Introduction
Population aging worldwide is marking a transition in different social, cultural, economic and labor market aspects (1). It is also transforming disease profiles, as chronic noncommunicable diseases have increased (2, 3) and there is a higher prevalence of multimorbidity (4, 5). Associated with this, the prevalence of dementia (6, 7) and pathologies with functional dependence has increased, which has led to the development of care modalities to meet this demand, particularly home care (1).
Wieland et al. (8) defined home visits as a model of health care in the patient’s residence with the aim of promoting, slowing down or minimizing the impact of disease and disability. Home care programs are defined as a health service that aims to provide continuous medical care to patients with special conditions that cannot be treated on an outpatient basis and do not require hospitalization to resolve them (9). This care can be provided in different scenarios: for patients with functional dependence or disability who are unable to attend outpatient consultation, which is a first level of care, or as home hospitalization, to avoid overcrowding of hospital beds (10, 11).
In Colombia, home care was implemented as an option for chronic patients affiliated with the National Institute of Social Security, in response to the need indicated by legal rulings, which required home medical and rehabilitation services.
Currently, home care is offered by different health care institutions dedicated exclusively to this branch, which has become more attractive because it has managed to reduce hospital occupancy and optimize costs. This care is usually provided by general practitioners (12). Despite the change in the population, in the needs of elderly patients and the growth of geriatrics and psychogeriatrics in the country as a response to these (13, 14), there are few programs for the elderly in this modality, so it is important to know and assess its benefits, especially when there is no concrete data in the literature regarding home care in geriatrics in Colombia. For this reason, it is pertinent to carry out a study to evaluate the effect of home care programs on different variables, such as the number of hospitalizations and emergency room admissions, given their impact on the lives of the elderly and their families, and on the Health System. In addition, to describe the characteristics of the user population to establish a clearer picture of the benefits of home care in our country.
Materials and methods
Design: Longitudinal study of before and after type
Study population: Based on the medical records of the population of the home care program of the Intellectus Memory and Cognition Center of the Hospital Universitario San Ignacio, from 2011 to 2016, which met inclusion criteria and the results of a structured interview conducted with patients or relatives of patients who completed one year of follow-up.
Inclusion criteria: Patients aged 65 years or older attended by the home geriatrics service; baseline morbidity: chronic disabling diseases and major neurocognitive disorder, among others; basic functionality: Barthel less than 60; minimum follow-up of one year in the home care program.
Exclusion criteria: Incomplete data, less than 8 home visits in the year of follow-up, non-acceptance at the time of telephone follow-up.
Intervention: The effect of the home care program of the Intellectus Memory and Cognition Center in Bogotá D.C., Colombia was evaluated. It is a program run by specialists in geriatrics and psychogeriatrics, which carried out a one-year follow-up with a minimum of eight follow-up appointments at home. The target population was elderly people with a high burden of morbidity, physical or mental disability, with multiple visits to health services, both specialties and hospitalizations, complexity in chronic management and difficulties of transfer to outpatient care.
Data collection methodology: Non-probabilistic convenience sampling. All patients who met the inclusion criteria were included. The lists of patients attended by the home care program of the Intellectus Memory and Cognition Center of the Hospital Universitario San Ignacio, from 2011 to 2016, were reviewed. From the list of patients, eligibility for the study was determined by reviewing the medical records and selection was made using the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Once the data of the patients who met these criteria were established, the initial information was collected in the database. It included sociodemographic data, telephone number extracted from the electronic medical record, clinical and functional characteristics. Those who had completed one year of follow-up were given a structured telephone interview that inquired about the number of emergency room admissions and hospitalizations, which can be found in the Annex at the end of the article. Two physicians trained in the aforementioned instruments collected the data.
The number of hospitalizations and the number of emergency room visits were considered as outcome variables. On the other hand, within the demographic variables, age, sex, schooling, marital status and socioeconomic stratum were taken into account, which were classified as low, middle and high (1 and 2 being low; 3 and 4 middle, and 5 and 6 high).
Analysis plan: For the descriptive analysis of the data, continuous variables are reported as averages and standard deviations. In the case of variables with normal distribution, they are presented as medians, and in interquartile ranges if this assumption is not met. Categorical variables are reported as frequencies and percentages. To establish the difference between two dependent variables, the paired t-test was used, which determines the pre-post intervention differential efficacy in hospitalizations and emergency room visits. A margin of error of 0.05 and a reliability of 95% was established for all analyses. The statistical package used was Stata, Windows version.
Results
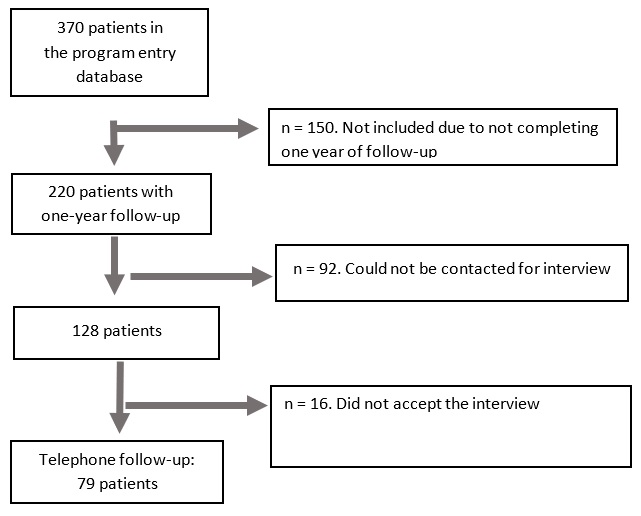
Among the patients evaluated in the home care of the Intellectus Memory and Cognition Center from 2011 to 2016, we found a total of 370 patients. Of these, 79 who met the inclusion criteria entered the study (Figure 1).
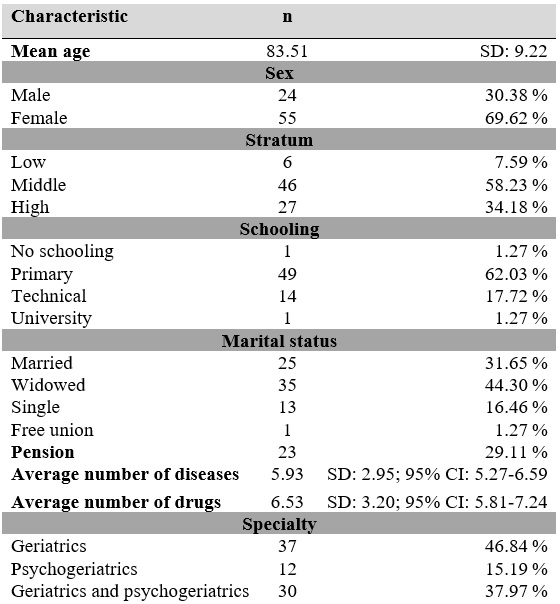
The mean age of the patients selected for the study was 83.51 years (SD: 9.22 years), 55 patients (69.62%) were women. In terms of belonging to different socioeconomic strata, 65.8% corresponded to middle and low socioeconomic strata. More than 60% of patients completed primary education; 17.72% of patients completed secondary education, and 17.72% of patients studied a technical career. The most frequent marital status was widowhood, with 44%, and 29.11% of the patients reported having a pension. The mean number of diseases and drugs was 5.93, with a SD of 2.95 (95% CI: 5.27-6.59), and 6.53, with a SD of 3.20 (95% CI: 5.81-7.24), respectively (Table 1).
The pathologies most frequently found in the study were arterial hypertension (73.42%), major neurocognitive disorder (63.2%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (32.91%), hypothyroidism (26.58%), type 2 diabetes mellitus (24.05%) and urinary tract infection (21.5%). The most prevalent cardiovascular diseases were coronary heart disease and atrial fibrillation. On the other hand, only one patient was using gastrostomy.
In addition, it was found that the most frequent neoplasms were breast and skin cancer (2.53% each), and as complications of different geriatric syndromes, 10.13% of the patients had pressure sores. It was also found that 12% of the patients suffered from some nutritional deficiency (iron, vitamin D or cyanocobalamin).
Among the neurocognitive disorders, we found that Alzheimer’s disease was the most prevalent, in 29.11% of the patients in the study. Other etiologies were vascular (5.06%), Lewy bodies (2.53%) and mixed (18.99%). The majority of patients were at an advanced stage of the disease, 40.51%, followed by moderate and mild stage, 20.25% and 2.53%, respectively. Regarding neuropsychiatric symptoms, the most frequent was aggressiveness, 18.99%, followed by depression, 16.46%.
The most common neurological pathology after major neurocognitive disorder, was cerebrovascular disease, with 15.19%.
At the time of program entry, the average number of drugs was 6.53 per person, especially antihypertensive drugs (46.84%), proton pump inhibitors (41.77%), antipsychotics (37.97%), analgesics (36.71%) and antiaggregants (32.91%). Other commonly prescribed drugs were serotonin reuptake inhibitors (26.58%), acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (8.86%), memantine (7.59%) and benzodiazepines (6.33%) (Table 2).
Regarding the outcomes of interest, the mean number of hospitalizations was reduced from 1.91 (SD: 1.82; 95% CI: 1.50-2.32) to 0.96 (SD: 1.43; 95% CI: 0.66-1.26) with a statistically significant difference (p = 0.0002). The average number of emergency room visits decreased significantly (p = 0.0003) from 2.20 (SD: 1.91; 95% CI: 1.77-2.63) to 1.20 (SD: 1.69; 95% CI: 0.82-1.58).
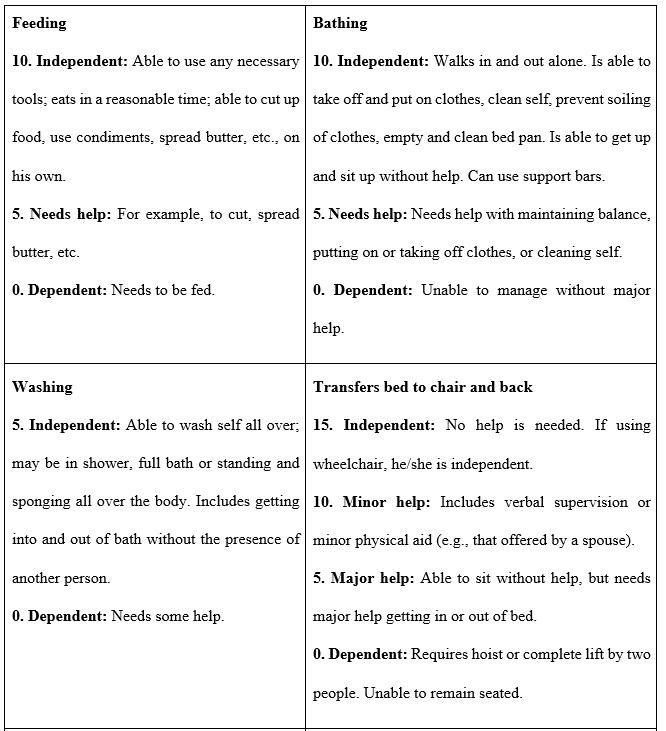
Regarding functionality, a decrease from 40.56 (SD: 33.05; 95% CI: 33.16-47.97) to 31.64 (SD: 31.24) at 1-year follow-up was found, with a value of . = 0.025, which is statistically significant (Table 3).
Discussion
In our population we found a particular sociodemographic profile, given by a predominantly female population, over 80 years of age, widows, with basic primary schooling and no pension.
It is striking the low number of patients institutionalized in care homes, despite the high frequency of people with major neurocognitive disorders in moderate and advanced stages, dependence in basic activities of daily living, moderate on average, and with high frequency of behavioral symptoms, a scenario that becomes one of the main causes of admission to these long-stay units. Although not conclusive due to the characteristics of this study, a possible explanation could be the high mortality of this group of patients, which does not allow long-term follow-up. In a retrospective study conducted in Cuba in 2010, 30.2% of the patients died during the first year of admission to the institution, and 40.5% between the first and third year (15).
Our study showed that the population has a high frequency of dementias, the second most common pathology found, including Alzheimer’s disease (first cause), which is consistent with what is described in the literature (16), although it occurs in a smaller proportion. The most frequent behavioral symptoms are aggressiveness, depression and anxiety, which explains the high use of antipsychotics and antidepressants. The fact that more than 40% are in the severe stage of the disease implies an increased risk of developing geriatric syndromes, such as immobility, malnutrition and pressure sores. This scenario explains why the program includes psychiatrists and geriatricians.
The population is multimorbid, with an average of 5.93 diseases per person. The most frequent is arterial hypertension, followed by major neurocognitive disorders. Respiratory, metabolic, and cardiovascular diseases are also common, leading to high medication use. The study population has an average of 6.53 medications, which is considered polypharmacy. This last term has different definitions due to the number of drugs (more than 3 or 5) or unnecessary drugs (17).
Our results contrast with those of the 2016 study by Cano-Gutierrez et al. (18). That study showed a similar profile of people, with a predominance of women and low schooling, with a frequency of chronic conditions that does not include neurodegenerative or psychiatric diseases among the main ones, so the drug profile is given for cardiometabolic and pulmonary diseases. However, in a secondary analysis of the SABE (Health, Well-being and Aging) Survey, conducted in Bogota in 2012, it was documented that depression is a prevalent disease, with a percentage of 26.3%, and the population with this diagnosis had similar characteristics to those of the current study population: being a woman, low educational level, not being a pensioner, history of arterial hypertension and diagnosed mental illness, among others (19). Thus, in this study, a large percentage of home patients report use of antipsychotics and serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
There is a low frequency of patients with neoplasia or in palliative care, this is due to a patient selection bias, since they are not included in the program and are referred to other providers.
The 12-month follow-up ensures at least 8 visits for each patient, as it is a model of programmed specialized care, which allows effective interventions with an impact on the patient and their family environment, as described by some researchers (20).
The baseline functional status of patients, specifically for basic activities of daily living, reflects a moderate degree of dependence on average and a significant decline at one year with the program, which is directly related to the morbidity profile of this population and to the natural course of chronic and degenerative diseases (21).
The reduction in the number of emergency room visits and hospital admissions is noteworthy, with a statistically significant difference. Several reasons could explain this: the continuity of the monthly visit allows more time to educate family members about the patient’s condition, allows self-regulation of visits to hospital centers, avoids complications of the patient condition, and the figure of “family doctors” has been created, so that patients and their families do not consult without having a prior opinion. In a study conducted in Spain in 2011 with a population very similar to ours of 157 chronic geriatric patients, followed for one year in home care and with the possibility of telephone access, showed a significant decrease in the number of on-demand or scheduled visits to health centers (20).
In our study, we performed additional analyses using simple linear regression and other multivariate logistic regression models, where bivariate analysis did not show a significant association between age, sex, average number of diseases and medications, functional status, with respect to the outcomes of number of hospitalizations or emergency room visits.
Conclusions and recommendations
As this is a longitudinal study of before and after type, it is an alternative design when it is not possible to randomize an intervention or have a control group. The disadvantage is that it is not possible to control the homogeneity of the group or to control factors external to the intervention. However, the decrease in the number of hospitalizations and emergency room visits suggests that this was mainly due to the treatment carried out, since despite the evolution of the diseases and the increase in the age of the patients, at the beginning of the intervention there were more emergency room visits and hospitalizations.
The results of this study serve to expand research on this type of program, since in Colombia research is needed to account for the outcomes of transferring specialized medical services to patients’ homes.











 text in
text in