental and functional complications which lead to physical, cognitive and psychosocial disability 11,12, with high costs for the healthcare system 13, thus becoming a public health issue 4. In 2017, Colombia reported 224,187 deaths, 62% of which were in people over the age of 65, with sepsis being the fifth cause of death, nationwide 14. Thus, the objective of this study was to determine the effect of multimorbidity and geriatric syndromes on mortality in OAs hospitalized for sepsis in an acute geriatric unit.
Materials and methods
Design
An observational, analytical nested case-control study was carried out in a cohort of patients diagnosed with sepsis and cared for in an acute geriatric unit.
The study protocol was approved as a no-risk study by the Technical-Scientific and Bioethical Committee of Universidad Libre and Clínica Universitaria Rafael Uribe Uribe. The patients or some caregivers were interviewed to obtain information during hospitalization. There were no conflicts of interest
Study population
Of the cohort of 2,054 OA patients 60 years old or older seen at Corporación Universitaria Rafael Uribe Uribe (CURUU) in Cali (Colombia) from January 2012 to September 2015, all met at least one of the following inclusion criteria for treatment in the acute geriatric unit (AGU): taking eight or more medications, a subacute cerebrovascular event, a disabling illness or prior severe or total functional dependence, frequent hospital readmissions (two or more per month), prior mental conditions (delirium on admission or baseline dementia), the presence of multiple geriatric syndromes (frailty, pressure ulcers, falls), body mass index less than 20 kg/m2, an inadequate support network, living in a geriatric institution, or patients over the age of 80 with an acute medical disease. From this cohort of 2,054 patients, the records of those diagnosed with sepsis were reviewed, with cases being defined as all the records in which death occurred within 30 days of admission, and controls being the survivors. Pairing was done with one case for every two controls.
Informed consent was obtained from every patient or from a relative or caregiver, in cases where the OA was unable to fill it out. Subsequently, the questionnaire was applied, which was completed on admission by one of the physicians on the interdisciplinary team trained to collect the standardized data from the comprehensive geriatric assessment (CGA) scales.
The data obtained was extracted from the geriatric interdisciplinary team's database, who assessed and treated the patient, family and caregivers, based on the biopsychosocial model, during their hospital stay. Thus, each professional involved applied geriatric clinical measurement scales from his/her discipline, as follows: geriatrician: information related to the biological domain (cause of hospitalization, comorbidities, death, medications); physical therapist: information related to the functional domain (activities of daily living); psychologist: information related to the mental domain (depression, delirium, cognitive impairment); and social worker: information related to the social and family domain (sociodemographic variables, the presence of a caregiver, relationship with the caregiver, and social/familial condition).
Outcome
Mortality within 30 days of admission to the AGU. The information on mortality was provided by the Valle del Cauca Departmental Secretariat of Health through death certificates up to October 2015.
Main independent variable
Sepsis was diagnosed based on clinical signs and symptoms of a systemic inflammatory response as a host response to infection associated with biological laboratory markers such as leukocytosis, neutrophilia, C-reactive protein and microbiological isolation, when possible, along with the support of imaging tools showing findings compatible with an infectious process 1,15. It is important to keep in mind that the study was carried out in a hospital unit, and not in intermediate or intensive care, where variables such as SOFA or APACHE are not routinely used to determine the patients' severity of illness.
Covariables
The analysis included age, sex and known variables which could affect the outcome; laboratory values were used as numeric variables. The multimorbidity model was defined as the presence of two or more chronic conditions which cannot be cured but can be controlled using medications or other treatments; in other words, chronic diseases 16. Functional status was assessed using the Barthel Index (BI) which evaluates 10 basic activities of daily living, assigning a predetermined value for autonomy/independence on admission; the score ranges from 0 to 100, with 0 being maximum dependence and 100 total independence. The BI has been recommended as the instrument of choice for measuring physical disability and was used as a numeric and categorical variable. A BI score less than 60 was considered to be disability 17,18, which was defined as a difficulty or limitation in carrying out basic activities of daily living 19.
For evaluating delirium, the Confusion Assessment Method (CAM) was used, which evaluates four characteristics: acute onset and fluctuating course, inattention, disordered thinking and a change in level of consciousness, with the presence of characteristics 1 and 2 and 3 or 4 being considered positive for delirium 20. Kidney function was assessed through the estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) using the equation derived from Levey et al.'s study (Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study equation [MDRD-4] or MDRD-IDMS) 21, and chronic kidney disease (CKD) was defined as a GFR less than 60 ml/min/1.73 m2 or kidney injury present for three months or more, based on the 2013 KDIGO definition. Kidney injury markers were not considered for the definition of CKD 22.
Analysis plan
Descriptive statistics were used to summarize the characteristics of the study population. Quantitative variables were presented using their measures of central tendency and dispersion. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was used to compare the distribution of the data. Qualitative variables were summarized as percentages and presented in frequency tables. The statistical significance of the bivariate associations with the outcome variable (30-day mortality) was analyzed using the Mann-Whitney U test for numerical variables and Chi2 or Fisher's exact test for dichotomous variables, as applicable, taking a p value < 0.05 as significant for rejecting the null hypotheses.
For exploring the multivariate association between the exposure variables and the outcome variable, the odds ratio (OR) was used as the measure of association, with its respective 95% confidence intervals (95%CI).
The morbidity and mortality and geriatric syndrome models were defined as theoretical constructs which encompass a set of interrelated aspects. The variables which showed a statistical significance <0.5 in the bivariate analysis were used to create these models. All the data was recorded in Excel and analyzed with IBMSPSS version 20.0 software.
Results
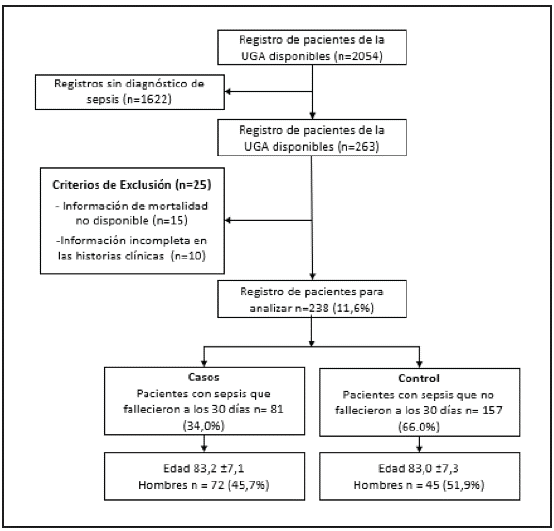
Of the 2,054 records of patients cared for in the AGU at Corporación Universitaria Rafael Uribe Uribe (CRUU), 238 met the inclusion criteria for analysis in this study and were selected. The reasons for exclusion are shown in Figure 1.
The average age was 83.2±7 years, and 52.1% were women. Ninety-nine percent of the patients had some chronic disease, with hypertension (73.9%) and diabetes mellitus (31.1%) being the most frequent. Likewise, cerebrovascular disease (CVD) and CKD had statistically significant differences between the groups in favor of cases (deceased patients), which was borderline for coronary disease (Table 1). The bivariate analysis for the geriatric syndromes model showed statistically significant differences for 30-day mortality after admission to the AGU: 48% for cases with delirium and 87% for cases with disability (Table 1).
Table 1 Sociodemographic, mental and functional characteristics of the study population.
| Characteristics | General | Status after sepsis diagnosis | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) (n=238) | Deceased n (%) (n=81) | Alive n (%) n=157 | ||
| Age* | 83.15±7.12 | 83.02±7.31 | 83.22±7.05 | 0.84t |
| Male | 114 (47.90) | 42 (51.85) | 72 (45.86) | 0.38 |
| HTN (n=234) | 173 (73.93) | 61 (75.31) | 112 (73.20) | 0.73 |
| Hypothyroidism | 35 (14.71) | 10 (12.35) | 25 (15.92) | 0.46 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 74 (31.09) | 25 (30.86) | 49 (31.21) | 0.96 |
| Congestive heart failure | 27 (11.34) | 10 (12.35) | 17 (10.83) | 0.73 |
| Coronary disease | 16 (6.72) | 9(11.11) | 7 (4.46) | 0.05 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 48 (20.17) | 23 (28.40) | 25 (15.92) | 0.02 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 16 (6.72) | 7 (8.64) | 9 (5..3) | 0.40 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 30 (12.61) | 16 (19.75) | 14 (8.92) | 0.02 |
| Arterial occlusive disease | 11 (4.62) | 5 (6.17) | 6 (3.82) | 0.52f |
| Multimorbidity | 236 (99.16) | 80 (98.77) | 156 (99.36) | 1.00 |
| Anemia | 9 (3.78) | 4 (4.94) | 5(3.18) | 0.49 f |
| Dementia | 43 (18.07) | 17 (20.99) | 26 (16.56) | 0.40 |
| Neoplasms | 22 (9.24) | 9(11.11) | 13 (8.28) | 0.48 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 49 (20.59) | 16 (19.75) | 33 (21.02) | 0.82 |
| Polypharmacy | 134 (56.30) | 50 (61.73) | 84 (53.50) | 0.22 |
| Delirium | 66 (27.73) | 39 (48.15) | 27 (17.20) | 0.00 |
| Disability | 158 (66.39) | 71 (87.65) | 87 (55.41) | 0.00 |
| Hospital stay (days)** | 10 (6 - 15) | 11 (5 - 21) | 10 (7 - 14) | 0.31m |
| *Mean and standard deviation; **Median and interquartile range; Student's T; m Mann - Whitney - Wilcoxon; Wisher's exact test. | ||||
Regarding the site of infection, urinary tract infection was found to be the most frequent cause of hospitalization, followed by pneumonia and soft tissue infections with 42.9, 38.7 and 16.0%, respectively. Microbiological isolation was achieved in 43.2% of the cases, 100% of which belonged to the Enterobacteriaceae family, with Escherichia coli being the most common causal agent in 46.6%, with a natural resistance pattern in 11.8% (Table 2).
Table 2 Microbiological characteristics of the study population.
| Characteristics | General | Status after the sepsis diagnosis | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) (n=238) | Deceased n (%) (n=81) | Living n (%) n=157 | ||
| Microbiological isolation | 103 (43.28) | 29 (35.80) | 74 (47.13) | 0.10 |
| Escherichia coli: natural pattern | 28 (11.76) | 1 (1.23) | 27 (17.20) | 0.00 |
| Escherichia coli: ESBL | 20 (8.40) | 6 (7.41) | 14 (8.92) | 0.69 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae: natural pattern | 7 (2.94) | 0 (0.00) | 7 (4.46) | 0.10f |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae: ESBL | 11 (4.62) | 6 (7.41) | 5(3.18) | 0.19f |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae: KPC | 3 (1.26) | 3 (3.70) | 0 (0.00) | 0.04f |
|
f Fisher's exact test. ESBL: Extended spectrum B-lactamases, KPC: Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase | ||||
In the multimorbidity model, the bivariate analysis showed that CKD (OR 2.5, 95% CI 1.2-5.5; p=0.017) and CVD (OR 2.1, 95% CI 1.1-4.0; p=0.023) were statistically significant variables (Table 3). For the geriatric syndromes model, delirium (OR 4.5, 95% CI 2.5-8.2; p<0.001) and disability (OR 5.6, 95% CI 2.7-11.9; p<0.001) (Table 4) were statistically significant.
Table 3 Risk factors for 30-day mortality from sepsis. Results of the logistic regression of the model consisting of multimorbidity variables.
| Multimorbidity | Cases (n=81) (%) | Controls (n= 157) (%) | OR | CI (95%) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cerebrovascular disease | 28.4 | 15.9 | 2.1 | 1.1 - 4.0 | 0.023 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 19.8 | 8.9 | 2.5 | 1.2 - 5.5 | 0.017 |
| Coronary disease | 11.1 | 4.5 | 2.7 | 0.9 - 7.5 | 0.052 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 30.9 | 31.2 | 1.0 | 0.6 - 1.8 | 0.956 |
| Hypertension | 75.3 | 73.2 | 1.1 | 0.6 - 2.1 | 0.727 |
| Arterial occlusive disease | 6.2 | 3.8 | 1.7 | 0.5 - 5.6 | 0.671 |
Table 4 Risk factors for 30-day mortality from sepsis. Results of the logistic regression according to the model consisting of geriatric syndrome variables.
| Geriatric syndrome | Cases (n=81) (%) | Controls (n= 157) (%) | OR | CI (95%) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delirium | 48.1 | 17.2 | 4.5 | 2.5 - 8.2 | <.0001 |
| Dementia | 21.0 | 16.6 | 1.3 | 0.7 - 2.6 | 0.400 |
| Disability | 87.7 | 55.4 | 5.7 | 2.7 - 11.9 | <.0001 |
| Polypharmacy | 75.3 | 73.2 | 1.1 | 0.6 - 2.1 | 0.727 |
The multiple regression analysis, which included all the significant variables from the multimorbidity and geriatric syndrome models, showed that CKD (OR 2.1, 95% CI 1.14.8, p=0.037), delirium (OR 3.1 95% CI 1.6-5.8; p=0.001) and disability (OR 3.4 95% CI 1.5-7.5; p=0.002) were statistically significantly associated with 30-day mortality in OAs hospitalized for sepsis in an AGU (Table 5).
Table 5 Risk factors for 30-day mortality from sepsis. Results of the logistic regression according to the final model consisting of significant variables.
| Variables | OR | CI (95%) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cerebrovascular disease | 1.5 | 0.7 -3.0 | 0.274 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 2.1 | 1.1 - 4.8 | 0.037 |
| Delirium | 3.1 | 1.6 - 5.8 | 0.001 |
| Disability | 3.4 | 1.5 - 7.5 | 0.002 |
Discussion
In this study, we evaluated the presence of multimorbidity and geriatric syndromes as risk factors for mortality in a Colombian OA population hospitalized for sepsis in an AGU. As seen in the results, CKD, delirium and disability were the main factors associated with 30-day mortality in OAs hospitalized for sepsis.
Studies have shown that age is an independent risk factor for mortality both for all causes as well as for sepsis 5,12, also suggesting that multimorbidity plays an important role in this aspect 4,23, as seen in a retrospective study evaluating the outcomes of adults with severe sepsis admitted to 171 ICUs in Australia and New Zealand. This study reported a 14% mortality rate in patients without comorbidities vs. 26.4% in patients with multimorbidity, which was statistically significant (p <0.001). In this same cohort, adults who were 44 years old or younger had a 7.3% mortality rate vs. 30.4% in adults 85 years old or older (p <0.001) 4. This agrees with the findings of our study, in which 30-day mortality was 34% and more than 99% of the patients had multimorbidity.
Furthermore, an increased risk of death has been found in patients with a history of CKD and lung disease 24-28, justifying admission to the ICU when the Charlson index is ≥ 3 29. This may be due to an immunological disorder in patients with CKD, as they tend to develop leukocyte abnormalities, coagulation disorders and hypercoagulability states which lead to greater mortality in patients with sepsis 30, similar to our study in which there were statistically significant differences between the mortality of people without CKD (8.9%) and those with CKD (19.8%), with a 110% greater chance of dying in OAs with sepsis and CKD compared with OAs with sepsis but without CKD.
Comprehensive geriatric assessment is considered to be the cornerstone of geriatric practice, an essential tool for approaching geriatric syndromes which could be the first sign of an infectious process in OAs 9, and an interdisciplinary teamwork model, caring for patients at different care levels (acute units, mid-stay units, day hospitals, home care). Within this group of syndromes, the role of delirium as a predictor of mortality stands out. Pisani et al. reported that for OAs 60 years old or older admitted to the ICU, the greater the number of days with delirium, the greater the risk of mortality in the year following admission (HR 1.10; 95% CI, 1.02-1.18) 31. Likewise, the meta-analysis published by Salluh et al. showed a greater mortality (RR 2.2, 95% CI from 1.78-2.70; p<0.001), longer duration of mechanical ventilation (p <0.001) and longer hospital stay both in the ICU (p <0.001) as well as the general ward (p<0.001) in patients who developed delirium during their hospital stay 32, along with greater mortality. This finding was seen in our study, in which patients who developed delirium had a 2.1 times greater chance of dying than OAs without delirium.
Another condition included in the analyses was the presence of disability assessed using the BI. As indicated by Wu L W et al. in their 2016 cohort of 1,834 patients from 60 to 84 years old, disability doubles the risk of death from any cause (HR 2.3 [95% CI 1.3-3.9], p<0.005) 33. Likewise, other studies have shown an association between disability and long-term mortality in patients hospitalized for infectious processes. In a retrospective study of Spanish patients between 75 and 84 years old hospitalized for pneumonia, Núria Torner et al. found that the factors significantly associated with 30-day mortality were: having any degree of disability (OR 3.7, 95% CI, 2.3-5.8; p <0.001), age > 85 years (OR 3.0, 95% CI, 1.7-5.3; p <0.001), impaired cognitive function (OR 1.9, 95% CI, 1.2-3.1; p = 0.005) and ICU admission (OR 2.6, 95% CI, 1.7-5.2; p = 0.009) 34. Cillóniz C et al. also carried out a prospective observational study of 2,149 adult patients with pneumonia over a period of 12 years, whose results showed that mortality increased with age (65-74 years, 6.9%; 75-84 years, 8.9%; > 85 years, 17.1%; P <.001) and was associated with an increase in chronic conditions (neurological conditions causing disability; OR, 2.1; 95% CI; 1.5-2.1), pneumonia severity index IV or V (OR, 3.2; 95% CI, 1.8-6.0), bacteremia (OR, 1.7; 95% CI, 1.1-2.7) and the presence of multidrug-resistant germs (OR, 2.4; 95% CI, 1.3-4.3) 35. On the other hand, Quintero et al., in their study of OA patients hospitalized for pneumonia in an AGU recorded a 30-day fatality of 26.3%; 93% of those who died of pneumonia were dependent prior to hospitalization, compared with OAs without dependence, with a statistically significant difference, indicating that the independent predictors of mortality were: age 90 or above (RR=1.6; 95% CI: 1.1-2.7; p=0.04), multilobar involvement (RR=1.9; 95% CI: 1.1-3.3; p=0.02), elevated blood urea nitrogen (median ≥22.5; RR=3.9; 95% CI: 1.7-9.3; p<0.01), and a Lawton scale score of zero on admission (RR=3.2; 95% CI 1.1-9.8; p=0.04) 36.
With regard to the infectious process, 65-year-old OAs are more prone than young adults to have gram negative bacterial infections, as they have a 1.3 greater chance of being infected by these microorganisms 12. Within the Enterobacteriaceae family, Escherichia coli is the most commonly identified organism in urine cultures obtained from patients with urinary sepsis, occurring in 50% of cases, but other gram-negative bacteria may be present, such as Proteus spp, Klebsiella spp and Pseudomonas spp37. These findings are similar to those of our study in which the most common causal agent was Escherichia coli in 46.6%.
Furthermore, a prospective cohort study of OAs found a 24% mortality rate for patients with negative blood cultures and 31% for those with positive blood cultures 38, similar to our study, with the main source of infection being intra-abdominal (18.6%), followed by healthcare-associated pneumonia and community-acquired pneumonia with 17 and 12.4%, respectively 39, with the latter being the second cause of death in our study.
Despite the available reports, the data on the epidemiology and prognosis of sepsis in OAs in our setting is scant. This is partially explained by the fact that this population is excluded from most research studies 3,12, despite age being a known risk factor which independently predicts mortality, early death after hospital admission, and institutionalization 5,12,40, all of which lends greater relevance to our study.
This study's limitations include its retrospective nature which prevents the analysis of other variables which could affect the outcome, leading to information bias.
In conclusion, in our study of OAs hospitalized for sepsis, the main factors associated with mortality within 30 days of admission to an AGU were delirium, functional decline and CKD. Therefore, it is essential to identify and intervene in these factors to impact on the mortality of OA patients hospitalized for sepsis.











 text in
text in