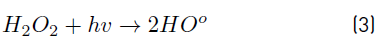1. Introduction
Cyanobacteria are unicellular photosynthetic organisms present in a wide range of aquatic ecosystems [1]. Cyanobacteria are very common in lentic ecosystems like reservoirs, especially in tropical zones where their growth is promoted by high temperatures and nutrient abundance. These conditions lead to eutrophication of aqueous systems, which in turn induces an unmeasured growth of phytoplankton; a phenomenon known as “bloom” [1]. In addition to other problems caused by eutrophication, this rapid and exponential population growth can lead to the production of so-called cyanobacterial toxins, also known as toxic secondary metabolites, produced by certain cyanobacteria, which threaten the health of humans and other living species. These detrimental effects are more significant for the animals that inhabit these ecosystems or humans that use the affected water for irrigation, recreation or water supply without efficient removal treatments [2].
Cyanobacteria include a wide variety of genera and species. Some of these produce very specific toxins, while others generate a spectrum of toxins with varied intoxication mechanisms, acting at the level of cells (cytotoxicity), organs like the liver (hepatotoxicity), or systems, like the nervous system (neurotoxicity) [2]. Moreover, these cyanotoxins have bioaccumulation potential [3].
Hepatotoxins are likely to be the most common cyanotoxins produced by cyanobacteria. They conform a structurally diverse group, including over 90 different microcystins (MCs) [4]. Microcystins and nodularins are the most frequently found cyanobacterial toxins in brackish and fresh water worldwide [2].
MCs are produced by many cyanobacterial genera, including Microcystis sp., Oscillatoria sp., Nostoc sp., Anabaena sp. and Anabaenopsis sp. The synthesis of these toxins is a very complex process, influenced by environmental conditions, and varying depending on each strain present in the water [2, 5]. The toxicity level of a mixture of these cyanotoxins will vary according to the kind of toxins present in the water. In fact, MC-LR is the general reference for MCs [5, 6]. Due to several intoxication reports, the World Health Organization (WHO) has suggested 1 µg L-1 as the maximum allowable concentration for MC-LR in drinking water.
MCs are water soluble molecules with a cyclic peptide structure composed of seven amino acids, and a lateral “Adda” chain with a double conjugated bond, as observed in Table 1. Its toxicity is thought to be explained by this. From a structural point of view, these molecules are characterized by their chemical stability. Indeed, MCs are resistant to boiling, chemical hydrolysis and oxidation at a pH close to neutrality. In natural water and under dark conditions, MCs can remain stable for months or even years [4, 6].
Many conventional treatment methods for drinking water production, such as coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation and filtration, allow the removal of cyanobacterial cells, thus preventing cell lysis and toxin release. However, under common operational conditions these traditional water treatment processes cannot guarantee the effective elimination of extracellular cyanobacterial toxins that were already present before the treatment began [5-7].
In order to tackle the problem of cyanotoxin pollution in water, previous studies suggest the application of advanced oxidation processes (AOPs). Among these, the combination of UV-radiation with an oxidizing agent such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) stands out as a viable solution for the remediation of water contaminated with cyanotoxins, by allowing the formation of the free hydroxyl radical (HO°), as a powerful oxidizing agent (E0=2.8 V) [8-12].
Keeping in view the facts mentioned above, MC-LR cyanotoxin removal efficiency using a UV/H2O2 system both in natural water and in distilled water was evaluated in the present work. For this purpose, different combinations of H2O2 initial concentration and UV irradiance were assessed using a multilevel factorial design of experiments with the aim of finding the optimal working conditions of the oxidation system to control the problem of MC-LR natural water pollution and, subsequently, to produce safe drinking water in compliance with all legally stipulated parameters for public consumption.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Reagents
A MC-LR standard solution bioreagent grade (from Microcystis aeruginosa) C49H74N10O12 (> 95.5% purity), HPLC grade, was obtained from Cyano Biotech GmbH (Berlin, Germany). 10 mL 500 µg L-1 was prepared using methanol as solvent. Hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 30% (w/w), was obtained from J.T. Baker (Ecatepec, Mexico State, Mexico) and anhydrous sodium sulfite (Na2SO3 98% pure), from Carlo Erba Reagents (Sabadell, Spain). Methanol solvent used was LC/MS grade and supplied by J.T Baker. Deionized water, used for MC-LR determination, was obtained from a Millipore water purification system (Bedford, MA, USA).
2.2 MC-LR determination
MC-LR concentration was monitored over time using an ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometer UHPLC-MS/MS (Waters Acquity H-Class), (Xevo TQD). The toxin was previously extracted and concentrated using solid phase extraction (SPE) procedure.
Each sample was filtrated through mixed cellulose ester filters with 0.45 μm pore size. Subsequently, MC-LR was extracted following the SPE procedure for concentrating and cleaning the toxins with a 200 mg/6 mL Hidrophilic Lipohilic Balance cartridge. The cartridge was initially purged with 10 mL of methanol, followed by 10 mL of deionized water. After that, 100 mL from each previously filtrated water sample was vacuum-filtrated through the cartridge at a 3 mL min-1 flux. 5 mL of deionized water was then added and the cartridge were left to dry for 30 min. Afterwards, the analytes were eluted with 10 mL of 90/10 methanol/deionized water. Finally, each sample was dried with nitrogen gas for around 3 h and resuspended in 1 mL of 90/10 methanol/deionized water. The sample was then filtrated, this time through a 0.22 μm nylon membrane filter, and deposited in a certificated LC-MS/MS vial. In this way, a 100 concentration factor was obtained. In addition to the sample analysis, a replicate, an enriched sample, a 20 µg L-1 control and a blank were used as analytical controls and were analyzed according to the quality management system of GDCON research group.
With respect to the chromatographic conditions, 20 μL of each prepared sample was injected into the LC-MS/MS system. For separation purposes, a 2.1 mm X 50 mm ACQUITY UPLC BEH Shield RP18 column of 1.7 μm particle size was used. UHPLC conditions were as follows: 30 °C column temperature, 0.25 mL min-1 flux and 10.5 min running time. Deionized water was used in the mobile phase with 20 mM ammonium formate along with an organic solution consisting of LC-MS/MS grade methanol with 20 mM ammonium formate. Meanwhile, operating conditions for the mass spectrometer were 150 and 350 °C as the source and desolvation temperatures, respectively; 650 and 50 L h-1 as the desolvation and cone gas flux; ESI (+) ionization mode and 3.7 kV capillarity voltage.
For the quantification of the MC-LR, a calibration curve was constructed from 5-80 µg L-1 (5, 10, 30, 50, 60 and 80 µg L-1). The quantification limit (LoQ) was 5.0 µg L-1. The lowest value detected in the samples was 0.05 µg L-1 (LoD). Samples were quantified using the linear regression obtained from the calibration curve.
2.3 Photochemical experiments and experimental design
For the MC-LR removal experiments, natural water from a wetland located in “El Porvenir”, in Rionegro (Antioquia, Colombia), and distilled water were used. Their physicochemical characteristics are listed in Table 2.
A 2 L effective capacity jacketed photochemical reactor with 4 germicidal low pressure lamps emitting mainly at 254 nm with 0.63 mW cm-2 irradiance, verified through a UVX radiometer (Upland, CA, USA), was used for the UV-radiation simulation. H2O2 was evaluated at 15 and 30 mg L-1concentration levels. The reaction solution temperature was kept stable with the external refrigeration jacket. Homogeneity was kept through continuous agitation at 260 rpm. Before starting the experiments, the UV lamps were warmed up for 30 min to ensure stable emission. Samples were spiked with 20 µg L-1 MC-LR. Aliquots of 100 mL were withdrawn at different time intervals during the oxidation treatment. In order to stop the action of H2O2, Na2SO3 was added immediately. Residual MC-LR in the reaction solution was analyzed through the SPE-UHPLC-MS/MS method previously described. In Figure 1, the experimental setup, composed of the photochemical reactor, the solid phase extraction (SPE) procedure and the ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometer, is illustrated.
The effects of the oxidizing agent and the UV-radiation, in terms of UV irradiance, were evaluated using a multilevel factorial design of experiments (DOE), resulting in 6 runs, which were executed randomly. Every run was carried out in triplicate and average values were reported. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) test was conducted and a second-order regression model, described by Equation (1), was built
Where y denotes the removal percentage of MC-LR for 30 min of treatment; β 0 is the intercept; β i , β i, β ii , and β ij refer to the linear, quadratic and interaction regression coefficients, respectively; x i represents the levels of the independent variables; and ε is the experimental error.
By optimizing the response variable, the optimal operating conditions that allow obtaining the highest removal of MC-LR for each factor within the experimental domain were found in distilled water for 30 min of treatment. Under the calculated optimal working conditions, the MC-LR elimination efficiency of the oxidation system for a reaction time of 60 min was investigated and compared to that found for the removal of MC-LR in fresh natural water.
The statistical treatment of the experimental data was performed using Statgraphics Centurion XVII (Statpoint, Warrenton, USA).
3. Results and discussion
Promising results were obtained for the UV/H2O2 system, both in the distilled and natural water tested. Removal values higher than 99% were achieved.
3.1 Optimization studies of the UV/H2O2 system operating conditions
For the implementation of the UV/H2O2 system, a multilevel factorial DOE was performed. For this purpose, the UV irradiance and the H2O2 content were considered as main factors and were evaluated at 2 (0 and 0.63 mW cm-2) and 3 (0, 15 and 30 mg L-1) levels, respectively. The response variable was the removal percentage of MC-LR at 30 min of treatment, in order to discern their optimal working conditions and to examine the effects of the two controllable variables selected for studying the efficiency of the system. In Table 3, the DOE matrix composed of 6 runs executed randomly, and the levels of the considered factors are listed. Additionally, the experimental and calculated removal percentages of MC-LR cyanotoxin are reported.
Table 3 Selected factors levels, experimental matrix and MC-LR removal percentages by the implementation of the UV/H2O2 system

In order to build the second-order regression model that correlated the removal percentage of MC-LR with the UV/H2O2 system factors, ANOVA test was performed [Table 4]. It can be observed that the UV irradiance, the oxidizing agent and the interaction effect of both factors were significant from a statistical point of view at 95% of confidence interval due to the low p-values (lower than 0.05) and large F-ratio associated with. The quadratic term for H2O2 concentration resulted to be statistically non-significant; however, since its p-value was near 0.05, it was included in the second-order polynomial regression model.
Table 4 Analysis of variance (ANOVA) describing the removal of MC-LR cyanotoxins by the UV/H2O2 system

The second-order regression model resulting from the ANOVA test is described by Equation (2).
The adequacy and significance of the developed regression model representing the removal of MC-LR cyanotoxin were studied. The model resulted to be statistically significant (regression p-value was 0.0125 at 5% of significance level), explaining the 99.99% and 99.96% of the variability in the MC-LR cyanotoxin elimination efficiency by the resulting determination coefficient and the adjusted determination coefficient (R2 and R2adj, respectively). Additionally, Shapiro-Wilk test p-value (0.18734) was higher than 0.05, which indicated that the obtained experimental data were normally distributed. In addition, constant homoscedasticity and factor independency assumptions were also accomplished. Therefore, from those results, it can be concluded that the second-order regression model built can adequately and significantly predict the efficiency of the oxidation system studied for reducing the concentration of MC-LR in distilled water.
The magnitude and significance of the effects of the variables as single, quadratic and interaction effects are shown in the Pareto chart [Figure 2]. It can be observed that the UV irradiance and the H2O2 concentration developed a significant positive effect on the removal of MC-LR cyanotoxin in distilled water, as well as the interaction effect between the irradiance and the oxidizing agent. That positive impact of the UV irradiance and the H2O2 content on the oxidation system can be also observed from Figure 3, representing the effect of the main factors. This is indicative that the elimination of MC-LR in distilled water increased as the factors went from their low to their high levels.

Figure 2 Pareto chart for the regression model describing the removal of MC-LR cyanotoxin in distilled water by the UV/H2O2 system. [H2O2]0= 0-30 mg L-1; UV-C irradiance = 0-0.63 mW cm-2; [MC-LR]0~ 20 µg L-1; treatment time= 30 min
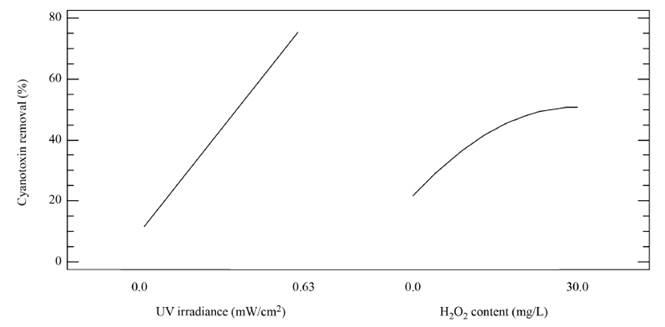
Figure 3 Main effect plot for the regression model describing the removal of MC-LR cyanotoxin in distilled water by the UV/H2O2 system. [H2O2]0= 0-30 mg L-1; UV-C irradiance = 0-0.63 mW cm-2; [MC-LR]0~ 20 µg L-1; treatment time=30 min
The positive influence of the UV irradiance on the system can be explained from the important role developed by this factor in photon-based AOPs, such as the UV/H2O2 system. In fact, irradiance resulted to be the most significant factor on the UV/H2O2 system for the removal of MC-LR cyanotoxin within the experimental domain tested, since the amount of HO° formed has been reported to be closely related to the amount of photons interacting the reaction solution and producing the homolysis of H2O2, as described by Equation (3), resulting in an improvement of the oxidation system efficiency.
In turn, the H2O2 concentration influenced positively the system under the experimental conditions tested here, as observed in Figure 2 and 3. Nonetheless, in Figure 3 a slight curvature can be evidenced near the high level of the oxidant content (30 mg L-1). It must be noted that, it has been generally stated that, at a low H2O2 level, the oxidation efficiency of the system is limited by the low HO° production, which increases by increasing the H2O2 concentration (Equation (3)], up to a certain point where an excessively high content of H2O2 inhibits the degradation rate, as it would be the case if the concentration of H2O2 was extended beyond 30 mg L-1, keeping constant the irradiation value of 0.63 mW cm-2. This phenomenon can be ascribed to the scavenging effect on HO° developed by the oxidant (H2O2), as represented in Equation (4), and the subsequent side effect reactions described by Equations from (5) to (8) [12]. In this scenario, any competitive reaction would reduce the MC-LR degradation rate [8]. According to this, the H2O2 threshold concentration was not reached in this study within the experimental domain. The H2O2 threshold concentration has been reported to vary for each particular case. For example, in general terms, the oxidant threshold level rises with the rise of the UV fluence [13]. Furthermore, the H2O2 threshold concentration varies according to the pH of the solution, the diverse components present in water and the cyanotoxin concentration [10]. Additionally, it is important to note that a lower initial MC-LR concentration has been evidenced to lead to a higher and more efficient removal [12]. This fact could be explained by the relative increase of the molar ratio H2O2/MC-LR as the toxin concentration is decreased [10].
The positive effects of the UV irradiance and the H2O2 concentration can also be observed from the sign “+” of the regression coefficients for these linear factors in the regression model represented by Equation (2). Additionally, these effects can be found in Figure 4, where the response surface and contour plot estimated by the regression model built are illustrated. From the figure, the optimal working region was observed to be located at 0.63 mW cm-2 and close to 30 mg L-1 H2O2. In order to find exactly such as operating conditions, the response variable was optimized. The optimal conditions for achieving the highest elimination of MC-LR by the application of the UV/H2O2 system within the experimental domain were exactly: 0.63 mW cm-2 and 30 mg L-1 for the UV irradiance and the H2O2 content, respectively.
3.2 Removal of MC-LR cyanotoxin by the UV/H2O2 system operating under optimal conditions
After evaluating the influence of each main factor and optimizing the oxidation system. Further experiments were conducted for assessing the MC-LR cyanotoxin removal capacity of the UV/H2O2 process under optimal working conditions by extending the reaction time at 60 min using distilled water. Results are represented in Figure 5. It can be concluded that by increasing 30 min the treatment time, the oxidation potential of the system was improved since higher MC-LR removal was observed, reaching a reduction of the MC-LR content of 99.73%.

Figure 5 Removal profile of MC-LR cyanotoxin vs time during the UV/H2O2 system application in distilled water under optimal operating conditions. [H2O2]0= 30 mg L-1; UV-C irradiance= 0.63 mW cm-2; Co~ 20 µg L-1
Additionally, control experiments were performed using the sole action of the UV irradiance and that of the H2O2 content to verify that the positive results obtained in MC-LR cyanotoxin concentration reduction were ascribed to the role of the HO° produced by the combined action of the factors governing the oxidation system. Dark experiments without irradiation or H2O2 were also conducted in order to evaluate the hydrolytic behavior of the target cyanotoxin.
As illustrated in Figure 5, an irradiance of 0.63 mW cm-2 achieved about 49% (48.96%) of the cyanotoxin removal for a treatment time of 60 min, starting at 19.26 and finishing at 9.83 µg L-1 MC-LR. Although a higher removal of MC-LR was obtained compared to the action of H2O2 alone, the elimination percentage was lower than that achieved through the coupled UV/H2O2 system, as indicated previously. These results were consistent with the literature. It has been previously stated by several authors that direct MC photolysis results are low in comparison with those obtained when combining UV-C radiation with the action of an oxidizing agent such as H2O2 [8-10, 12, 14]. It is important to consider the varying conditions under which the reported studies were performed, including the initial toxin concentration, oxidizing agent concentration, UV irradiance used and even the environmental conditions or the physicochemical properties of the water tested. For example, a high MC-LR concentration has been found to cause high optical density, leading to an interference in the UV radiation penetration. Consequently, a low UV light was absorbed by the H2O2 molecules, decreasing the HO° production. In addition, a high MC-LR concentration also can produce a wide range of reaction by-products which could compete with the MC-LR for the HO° during the treatment [12]. For the conditions used in the current research, this phenomenon did not represent a problem.
With regard to the experiments using H2O2 without UV radiation (also shown in Figure 5], no significant MC-LR removal was achieved for a reaction time of 60 min. The effect of 30 mg L-1 H2O2 was also evaluated for a reaction time of 72 h. Even after this extended treatment time, no effect above 13% was obtained. This phenomenon can be explained by the fact that H2O2 alone can take days to work, so no effective removal action can be achieved in short experimentation periods. This has been noted by other authors [15-18]. In fact, a H2O2 concentration of 60 mg L-1 for 3.5 h under dark conditions was used and no damage was found to cyanobacteria cellular integrity [15]. Meanwhile, in the experiments performed in a shallow lake, cyanobacteria concentration dropped by 90% in 3 d and by 99% in 10 d with the application of 2 mg L-1 H2O2 to all the lake [16]. Nevertheless, it is emphasized that it is difficult to compare laboratory with field results, given the variations among the water matrix quality and the hydraulic and environmental conditions in both scenarios, which affect the oxidizing reaction efficiency.
3.3 Removal of MC-LR cyanotoxin in fresh natural water by the UV/H2O2 system under optimal operating conditions
As mentioned above, the intrinsic properties of the water to be used for evaluating the efficiency of a particular treatment is an issue of special concern, especially when scaling-up a laboratory process. In this regard, the oxidation capacity of the UV/H2O2 system under optimal working conditions was also assessed using fresh natural water containing 20 µg L-1 of the target cyanotoxin. As shown in Figure 6, and in comparison with the results illustrated in Figure 5 for the combined action of the UV irradiance and the H2O2 content, although positive results were obtained, the reduction of MC-LR in fresh water was slower for the first treatment stages, since 66.12% MC-LR removal was achieved using a H2O2 dose of 30 mg L-1 for 10 min of treatment compared to the removal extent obtained in distilled water (88.50%). This could be explained by the influence of natural constituents of fresh water including Cl-, NO3 -, PO4 3-. CO3 2- and SO4 2- in the elimination of MC-LR, since the presence of these ions can limit the removal of MC-LR. Indeed, NO3 - could also reduce the UV light intensity reaching the aqueous solution by acting as an internal filter, and the CO3 2- could eliminate HO° [8, 10-12]. Furthermore, it has been established that the efficiency of the UV/H2O2 system was affected not only by the organic matter levels and alkalinity, as mentioned in the majority of studies, but also by the presence of transition metals in natural water [19], including iron. This can be ascribed to the occurrence of other AOPs, such as the Fenton and photo-Fenton processes, which could increase the oxidation capacity of the treatment system. As shown in Table 2, low dissolved iron content was found in the natural water tested; therefore, the occurrence of the Fenton or photo-Fenton AOPs, was unlikely and, subsequently, the improvement of the MC-LR cyanotoxin removal capacity of the oxidation system with regard to that found in distilled water.
Nonetheless, in spite of that, once the treatment time was extended 60 min, similar reduction values were obtained for both water matrices (99.59% for the fresh water and 99.73% for the distilled water), as it can be observed by comparing Figure 5 and 6. These promising results could be ascribed to the absorbance of the natural water at a 254 nm wavelength, which was fairly high compared to that of distilled water, as observed in Table 2; thus the probability of the UV light photons impacting H2O2 molecules was higher. This would result in H2O2 photolysis, instead of the UV light impact affecting only the organic matter and other constituents naturally present in the tested water, and, therefore, in the improvement of the HO° production. Furthermore, according to the literature, pH of the water tested has been evidenced to have an influence on the oxidation capacity of the system. Indeed, it has been reported that neutral and slightly acid conditions were appropriate for MC-LR degradation. The acid conditions of the water matrices tested here could have favored the removal efficiency in the natural water samples with a pH of 5.8 and in the distilled water samples with a pH of 6.3 [Table 2] [12].

Figure 6 Removal profile of MC-LR cyanotixn vs time during the UV/H2O2 system application in fresh natural water. [H2O2]0= 15 and 30 mg L-1; UV-C irradiance=0.63 mW cm-2; Co~ 20 µg L-
Natural water was also used to determine the efficiency of the oxidation process on removing MC-LR cyanotoxin at 0.63 mW cm-2 reducing the content of H2O2, as observed in Figure 6. Similar results were obtained by using 30 and 15 mg L-1 of H2O2; particularly, a removal of the target cyanotoxin of 99.59 and 98.08% were achieved, respectively, which were below the WHO recommended limit for MC-LR in drinking water. This indicates that the content of H2O2 for treating 20 µg L-1 of MC-LR cyanotoxin can be reduced by half, saving in operating costs. On the other hand, it is important to note that from the author’s knowledge, H2O2 residual concentration after applying the treatment under similar working conditions is reduced by about half with respect to the initial content. This fact, added to the unstable character of H2O2, as described by Equation (9), leads to the necessity of using an additional disinfection agent to guarantee water disinfection when it is not consumed immediately.
Therefore, by using the UV/H2O2 system, high efficiencies in the removal of MC-LR cyanotoxin in fresh water under the operating conditions tested here were achieved. Nonetheless, further studies are suggested to be conducted in order to study the influence of the radiation intensity tested at different irradiance values since the H2O2 photolysis rate has been reported to be directly correlated with UV irradiance, and, therefore, in general terms, a high UV intensity improves the quantity of HO° produced, while a low UV intensity limits photolysis [12]. However, it has been found that, even when a higher UV intensity contributes to a higher removal rate, it was not directly correlated to the toxin degradation rate [10]. Therefore, there is a point where the increase of UV intensity is not economically efficient as it will have a very small effect on the degradation rate.
Additionally, different constituents and physicochemical characteristics of the water matrix tested could influence the reaction, due to the trapping of HO° and/or the reduction of the UV radiation penetration in the water [10-12], as indicated above. On the other hand, degradation by-products identification and relative quantification are recommended to be carried out since some of the reaction intermediates formed can be more toxic than the parent substances, even though it has been demonstrated that the by-products originated from MC-LR degradation with UV-C light were not toxic, because this reaction general occurs on the double conjugated bond from the aminoacidic fraction Adda ((2S,3S,4E,6E,8S,9S)-3-amino-9-methoxy-2,6,8-trimethyl-10-phenyl-4,6-decadienoic acid) which is the responsible for the hepatotoxic effect of the toxin [20].
4. Conclusions
Preliminary studies in distilled water spiked with 20 µg L-1 MC-LR cyanotoxin showed that the combined action of the H2O2 dose and the UV radiation incidence significantly influenced the MC-LR removal after the AOP application. Under optimal operating conditions (0.63 mW cm-2 UV irradiance and 30 mg L-1 H2O2 content), a reduction of the MC-LR initial content of 99.73% was observed, being the oxidation capacity of the system faster during the first initial stage of the process application, since around 88.50% MC-LR removal was achieved in only 10 min of treatment. Additionally, UV irradiance alone was shown to be more effective than the degradation found with the sole action of H2O2, as at 60 min of treatment removal percentages were still not significant.
When evaluating the oxidation potential of the UV/H2O2 system in natural fresh water, an effective MC-LR removal was also observed using the combined action of UV irradiance and the oxidizing reagent H2O2, reaching a removal percentage of 99.59%, which was well below the recommended limit of 1 μg L-1 established by the WHO for MC-LR in drinking water. A H2O2 content of 15 mg L-1 was also tested and, although 98.08% of MC-LR elimination was found for a reaction time of 60 min, the WHO advisable limit was not surpassed.
In this way, the application of the UV/H2O2 system could be considered as an alternative treatment to be used for producing drinking water, providing the accomplishment of the whole set of water quality standards included in the legislation.