Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has impacted all countries in the world and significantly influences the economy, social aspects, and health (Severo et al., 2021). Research shows the SARS-COV-2 virus COVID-19 occurs by contact with secretions that are contaminated by humans, through contact with a contaminated surface, and inhalation of virus particles (Chhikara et al., 2020). The use of masks, cleaning environments and surfaces, social distancing, hand washing and avoiding the use of shared objects are among the main practices to prevent infection (Martinelli et al., 2020).
At the beginning of February 2020, Brazil declared COVID-19 a public health emergency of national importance. Data on active cases and deaths by the disease were made available by health authorities (Mucinhato et al., 2022; Severo et al., 2021). Therefore, the COVID-19 pandemic allowed knowledge of actions on the disease in Brazil and, consequently, the determination of public policies aimed at reducing the increase in the number of cases (Rodrigues et al., 2021a).
Brazilian society faces the need to find alternative paths for its development in the face of the COVID-19 pandemic (Da Silva et al., 2020). This trajectory is unknown and results in a challenge in projecting possible future scenarios in which consumers need to make decisions (Cordeiro et al., 2021). Based on this, there are some problems to assess how consumer behavior could be affected by the new contexts experienced by the population (Maragoni-Santos et al., 2021), which is particularly important when considering that the current behavior of the Brazilian consumer emphasizes the consequences of the consumption background (Da Silva et al., 2020).
According to cultural and nutritional habits, Brazilian society chooses certain foods for a meal (Silva et al., 2021). The selection of food requires identification and classification as suitable or not for consumption (Rodrigues et al., 2021b). Therefore, in addition to biogenic factors, food sealing is also related to social and environmental aspects. In countries with a capitalist economy, consumers have great autonomy in purchasing their food (Cordeiro et al., 2021). Hence, the behavior of the Brazilian consumer must be analyzed through the interactions of the organism, in an attempt to understand the relationship with the environment (Silva et al., 2021). The Brazilian population is inserted in the consumer market with purchases, which reflects a behavior that adopts dietary decisions according to the economic and health context (Hakim et al., 2021).
Since there is no effective treatment available for COVID-19, one of the measures to contain the virus is physical distancing and isolation (Maragoni-Santos et al., 2021). Therefore, several institutions, businesses and non-essential businesses and other businesses that serve meals or food for consumption on site remained closed during the most critical days of the pandemic. In Brasil, supermarket chains were strengthened through virtual sales (Medeiros et al., 2021) and an increase in the use of ready-to-eat delivery applications (Horta et al., 2021).
During the pandemic people used to spend more time at home, thus being exposed to food advertising on the internet and television, especially processed foods. This reality enabled the rescue of culinary skills and food preparation, as well as the use of social networks to increase the consumption of healthy foods (Santos et al., 2022). In addition, the COVID-19 pandemic established important challenges to collaborative consumption offerings such as product-service systems (Horta et al., 2021).
In light of the above, this article aims to address the COVID-19 pandemic and its implications for food consumer behavior in Brazil, providing for the reader a refined and critical analysis of the main research studies carried out, difficulties, keywords, researchers, among other information, through a bibliometric analysis. This research sought to broaden the literature on trends and challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic and its implications for the food consumer behavior in Brazil. With this article we expect to contribute to the subject, since no studies using the systematic literature review to relate these themes to each other were identified.
The importance of this work is grounded in the fact that social isolation stopped the business world for a while, but companies are slowly returning to routine and, therefore, marketing professionals must be prepared for the new se-cenario; after all, marketing teams will need to be able to reinvent and innovate. To start restructuring the business, the first step is to analyze what happens outside the company, that is, consumer behaviors and habits. From this perspective, knowing consumer behavior is no longer an option but has become a survival factor.
Understanding consumer behavior is essential to know the reasons leading people towards purchasing decisions. With the COVID-19 pandemic, the food sector was strongly impacted by several changes in consumer habits. People began to adopt domestic food safety practices and increase food purchases in supermarkets. In addition, people tend to spend more time at home, which increases the number of food advertisements on the internet and television (Maragoni-Santos et al., 2021; Silva et al., 2021). Other aspects can be observed as negative factors for the food trade sector; for example, consumers avoid places and services with greater movement of people and have reduced meat consumption, as well as overall food consumption as a precaution against the greater likelihood of losing their jobs (Quevedo-Silva et al., 2022). Therefore, marketing strategies need to be assertive to conquer and satisfy consumers.
The study is structured as follows. This section presented the initial considerations, the purpose of the study and its originality. The next section brings the theoretical background and the methods adopted. Then, the main trends and discussions on the theme and their theoretical basis will be presented. Finally, some final considerations will be drawn.
Theoretical background
The objective of marketing is to analyze consumers' behavior, satisfying and meeting their desires and needs, so it is up to the consumer to analyze their aspect as an individual and group, in addition to the ways in which they use certain product or service (Bravo et al., 2011; Kotler, 2000).
To understand consumer behavior it is necessary to establish a relationship between stimulation and response. The stimuli from the environment (social, cultural and political) and from marketing (product, price, place and promotion) are part of the consumer's consciousness. However, what leads to the act of purchase are the consumer's characteristics (physical, personal and psychological) and the decision phases that arise from a problem, leading to the search for information, search between alternatives, and the act of purchase (Kotler, 2000).
According to Franco and Franco (2018), the search among alternatives is the stage that involves the various factors that will best meet a consumer's needs, such as price, product characteristics, delivery time and good service. Accordingly, the benefits assessed by the consumer can be influenced by economy, quality, safety and status, among others. Therefore, it becomes essential to evaluate the business from the point of view of consumer's needs and requirements. Based on this information, it is necessary to carry out market research on segmentation, where another relevant aspect emerges: the lack of certainty about the profitability of a specific segment, which is one of the most common barriers identified by consumer behavior studies (Bravo et al., 2011; Velázquez et al., 2008).
Regarding food consumer behavior in Brazil, it has been observed that local consumers are increasingly experiencing substantial changes in the food sector as a result of factors such as the phenomenon of globalization, different habits and customs, and the speed in the delivery of information (Almeida & Almeida, 2021; Amaral et al., 2021).
In recent years, Brazilian consumers have been disappointed in their search for safe and good quality food. Moreover, they are concerned about the fact that the same quality and food safety contained in exported agricultural products do not always correspond to what is distributed in the Brazilian domestic market (Martinelli et al., 2020; Smaira et al., 2021; Quevedo-Silva et al., 2022). Also, given the importance of studying consumer behavior during the COVID-19 pandemic, in Brazil several areas of scientific knowledge became interested in this phenomenon and investigated its implications for food consumer behavior; among these areas, we can mention economics, administration (marketing), health studies, and psychology (Campos et al., 2021; Cordeiro et al., 2021; Da Silva et al., 2020; Rodrigues et al., 2021a).
With the arrival of the COVID-19 pandemic in Brazil, in February 2020, most of the population became more averse to risks, not only related to health, but also to the impact of family income. In this way, in relation to food consumer behavior, the greatest impact was observed from July 2020, with a reduction in household income and greater consumer caution towards food consumption (Campos et al., 2021; Cavalli et al., 2020). In 2021, with the advancement of the vaccination program, a more favorable scenario began for businesses in the food sector, such as supermarkets and restaurants (Aureliano-Silva et al., 2021; Hakim et al., 2021).
The impacts of food consumer behavior in Brazil due to the COVID-19 pandemic demand innovation and new practices in companies' operations and the way organizations adapt to constant changes (Campos et al., 2021). The pandemic brought a very challenging context, so creativity is important to overcome difficulties for businesses. With the lockdown measures implemented in several organizations there were changes such as a standstill in their activities, practices and customs. Therefore, keeping in touch with customers and attracting new ones became a major issue for maintaining competitiveness within the market (Almeida & Almeida, 2021; Hakim et al., 2021).
This moment requires specific marketing strategies, for example, the structuring of social media and websites. Brazilian marketing actions must be present even during social distancing through the technological and virtual context (Quevedo-Silva et al., 2022). Among the main insights towards food-related consumer behavior and marketing actions in times of COVID-19 we can mention the following: internet access is a business opportunity due to the uncertainty around the pandemic; there was an improvement in practices related to food consumer behavior in an efficient manner in a difficult period with the new COVID-19; the search for new tools to promote business becomes critical for businesses; access to social networks has increased during the pandemic (Martinelli et al., 2020).
During the COVID-19 pandemic, organizations in Brazil must engage with their customer base to identify food consumer behavior. There is the possibility that a share of customers will leave for economic reasons, therefore, a good relationship with everyone is essential. In this context, offering materials, email marketing, content marketing, and communicating relevant content is key to maintaining a stable relationship with custormers (Smaira et al., 2021).
Hakim et al. (2021) studied consumers' perceived risk and intention to visit restaurants during the pandemic in Brazil. Consumers' needs do not disappear and may even increase, but during a pandemic their behavior can vary according to the stages of disease progression. According to Horta et al. (2021), as a form of prevention, many consumers have avoided physical stores and are increasingly turning to the delivery service to buy food and other products.
According to Severo et al. (2021) the COVID-19 pandemic has been fundamental in people's behavioral change and has influenced sustainable consumption, environmental awareness and social responsibility. Farias and Araujo's (2020) focus seems to be on the regions impacted by COVID-19 that showed large variations in the prices of traded products and short-chain food supply platforms, which have been essential to ensure domestic food security. Hakim et al. (2021) highlight in their research a broader scope, presenting concerns about consumer confidence, adequate pricing, solidarity and trust related to health surveillance, which help predict the intention of customers to visit a restaurant.
The next section presents the research methods used by the authors in this study.
Methods
A bibliometric analysis was conducted to acomplish the objectives of this research. The Methodi Ordinatio (Pagani et al., 2015) was used to select the articles to be analyzed, as shown in figure 1. For this study, the authors used the Scopus and Web of Science databases in order to identify research and review articles related to the subject topic, and within no time limit. The selection of these databases is explained in the fact that both are the largest repositories of abstracts and bibliographic references of peer review scientific literature, thus allowing a multidisciplinary scientific view and the integration of applied and technological research (Falagas et al., 2008). Scopus and Web of Science feature high-impact journal coverage and, according to results reported by Norris and Oppenheim (2007), both databases provide a broad bibliographic coverage in Social Sciences.
The set of keywords used in the search was defined using truncation symbols and Boolean operators. After searching the databases, a total of 163 articles were found (figure 1).
Thereafter, a series of filters and ranking techniques were applied in order to find the most relevant and highest impact studies to be fully analyzed, since the assessment of all the documents obtained after the database search would be impractical time wise. Therefore, 163 articles initially comprised the sample. Afterwards, the articles identified as duplicates were eliminated and consequently 160 records were kept. Subsequently, after the article title filter, 93 papers remained. Records that were unrelated to the topics of interest in this research were removed, thus leading to a sample of 45 articles. In this way, the Methodi Ordinatio suggests an equation that makes it possible to weigh the impact factor (IF) and the number of citations of each article in the respective journal in order to weigh the importance of each article. The identified article was placed in the following equation: (InOrdinatio coefficient). The IF (using Journal Citation Reports - JCR) and number of citations (using Google Scholar) were obtained in February 2022.
The coefficient of this methodology evaluates the year of publication, and the researchers authoring this paper provided a score between 1 and 10 (the closer to 10, the greater the relevance for researching articles from current years). Then, we selected a coefficient of 5 since the content of publications from previous years is also relevant for the study, as we did not limit the year in the database search.
In doing so, only 25 remained for complete reading. Thus, a total of 25 articles were included in the final portfolio.
The analysis of articles presents the following exclusion steps: (i) complete portfolio = 163; (ii) exclusion of duplicate items = 163 - 3 = 160; (iii) exclusion of articles by titles = 160 - 67 = 93; (iv) exclusion of articles by abstract = 93 - 48 = 45; (v) exclusion of articles for full reading = 45 - 20 = 25.
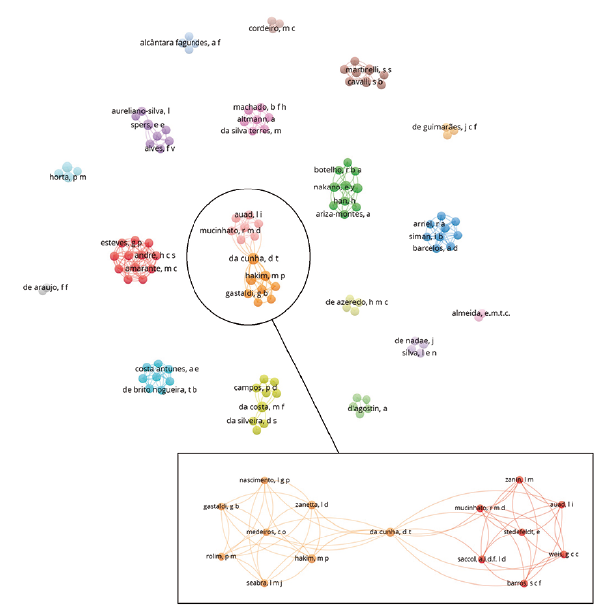
Therefore, the final portfolio comprised 25 articles related to the COVID-19 pandemic and its implications for the food consumer behavior in Brazil. These 25 high-impact articles were selected for evaluation in the results section. All documents were managed using EndNote X6 reference manager. The construction of co-occurrence (figure 2) and co-authorship (figure 3) visual maps was made using Microsoft Visio and vosviewer software. Titles and abstracts were considered for the elaboration of the visual map, adopting vosviewer full count method. The construction of the co-authored map adopted bibliographic data, the authors of the unit of analysis, co-authorship as a type of analysis, the complete counting process as a counting method, and groupings according to the number of documents per author (figure 3).
As for the results of the article, spreadsheets were used to calculate the InOrdinatio coefficient. To investigate the complete analysis of the final portfolio certain characteristics were considered, therefore, not all articles investigated all the themes adopted in this article. Besides the characteristics analyzed -such as the journal's impact factor, number of citations, journal, year of publication, and the authors who have already been cited-, other aspects explored and analyzed were: main themes, objectives and results, future study suggestions, main conclusions, and any other analyzes made by the authors.
With the methodology described above, the authors of this paper do not claim that this research is exempt from limitations. However, they expect to make an important contribution to the body of literature on the subject. Besides, the authors are aware that no research was identified analyzing the joint context of the titles of interest to this article.
Discussions of the characteristics found in the selected studies
In this section we will present the categories of the articles included in the final portfolio and the InOrdinatio index, according to the methodology developed by Pagani et al. (2015). Examined articles were classified departing from those with the highest coefficient. Table 1 presents the final list of articles in the portfolio, where we can observe that several journals are publishing contributions on the COVID-19 pandemic and its implications for food consumer behavior in Brazil.
Table 1. Result of a bibliometric analysis.
| No. | Title | Journal | Citations | JCR | InOrdinatio | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on environmental awareness, sustainable consumption and social responsibility: Evidence from generations in Brazil and Portugal | Journal of Cleaner Production | 114 | 9.297 | 159 | Severo et al. (2021) |
| 2 | Will COVID-19 affect food supply in distribution centers of Brazilian regions affected by the pandemic? | Trends in Food Science & Technology | 44 | 12.563 | 84 | Farias and Araujo (2020) |
| 3 | Should I stay, or should I go? Consumers' perceived risk and intention to visit restaurants during the COVID-19 pandemic in Brazil | Food Research International | 26 | 6.475 | 71 | Hakim et al. (2021) |
| 4 | The COVID-19 pandemic and its implications for the food information environment in Brazil | Public Health Nutrition | 15 | 4.022 | 60 | Rodrigues et al. (2021a) |
| 5 | Digital food environment during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic in Brazil: An analysis of food advertising in an online food delivery platform | British Journal of Nutrition | 10 | 3.718 | 55 | Horta et al. (2021) |
| 6 | Food packaging wastes amid the COVID-19 pandemic: Trends and challenges | Trends in Food Science & Technology | 8 | 12.563 | 53 | Oliveira et al. (2021) |
| 7 | Consumer emotions and collaborative consumption: The effect of COVID-19 on the adoption of use-oriented product-service systems | Sustainable Production and Consumption | 8 | 5.032 | 53 | Medeiros et al. (2021) |
| 8 | COVID-19 pandemic sheds light on the importance of food safety practices: Risks, global recommendations, and perspectives | Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition | 6 | 0 | 51 | Maragoni-Santos et al. (2021) |
| 9 | The use of food delivery apps during the COVID-19 pandemic in Brazil: The role of solidarity, perceived risk, and regional aspects | Food Research International | 5 | 6.475 | 50 | Zanetta et al. (2021) |
| 10 | Behavioral predictors of household food-safety practices during the COVID-19 pandemic: Extending the theory of planned behavior | Food Control | 0 | 5.548 | 50 | Mucinhato et al. (2022) |
| 11 | The effect of COVID-19 on the purchase intention of certified beef in Brazil | Food Control | 0 | 5.548 | 50 | Quevedo-Silva et al. (2022) |
| 12 | Consumer behaviour in relation to food waste: A systematic literature review | British Food Journal | 0 | 0 | 50 | Santos et al. (2022) |
| 13 | Effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on food habits and perceptions: A study with Brazilians | Trends in Food Science & Technology | 3 | 12.563 | 48 | Rodrigues et al. (2021b) |
| 14 | Poor eating habits and selected determinants of food choice were associated with ultraprocessed food consumption in Brazilian Women during the COVID-19 Pandemic | Frontiers in Nutrition | 2 | 6.576 | 47 | Smaira et al. (2021) |
| 15 | COVID-19 and the fragility of Brazilian small farming resilience | Brazilian Journal of Operations and Production Management | 2 | 0 | 47 | Cordeiro et al. (2021) |
| 16 | Eating competence among Brazilian adults: A comparison between before and during the COVID-19 pandemic | Foods | 1 | 4.35 | 46 | Queiroz et al. (2021) |
| 17 | The effect of online reviews on restaurant visit intentions: Applying signaling and involvement theories | Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Technology | 1 | 4.26 | 46 | Aureliano-Silva et al. (2021) |
| 18 | Attitude and behavioral changes of dairy consumers during the new coronavirus pandemic in Brazil | International Journal of Dairy Science | 1 | 0 | 46 | Almeida and Almeida (2021) |
| 19 | Consumer behavior during the COVID-19 pandemic: Latent class analysis on coping attitudes and buying habits | Estudios Gerenciales | 1 | 0 | 46 | Amaral et al. (2021) |
| 20 | Strategies for the promotion of healthy, adequate and sustainable food in Brazil in times of COVID-19 | Revista de Nutrição | 6 | 0 | 46 | Martinelli et al. (2020) |
| 21 | Quality of life of vegetarians during the COVID-19 pandemic in Brazil | Nutrients | 0 | 5.717 | 45 | Hargreaves et al. (2021) |
| 22 | Consumer fear and healthy eating during COVID-19 pandemic | Marketing Intelligence & Planning | 0 | 0 | 45 | Campos et al. (2021) |
| 23 | COVID-19 Pandemic: Why Does It Matter for Consumer Research? | Revista Brasileira de Marketing | 0 | 0 | 45 | Silva et al. (2021) |
| 24 | The COVID-19 pandemic: Paths for future research in marketing involving the regulatory role of prosocial consumption | Revista Brasileira de Marketing | 3 | 0 | 43 | Da Silva et al. (2020) |
| 25 | Family farming in times of COVID-19 | Revista de Nutrição | 2 | 0 | 42 | Cavalli et al. (2020) |
Source: authors.
The authors of this paper ranked the journals in the sample that published the most papers on the topic studied (in descending order): Trends in Food Science & Technology (3 publications), Food Research International (2), Food Control (2), and Revista Brasileira de Marketing (2). The trend of the journals that published the most on this topic has not changed over the years. Periodicals publishing contents about the COVID-19 pandemic are essential for understanding the behavioral change of consumers towards variations in product prices and the confidence related to the health surveillance process.
The analysis of results was conducted based on the 25 articles selected through the Methodi Ordinatio, as presented in the methodology section. For this stage, we prepared a visual map based on text data, including for analysis only the title and abstract of the selected papers that reported a complete count of terms. For the visual map, a minimum of 5 occurrences was established. The map concluded a total of 33 occurrences (figure 2). In addition, a timeline was delimited to identify the main themes according to the year of publication and the relationships between these terms. Several terms were identified in the list of the object of study on the COVID-19 pandemic and its implications for food consumer behavior in Brazil.
Figure 2 shows the terms in a timeline perspective. Based on this visual representation, it can be said that the terms "strategy," "family farming," "prosocial consumption," "social distancing" and "adoption" are the subjects of the first high impact studies. Moreover, the terms "COVID," "consumption," "Brazil," "restaurant," "food safety," "risk" and "home" comprise more recent approaches, since they appeared only in the last few years. The bibliometric analysis has some limitations for upholding our results. Therefore, the authors present in figure 2 the conclusions and findings of the articles based on the word count from abstracts, which allowed identifying that relevant research studies on the effects of COVID-19 over food supply in distribution centers in Brazilian regions affected by the pandemic are being published.
Based on the word count from abstracts, in 2020 there is a trend towards studies on subjects such as health promotion strategies, adequate and sustainable food in Brazil in times of COVID-19, future marketing research involving the regulatory role of pro-social consumption, and family farming during pandemic times.
The word count also shows that since 2021 research has presented themes related to the COVID-19 pandemic and environmental awareness, sustainable consumption, and social responsibility based on evidence from generations in Brazil, as well as research on consumers' perceived risk and intention to visit restaurants during the pandemic. In addition, some research has been identified on food advertising through online food delivery platforms.
In 2022, research evolved with experimentation, addressing topics such as household food-safety practices during the pandemic. Consequently, several studies have been carried out on the effect of COVID-19 on the purchase intention of certified beef in Brazil and consumers' behavior regarding food waste.
Apparently, there was an increase in the number of publications dealing with the impact of the pandemic over food consumer behavior. However, it still early to get conclusive remarks about trends, since our research is based on a bibliometric analysis. That said, this topic is still in an introductory phase, emerging as an important research area for development in the coming years. According to the final set of 25 articles, the paper with the highest impact factor was that by Severo et al. (2021), who studied the effects of COVID-19 pandemic on environmental awareness, sustainable consumption and social responsibility based on the evidence of Brazilian and Portuguese generations of people. The article with the second highest impact factor was that of Farias and Araujo (2020), who examined the impact of the pandemic on food supply in distribution centers at some Brazilian regions.
Despite the above, what can be concluded is the geographical location of conducted high impact research studies on the COVID-19 pandemic and its implications for the food consumer behavior in Brazil, as depicted in figure 2.
Figure 3 introduces the criteria used to build the co-authorship map, namely: (i) bibliographic data; (ii) complete counting method; (iii) author and co-author analysis level. The total count of authors and co-authors reached 117, with a total of 19 clusters, that is, authors who published the same study. The works by Hakim et al. (2021) and Mucinhato et al. (2022) include authors with common research interests, whose main research topics are: (i) risk perception; (ii) consumers' intention to visit restaurants during the COVID-19 pandemic in Brazil; and (iii) increased food security during the pandemic.
In Brazil, food insecurity increased during the last three months of 2020, time in which families did not receive financial resources from the government. Therefore, the behavior of food consumers reflected the conditions of a scenario of change. Food insecurity not only contributed to a reduction in food purchases, but also to the replacement of low-cost foods rich in nutrients and vitamins. Within this scenario, the marketing management area had to adapt food sales strategies at a lower cost for consumers through delivery apps. In addition, food companies have increased the publicity that advertises protective measures to prevent contamination risks of their staff and other demonstrations of care regarding consumers' health and safety (Hakim et al,, 2021; Mucinhato et al., 2022).
Considering the above, this section was aimed at addressing some of the main characteristics of the final portfolio of documents found in the literature. In the next section, a discussion seeking to present the highlights on the theme is presented by SWOT analysis, a tool that refers to the analysis and assessment of strengths (S), weaknesses (W), opportunities (O), threats (T) and other factors that influence a specific topic, which has proved to be important for the formulation of strategies, plans and the corresponding countermeasures (Wang & Wang, 2020).
swoT analysis results
Based on the concept proposed by Wang and Wang (2020), we conducted a SWOT analysis on the final portfolio of articles, identifying the opportunities, threats, strengths and weaknesses of the proposed theme. This analysis was performed only with the bibliometric results produced in vosViewer. Table 2 presents a SWOT matrix listing the results derived from the evaluation of the selected articles.
The strengths identified correspond to the studies that presented advancements in vaccination programs, home office work with a tendency to increase food consumption, household food safety practices, and increasing food purchases in supermarkets. Bearing this in mind, the COVID-19 pandemic clarifies the importance of food safety practices, risks, global recommendations and perspectives. In this way, the consumer starts to carry out domestic food safety practices and increase the purchase of food in supermarkets (Maragoni-Santos et al., 2021). As a result, consumers started seeking for more healthy options under the asumption that consuming certain food offers them safety, thus protecting them from contamination (Silva et al., 2021).
As for the weaknesses identified, studies show that consumers avoid crowded places and services. With this, restaurant owners and consumers began to adapt to a new reality and strengthen personal and environmental hygiene practices in order to avoid the transmission of COVID-19 (Farias & Araujo, 2020; Rodrigues et al., 2021a).
Poor eating habits and selected determinants of food choice were associated with ultraprocessed food consumption by Brazilian population during the COVID-19 pandemic (Smaira et al., 2021). This health and economic crisis impacted Brazilians' income and reduced meat consumption. As a consequence, the SWOT analysis shows as threats that the effect of this reality particularly affected the poorest, that is, those who earn up to a minimum wage, who experienced a reduction in their income. The main financial problems faced by the population are unemployment and indebtedness, which have a direct negative impact on meat consumption (Mucinhato et al., 2022; Quevedo-Silva et al, 2022).
In terms of opportunities, in Brazil there has been an increase in the use of food delivery apps during the pandemic (Horta et al., 2021). With the expansion of vaccination programs, a gradual relaxation in relation to prevention measures has been observed, allowing many consumers to return to normality in leisure activities (Zanetta et al., 2021). The most optimistic perspectives will depend on the continuity of the immunization process (Rodrigues et al., 2021a).
Conclusions
This article presented a systematic review of high-impact literature on the trends and challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic and its implications for food consumer behavior in Brazil. The Methodi Ordinatio was used to select and classify the articles examined in this research. The authors made some final considerations based on the final portfolio of articles, however, this systematic literature review does not exhaust the topic and it is not possible to establish concrete trends.
In Brazil, the understanding of the COVID-19 pandemic and its effects over food consumer behavior is at an early stage that requires practical research studies. Nonetheless, with the findings of the studies already published, it is possible to conclude that analyzing both attention to the consumer and fair price is essential.
Yet, several Brazilian studies have addressed COVID-19 and its consequences for consumer studies, with few studies on corporate social responsibility and sustainable consumption. Therefore, the topic of sustainable consumption is suggested as a complementary theme in consumer behavior studies in Brazil. Some research has been carried out on strategies to promote healthy, adequate and sustainable food in Brazil in times of COVID-19. Recent studies highlight the impact of the pandemic on environmental awareness, sustainable consumption and social responsibility. Research has also been conducted on the effect of COVID-19 on beef purchase intention and consumer behavior towards food waste, as well as on food supply in distribution centers in Brazilian regions.
One of the main concerns seems to be the implications of the COVID-19 pandemic for the consumer, since most studies approach the progress in vaccination programs, the increase in home office work, home food safety practices, and the increase in food purchases in supermarkets. The COVID-19 pandemic shows food safety practices, risks, recommendations and global perspectives, as shown by consumers' interest towards healthier food options, free from contamination. Finally, the health and economic crisis has affected the income of Brazilians, therefore reducing meat consumption among the population.
The COVID-19 pandemic has generated uncertainty and several impacts over food consumer behavior in Brazil, fostering changes in food consumption habits; e.g., consumers are more cautious while shopping. As a way of preventing the disease, many food consumers have avoided physical environments, therefore increasingly purchases through e-commerce in order to buy food and other products.
The main financial problems faced by people in the current scenario are unemployment and indebtedness, which has caused, for example, a reduction in meat consumption. Among the opportunities of this situation is an increase in the use of food delivery apps. The most optimistic perspectives will depend on the continuity of the immunization process.
This research has some limitations in the scope of its results, as we only used two databases. As a suggestion for future studies, including additional databases could help compare the results obtained. The authors of this work recommend marketing research topics involving the regulatory role of pro-social consumption and family farming in times of COVID-19.