Introduction
In 2018, cholelithiasis and cholecystitis ranked as the second most common gastrointestinal diagnosis in hospitals in the United States, with a total of 316,200 hospitalizations per year and a visit rate of 99.2 per 100,000 people. Additionally, they were identified as the fifth leading cause of readmissions in emergency services1,2. Gallbladder disorders are particularly important in the differential diagnosis of abdominal pain, which is the primary reason for emergency consultations among the adult population. Similarly, acute cholecystitis is one of the main conditions that may require surgical intervention3.
The majority of cholelithiasis cases develop asymptomatically4, and many are discovered incidentally during diagnostic imaging studies. However, the presence of symptoms and a lack of timely treatment can lead to significant complications such as acute cholecystitis, choledocholithiasis, cholangitis, or acute pancreatitis. Among these complications, acute cholecystitis stands out as one of the most common and is considered a leading cause of complicated intra-abdominal infections according to data from the World Society of Emergency Surgery (WSES)5. Although cholelithiasis is more common in women, the associated complications are more frequent in men6.
In Colombia, there are isolated epidemiological reports of the prevalence of cholelithiasis in patients with functional dyspepsia7, cholecystitis in histopathological studies8,9, and hospital records9; however, there are no studies on the national prevalence of this condition. The Individual Records of Health Service Provision (RIPS in Spanish), which document more than 500 million patient contacts with the health system each year10, have been widely used both to estimate the prevalence of numerous conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis11 or Sjögren’s syndrome12, and for studies on the burden of disease attributable to obesity and overweight13 or gastric cancer14.
Given its frequent presentation and the significant morbidity burden it represents, the objective of this study was to establish the prevalence of acute cholecystitis and describe the sociodemographic characteristics of patients in Colombia using the RIPS data.
Methods
This is a descriptive cross-sectional study using information from the Individual Records of Health Service Provision (RIPS). The sociodemographic information (sex, age, and location of care) of all individuals diagnosed with acute cholecystitis and cholelithiasis across the entire country, covering all health system enrollment schemes between 2018 and 2022, was extracted from the records. The filter “persons attended” was applied using the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) codes for acute cholecystitis and cholelithiasis (codes K800, K801, K804, K810, K818, and K819), and data on procedures were also gathered according to the Unified Classification of Health Procedures (CUPS in Spanish) for cholecystectomy (code 5121). A database was created in Microsoft Excel 2016, where the data were categorized by sex, age in years and in five-year age groups, and geographical divisions by department. For prevalence calculations, the official data from the National Administrative Department of Statistics (DANE) for 2019, projected from the 2018 national census, were used as the denominator. A description of the data obtained, including frequencies and prevalence rates per 100,000 inhabitants, was then conducted.
Since this was a secondary analysis of consolidated, anonymized, and publicly accessible data, it was deemed unnecessary to seek approval from a research ethics committee.
Results
Between January 2018 and December 2022, a total of 599,250 individuals were diagnosed with cholelithiasis without cholecystitis (449,918 women, 75.1%), which represents 1.18% of the general population. There were 343,254 cases of acute cholecystitis (240,193 women, 69.9%), with an unadjusted prevalence of 681 cases per 100,000 inhabitants (942 per 100,000 women, 414 per 100,000 men), resulting in a female-to-male ratio of 2.3:1. Of these patients, 24,876 (7.2%) had associated choledocholithiasis. Additionally, 92,964 cholecystectomies were performed in patients with acute cholecystitis (accounting for 27.1% of these patients); however, during the same period, a total of 278,386 cholecystectomies were recorded.
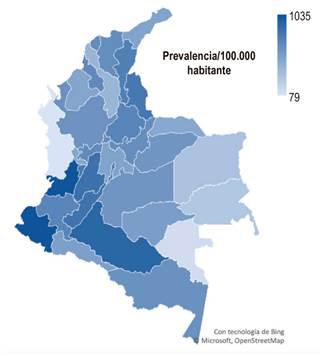
On a national level, the departments with the highest prevalence of acute cholecystitis were Nariño with 1,035 per 100,000 inhabitants, Valle del Cauca (1,027 per 100,000), followed by Caquetá (917 per 100,000) and Tolima (844 per 100,000), all located in the southwestern region of the country. The number of cases per department is shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Number of Cases of Acute Cholecystitis and Prevalence per 100,000 Inhabitants by Department for the Five-Year Period 2018-2022
| Department | Cases | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| Amazonas | 504 | 632 |
| Antioquia | 42,493 | 628 |
| Arauca | 1,336 | 489 |
| Atlántico | 17,332 | 673 |
| Bogotá | 61,890 | 747 |
| Bolívar | 8,894 | 405 |
| Boyacá | 8,432 | 657 |
| Caldas | 6,750 | 678 |
| Caquetá | 4,608 | 917 |
| Casanare | 2,306 | 604 |
| Cauca | 10,227 | 717 |
| Cesar | 8,087 | 750 |
| Chocó | 409 | 79 |
| Córdoba | 9,199 | 507 |
| Cundinamarca | 14,892 | 523 |
| Guainía | 123 | 279 |
| Guaviare | 654 | 557 |
| Huila | 10,061 | 831 |
| La Guajira | 5,530 | 518 |
| Magdalena | 8,642 | 658 |
| Meta | 6,310 | 610 |
| Nariño | 18,949 | 1,035 |
| Norte de Santander | 11,252 | 802 |
| Putumayo | 1,973 | 542 |
| Quindío | 4,542 | 785 |
| Risaralda | 4,871 | 501 |
| San Andrés | 165 | 209 |
| Santander | 15,020 | 715 |
| Sucre | 6,049 | 683 |
| Tolima | 12,018 | 844 |
| Valle del Cauca | 49,337 | 1,027 |
| Vaupés | 59 | 130 |
| Vichada | 246 | 311 |
| Total | 343,254 | 681 |
Source: Individual Records of Health Service Provision (RIPS), official SISPRO data.
The prevalence of acute cholecystitis by sex was 942 per 100,000 inhabitants for women and 414 per 100,000 inhabitants for men. The female sex showed a higher number of cases in all departments and age groups for each of the years analyzed. The age group with the highest number of cases was the 35-39 age group, with 32,858 cases, followed by the 30-34 age group (31,876 cases) and the 40-44 age group (30,748 cases). However, the prevalence of the disease consistently increased across all age groups, with the highest prevalence found in those over 80 years old (2,788 per 100,000 inhabitants). Cases in the pediatric population (aged 0 to 14 years) represented 2.3% of all reported acute cholecystitis cases during the period analyzed, with a prevalence of 63 per 100,000 inhabitants. The number of cases by age group and sex is shown in Table 2. The prevalence data by department during the period from 2018 to 2022 are illustrated in Figure 1.
Table 2 Number of Individuals Diagnosed with Acute Cholecystitis in Colombia and Prevalence per 100,000 by Five-Year Age Groups and Sex between 2018 and 2022
| Age (years) | Cases | Prevalence | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | Women | Men | Women | Total | |
| 0 to 4 | 1,357 | 2,222 | 61 | 104 | 82 |
| 5 to 9 | 681 | 725 | 31 | 35 | 33 |
| 10 to 14 | 1,316 | 1,825 | 61 | 88 | 74 |
| 15 to 19 | 2,178 | 7,048 | 100 | 338 | 216 |
| 20 to 24 | 3,418 | 16,752 | 156 | 798 | 470 |
| 25 to 29 | 5,407 | 23,655 | 253 | 1,154 | 695 |
| 30 to 34 | 6,832 | 25,044 | 355 | 1,318 | 834 |
| 35 to 39 | 8,361 | 24,497 | 501 | 1,396 | 960 |
| 40 to 44 | 8,823 | 21,925 | 589 | 1,372 | 993 |
| 45 to 49 | 8,715 | 20,590 | 645 | 1,398 | 1,038 |
| 50 to 54 | 9,367 | 21,011 | 700 | 1,417 | 1,077 |
| 55 to 59 | 9,745 | 20,032 | 813 | 1,494 | 1,173 |
| 60 to 64 | 9,126 | 17,046 | 964 | 1,569 | 1,287 |
| 65 to 69 | 8,525 | 13,704 | 1,201 | 1,653 | 1,444 |
| 70 to 74 | 7,389 | 1,076 | 1,475 | 1,764 | 1,634 |
| 75 to 79 | 6,226 | 8,577 | 1,946 | 2,047 | 2,003 |
| 80 or more | 8,713 | 12,949 | 2,782 | 2,793 | 2,788 |
| Total | 103,061 | 240,193 | 414 | 942 | 681 |
Source: Individual Records of Health Service Provision (RIPS), official SISPRO data.
Discussion
According to official records from the Ministry of Health, nearly 600,000 people were diagnosed with cholelithiasis in Colombia over the five-year period from 2018 to 2022, with 70% of them being women. This finding aligns with reports in the literature, which describe that women are almost twice as likely as men to develop gallstones. The main established risk factors include female sex hormones (which explains the reduction in cases after menopause), parity, the use of oral contraceptives, and estrogen replacement therapy. The pathophysiological explanation is that estrogens increase cholesterol secretion and reduce bile salt secretion, while progestins decrease bile salt secretion and alter gallbladder emptying, which can lead to stasis2.
Traditionally, it is described that cholelithiasis and cholecystitis are more common in women around the age of 40, during their reproductive years, and in those with obesity. Although the results show a higher number of cases in women (with a ratio of 2.3 to 1 compared to men), and the highest prevalence in the 35-39 age group, the prevalence of the disease increases with age, a finding similar to that reported in international literature15.
One noteworthy point is that, according to this registry, the pediatric population accounts for 2.3% of all acute cholecystitis cases in Colombia. Several studies have shown that this condition has been increasing in children over the past 20 years, and the acalculous variant accounts for 50% to 70% of all reported cases. In 2016 alone, pancreatobiliary diseases were the fourth most common cause of pediatric gastrointestinal emergency visits in U.S. hospitals, with cholelithiasis and cholecystitis comprising the largest group, totaling 10,948 cases, with an average hospitalization cost of USD 37,6072. This is even more significant considering the association of acalculous cholecystitis in this age group with viral infections (such as Epstein-Barr and hepatitis A), systemic lupus erythematosus, and Kawasaki disease16. The cause of the increasing prevalence of cholecystitis in this population remains under investigation. Some studies suggest the global rise in childhood obesity, as well as the earlier onset of puberty, which in females triggers an earlier hormonal influence, thereby increasing the risk of developing this disease17,18.
Additionally, ethnicity appears to play an important role not only in the prevalence of cholelithiasis but also in the type of gallstones. Cholesterol gallstones are more common in developed Western countries, while brown pigment stones in the bile ducts have historically been more prevalent in Asia. However, in developing Asian countries, there has been a shift from pigment stones to cholesterol stones, which has been attributed to a lower rate of chronic biliary infections and the adoption of a more Westernized diet19.
As previously mentioned, acute cholecystitis is a common condition worldwide, representing the most frequent complication of cholelithiasis and contributing to increased global mortality from other causes such as cardiovascular diseases and cancer20. The presence of gallstones has been associated with a higher risk of gallbladder cancer, bile duct cancer, and ampullary cancer21.
Notably, the percentage of cholecystectomies performed on patients with acute cholecystitis (27.1%) is below the average reported in other countries, where this procedure can be performed in up to 60% of patients with this diagnosis1,22. However, when reviewing the total number of cholecystectomies performed regardless of the associated diagnosis, the numbers increase significantly, suggesting that the majority of these procedures are likely performed on an outpatient basis in Colombia, similar to reports from other countries. In 2019, gallstone disease contributed to approximately 2.2 million outpatient visits in the United States, and 935,000 cholecystectomies were performed, most of them laparoscopic and outpatient (605,000), compared to laparoscopic procedures in hospitalized patients (280,000). This shift in management is due to more efficient intervention in treating this condition, which has contributed to reducing mortality rates by up to 70%4.
According to some studies, the prevalence of the disease has increased globally in recent years. This rise has been linked to a greater number of patients with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome23. Our study results show a similar increase in prevalence over the years, except for 2020, where a decrease in the number of cases was observed. This finding is related to the COVID-19 pandemic, during which there was a global reduction in consultations for non-communicable diseases due to social isolation measures24. In our study, the total number of records of people seen for all causes decreased in 2020, with a 14% reduction compared to 2019.
Despite being a highly prevalent disease globally, there were no national epidemiological data on its sociodemographic distribution in Colombia. Previous national epidemiological studies were based on hospital records or histopathological studies8,9. Among the limitations of this study are the common weaknesses in the analysis of administrative databases, including the potential for misclassification of ICD-10 diagnostic codes in medical records by healthcare personnel25. Additionally, codes such as “other cholecystitis” may include cases of chronic disease. Another limitation in estimating prevalence and its changes over the years is the increase in the number of care records each year, which may overestimate the disease rate. However, a larger number of annual care records at the departmental level ensures higher quality information and a more reliable report on the disease.
Conclusion
This study provides epidemiological information on acute cholecystitis in Colombia, drawn from the Ministry of Health’s database. The sociodemographic data align with the sex and age distribution reported in global literature, with the exception of the proportion of cholecystectomies performed, which is lower than the average in other countries. The higher prevalence observed in the southwestern part of the country warrants further studies and opens the door to population-based interventions targeting these regions.











 text in
text in