Water deficit in plants is more common in urban than in rural areas. This is due to the impervious surface and the high vapour pressure deficit of urban space, which is caused by high temperature and low relative humidity (Czaja et al., 2020). For instance, in the late afternoon, there is a difference of 2 °C between the city centre of Adelaide (Australia) and its suburbs. Meanwhile, there is a difference of 5.9 °C at midnight between the city and a rural area located 56 Km far (Soltani and Sharifi, 2017).
Water deficit can be caused by either water shortage in the substrate where the plants are growing and/or by the evaporative demand of the atmosphere (Grossiord et al., 2020). The evaporative demand can be represented by the potential evapotranspiration, which is the water loss of a reference crop through evaporation and transpiration under certain environmental conditions (Paredes et al., 2017). Taking evapotranspiration as a measurement of the integrated evaporative demand over time instead of a measure of time like days makes easier the comparison among studies of water deficit.
Water deficit is more frequent in young trees because the root confinement of urban space prevents water absorption (Czaja et al., 2020), while in adult trees, roots can reach deeper water sources. The consequence of water deficit is the reduction in physiological processes like photosynthesis (Flexas et al., 2012), transpiration, water absorption, hydraulic conductance, cell expansion and nutrient availability (Rouphael et al., 2012). In the end, the reduction of such variables reduces the tree growth and produces symptoms like wilt, yellow and brown leaves and in extreme cases tree death (Flexas et al., 2012).
Considering that climate change has been affecting water availability and that water has been used in activities different from irrigating urban trees, water has to be used efficiently to maintain urban health (Joy et al., 2020). To achieve this efficiency, there are strategies like efficient irrigation, understanding the site hydrology, determining tree water demand and planting species tolerant to drought conditions (Joy et al., 2020). Among these factors, determining the water tree requirements of each species and establishing their tolerance degree to drought in early stages are extremely useful for choosing species and planning irrigation in the city.
Water deficit affects several plant processes like growth, water status, photosynthesis and fertilization (Czaja et al., 2020), some of which can be used to identify trees undergoing water deficit (stress markers). These markers have been useful to decide when to irrigate trees and to identify tolerant species to water deficit. For example, Cole and Pagay (2015) found that stem water potential is useful for detecting drought in grapevine and that this potential is more stable under environmental conditions than stomatal conductance and leaf water potential. Although stomatal conductance and water potential can be used to assess the negative effects of impermeable surfaces (Savi et al., 2014), there is little information about which stress markers are useful to diagnose water deficit in most urban species, especially in native ones.
Additionally, long-term effects of water deficit can be diagnosed using the chlorophyll content or the growth rate (this last is even more important since the bigger is an urban tree, the more ecosystem services provides). Tree-ring and therefore stem growth analysis can be used to identify tolerant genotypes to drought and to assess their historical growth under different drought seasons (Britta and Rigling, 2012). Besides, when the stress is so severe that the photochemical molecules are damaged, chlorophyll is also affected by water deficit after stomatal conductance and water status (Flexas et al., 2012). Consequently, chlorophyll content and stem growth might also be used as markers of long-term water deficit.
In descending order, the variables considered to choose urban tree species have been: climate adaptation, pest and disease tolerance and ecosystem services provided (Sjöman and Busse Nielsen, 2010). In Bogotá (Colombia), urban trees have been chosen considering their tolerance to the urban environment, their aesthetic traits and their popularity, which are the reasons why most of the species planted are non-native. However, there has been deemed neither the role of native diversity on the forest adaptation to future climate conditions, the role in conserving rare tree species (Ordóñez and Duinker, 2014) nor that some native species probably thrive in urban conditions. For this reason, it is important to evaluate the suitability of native species for water deficit, a common condition in the urban environment.
All the species assessed in this research are native and have been used in urban forestry due to either their apparent tolerance to urban conditions or their ecosystem services. The species Citharexylum montanum M., Citharexylum sulcatum M. and Caesalpinia spinosa K. have been used as ornamental trees in Bogotá (Colombia) because of their tolerance to urban conditions like drought and high temperatures. Meanwhile, Inga edulis M. and Retrophyllum Rospigliosii P. have been mainly used because of their ornamental beauty and their particle deposition capacity (Vasquez and Maya, 2019).
Accordingly, the aims of this research were to i) make an approximation of water requirements for Citharexylum montanum, Citharexylum sulcatum, Caesalpinia spinosa, Inga edulis and Retrophyllum rospigliosii, ii) identify the most sensitive and the most tolerant species to water deficit, iii) evaluate how many days without irrigation can tolerate each species and iv) find variables that can be used to characterise water deficit in these species.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The experiment was carried out at "Universidad Militar Nueva Granada" in Cajica, Colombia (4°56'33.5502"N, 74°0'36.417"W) where the mean temperature and relative humidity were 14.2 °C and 40%, respectively. The evaluated trees had a basal diameter of 2.2-3.5 cm and a height of 1.7-2.0 m. Eight trees per species (C. montanum, C. sulcatum, C. spinosa, I. edulis and R. Rospigliosii) were planted in plastic bags filled with 60 litters of a mix of soil (pH of 6.1, organic carbon of 3.13%, wet density of 0.84 g cm-3, Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) of 35.2 cmol+ kg-1, porosity of 65% and Field capacity of 40% volumetric water content) and compost (pH: 6.9, organic carbon 9.94%, electrical conductivity 2.0 dS m-1, CEC: 35.2 cmol+ kg-1, bulk density: 0.84 g cm-3, C/N rate: 10.54) in a rate of 7:1 v v-1.
Treatments
Treatments started one month after planting. To reach the moisture level of each treatment, the soil was covered with plastic to prevent the soil moistening and water runoff. In each treatment, the irrigation was stopped at 12/10/2017 until each treatment reached the moisture level desired (when at least the soil of four trees reached the desirable volumetric moisture). The treatments were: control treatment (volumetric water content higher than 45% (TC)), volumetric water content of 20% (VM20), fifteen days after the soil had reached VM20 (T15) and thirty days after the soil had reached VM20 (T30). Each treatment represented a moment after irrigation had been stopped, e.g, For the VM20 treatment, the physiological traits were measured after the soil reached 20% of volumetric water content, for the T15 treatment, fifteen days after, and for T30 thirty days after. After having done the physiological measurements in each treatment, irrigation was restored and approximately one month later, growth variables were measured. In each measurement, eight trees for each treatment and each species were measured. Additionally, in four of eight bags where the trees were growing, ten grams of hydro-absorbent (polyacrylamide with a real density of 0.83 g cm-2 and a water retention capacity of 300 g H2O g-1) were mixed with the soil, and in the other four not.
Potential Evapotranspiration
To employ an energy variable instead of a chronological scale, the number of days was transformed into cumulative potential evapotranspiration units (mm) using the Hargreaves and Samani (1982) equation 1:
Where:
PE Potential evapotranspiration (mm day-1)
Tmean Average daily temperature (°C)
Tmax Average daily maximum temperature (°C)
Tmin Average daily minimum temperature (°C)
Ra Extra-terrestrial radiation (MJ m-2 day-1)
Soil moisture
To know the water consumption, every two days, the volumetric water was measured using a moisture sensor ML3 (Delta T Devices, ± 1% accuracy). The sensor was inserted in four points of the plastic bags until 15 cm deep and the volumetric water content was registered.
Stomatal Conductance and stem water potential
Stomatal conductance was measured with a steady-state porometer SC-1 (Decagon Devices) in two areas from a completely expanded leaf from the middle part of the tree´s canopy. Stem water potential was measured in one of the leaves used for measuring the stomatal conductance. Leaves were covered, for thirty minutes, with a plastic aluminized bag before the stem water potential measurements. After that, each leaf was cut down from the tree and the water potential was measured using a Schollander pressure chamber. Both stomatal conductance and stem water potential measurements were measured between 9:00 and 13:00 hours. Due to the small petiole of R. rospligiosii, a stem structure of approximately 8 cm long was taken for measuring its water potential.
Relative Chlorophyll content
These measurements were determined between 9:00 and 13:00 hours. Chlorophyll content was measured in four places of a leaf in three leaves completely developed of each tree using a chlorophyll meter MC-100 (Apogee Instruments, United Kindom).
Stem Height and Diameter Growth
Considering that the moisture of each treatment was reached on different dates (Table 1), growth variables were also measured at different times. For instance, growth measurements of V20 in I. edulis were done on 14/12/2017, but R. rospigliosii was measured on 09/02/2018 for the same treatment. Stem height and diameter were assessed using a meter and a digital calliper, respectively. The height was measured from the base to the apex of the stem, where there were two main stems, the longest was measured. The diameter was measured where the stem and the root joint. Tree growth was determined from the increase in height and diameter.
Fresh and dry leaf mass
One month after irrigation was restored in each species; fresh mass from one leaf of each tree was measured. After that, each leaf was dried in an oven at 80 °C for 48 hours. All growth variables, except fresh and dry leaf mass, were calculated by subtracting the initial measurement on 12/10/2017.
Data Analysis
To assess differences in volumetric soil moisture among species, a nonparametric profile analysis was conducted in which species, hydroabsorbent and potential evapotranspiration were the factors (Feys, 2016). For this a nonparametric rank-based analysis was employed for longitudinal data using the F2-LD-F1 design in nparLD package of R software (Noguchi et al., 2012). After identifying the differences between factors, the same profile analysis was used to evaluate differences between species.
To identify species potentially tolerant to water deficit and to determine stress markers, each treatment (VM20, T15 and T30) was compared with its respective control treatment (TC). The T-student or Wilcoxon Test was used depending on data normality (Shapiro test) and homoscedasticity (Levene test). All Statistical analyses were performed using R software version 3.5.3 (R. Core Team et al., 2017).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Water consumption by species
I. edulis spend less time in reaching the volumetric water content of 20% (32 days), meanwhile, C. sulcatum spent 73 days more and R. rospigliosii almost 90 more. Consequently, while I. edulis needed potential evapotranspiration (PE) of 154.3 mm to decrease the volumetric water content of soil from 45% to 20%, R. rospigliosii needed almost four times more energy (Table 1). Considering PE is a representation of the evaporation capacity of the atmosphere, I. edulis needed less energy (PE) to transpire the same water amount as the other species. This might have happened because of its bigger crown, which has more leaf area thus more surface for transpiration.
Considering that bags, where trees were growing, were impervious, moisture depletion was directly related to transpiration (Joy et al., 2020). The higher number of days necessary to reach VM20 of I. edulis in comparison to R. rospigliosii might be related to their relative growth, with I. edulis with the highest growth rate and R. rospigliosii with the lowest. Mitchell et al., (2012) mention that rapid growth species like Eucalyptus globulus and Eucalyptus smithii use more water than Pinus radiata, which has a lower growth rate.
Considering the water depletion order, the irrigation frequency should be: 1) I. edulis, 2) C. montanum, 3) C. spinosa, 4) C. sulcatum and 5) R. rospigliosii. Although, height and diameter are important traits for choosing and managing urban trees, it is necessary to consider the crown size and water consumption for choosing the frequency and volume of irrigation.
There were significant differences among species, among potential transpiration rates (time) and among the interaction Species-Evapotranspiration (Figure 1A), but not for hydroabsorbent. I. edulis followed by C. montanum had a higher water-consumption rate than the other ones. C. sulcatum and R. rospigliossi were the species with the slower water consumption (Figure 1B). In general, I. edulis showed a sharp decrease in volumetric water content while the rest of the species had a progressive decrease during the first thirty-two days when the cumulative transpiration was of 154 mm (Figure 1B). The water rate consumption of I. edulis (0.16% VM mm-1 EP) was two times higher than C. montanum (0.08% VM mm-1 EP) and three times higher than R. rospigliosii with 0.04 VM mm-1 EP.

Figure 1 A) Effect of Species, Hydroabsorbent, potential evapotranspiration and their interaction on volumetric water content (ANOVA-Type Statistic profile analysis) and B) Graph profile analysis plot for volumetric water content. sp: Species, Hyd: Hydroabsorbent, PE: Potential Evapotranspiration, ATS: ANOVA Type statistic, df: Degree of Freedom VM: Volumetric moisture. In B; species following by the same letters (C and D) are not significantly different according to non-parametric profile analysis (P<0.01).
Possible reasons why the hydroabsorbent did not affect soil moisture are: i) In experiments in which the hydroabsorbent raised soil water retention or tree growth (Subhadip et al., 2018), there were used sand or sandy soils, which held less water (Saha et al., 2020) than the soil used in this study, ii) Organic matter content of the soil used might have provided similar water retention (Paradelo et al., 2019) and nutritional functions of the hydroabsorbent and iii) the amount of hydroabsorbent polymer used here was five or until thirty times (Subhadip et al., 2018) less than the used in other experiments. In the Colombian context, because of hydroabsorbent price and soil type, applying more than 160 mg L-1 of this amend instead of compost will be profitless; consequently, as long as the soil had a high-water retention capacity, there is unnecessary to apply hydroabsorbent.
Physiological Response to Water deficit
At a volumetric water content of 20%, neither the chlorophyll nor the water status variables nor were affected, except the stem water potential of C. montanum (Table 1). After 15 days of having reached VM20 (T15), stomatal conductance and stem water potential decreased in I. edulis, C. sulcatum and R. rospigliosii and there was only a decrease in stem water potential for C. montanum and C. spinosa. After T30, several physiological variables felt: all in I. edulis, stomatal conductance and stem water potential in Caesalpinia spinosa, stomatal conductance in C. montanum, stem water potential in C. sulcatum and none of them in R. rospigliosii (Table 1). A soil moisture content of 20% VM may have been enough to supply the water requirements of all the species, except for C. montanum. In the soil used for this experiment 20% VM equals a tension of ~70cb which is not enough to induce water deficit in plants (Intrigliolo and Castel, 2004).
Each species showed a different response to water deficit: I. edulis showed first (T15) a reduction in stem water potential (-32% to Control) and stomatal conductance (-27%). Then, under severe stress (T30) I. edulis presented a reduction of 46% and 77% in both variables, respectively, and in chlorophyll content (-17%). C. sulcatum showed a reduction in gS (48%) and W.P (94%) at T15 and only a reduction of W.P (162%) at T30. On the other hand, R. rospigliosii only presented a decrease in gS (18%) and W.P (43%) at T15 but there was not effect on the treatments VM20 and T30. C. spinosa presented a similar pattern to I. edulis with a decrease of W.P and gS at T15 and T30, respectively (Table 2).
Table 2 Stomatal conductance (gS), stem water potential (W.P) and relative chlorophyll content (Chl) of Inga edulis, Citharexylum montanum, Citharexylum sulcatum, Caesalpinia spinosa and Retrophyllum rospigliosii submitted to three water deficit periods.
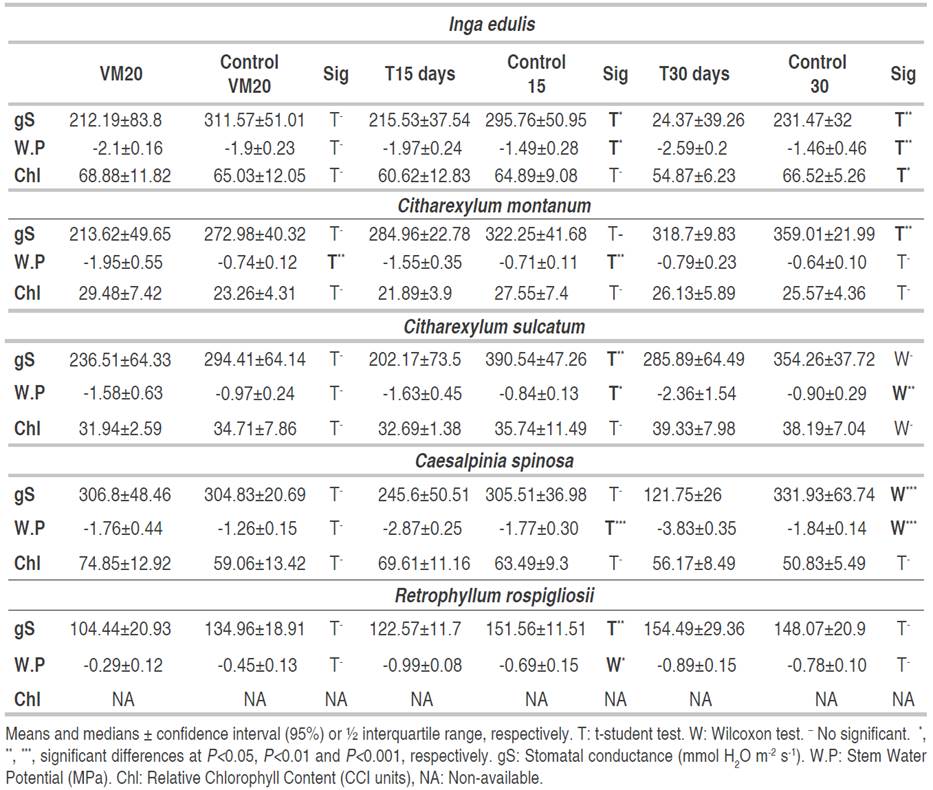
To reduce water loss, one of the first plant strategies to avoid water deficit is the stomatal closure (Osmolovskaya et al., 2018), meanwhile enzyme activity and Chl content decrease sharply when the water deficit changes from mild to severe (Flexas et al., 2012). In this study, there was a similar situation in which there was a reduction in stomatal conductance and stem water potential under T15, while, chlorophyll content diminished only in I. edulis after 30 days of having reached VM20 (Table 2). The chlorophyll content is less susceptible to mild than to severe water stress and there is a metabolic impairment consisting in inhibition of photosynthetic enzymes and a decrease in chlorophyll content (Flexas et al., 2012).
The quick decrease of water potential has been proved in the same species or species of the same genus. For example, Cordero (2016) proved that leaf water potential and stomatal conductance decreased faster than leaflet movement in C. spinosa. However, Stomatal conductance was more negative in that assay with stomatal conductance less than 150 mmol H2O m-2 s-1 in control plants and less than 25 mmol H2O m-2 s-1 in stressed plants.
In all the species, stem water potential was the first and in C. montanum and C. spinosa the first and only indicator of water deficit. This variable was the most susceptible to water deficit since there were 9 of 15 cases in which this potential decreased significantly while stomatal conductance (the second more susceptible) did it in six cases. Cole and Pagay (2015) found something similar: stem water potential was the best water deficit marker, being less sensitive to environmental conditions than stomatal conductance and leaf water potential. Deeming that the water potential of stem decreased faster than the stomatal conductance species from Citharexylum genus and C. spinosa might be anisohydric species.
Besides, the volumetric water content of soil correlated positively (spearman method, rho>0.65 and P<0.001) with stem water potential and negatively with stomatal conductance (rho<-0.5 and P<0.001) for all species, except for R. rospigliosii. A positive correlation between leaf water potential and the volumetric water content of the soil was also discovered by Cordero (2016) in C. spinosa. Its frequency to detect water deficit and its correlation with volumetric water content endorses the usefulness of stem water potential as a water deficit marker, and its use as a predictor of soil moisture.
Growth Response to Water deficit
As time passed, the effects of water deficit on tree growth were more severe (Table 3). The longer was the water deficit, the higher were the differences between the control and water deficit treatments. For example, after 15 days of having reached VM20, a few growth variables were affected by water deficit decreasing until 40%. However, after 30 days all the variables from all species decreased more than 50% except FLM and DLM. After the soil had reached a volumetric water content of 20%, none of the growth variables was affected except ΔBST in C. montanum. After 15 days, growth variables diminished in I. edulis, C. montanum and C. spinosa but not in C. sulcatum and R. rospigliosii. Meanwhile, after 30 days, at least one growth variable, except in C. Sulcatum, decreases in all species. A permanent growth reduction after 30 days of water deficit was also reported by Cordero (2016) in the same species C. spinosa after reducing water supply for more than 20 days.
Table 3 Increases of stem diameter (ΔBSD), diameter at breast height (ΔDBH), height (ΔHeight), fresh (FLM) and dry leaves mass (DLM) of Inga edulis, Citharexylum montanum, Citharexylum sulcatum, Caesalpinia spinosa and Retrophyllum rospigliosii submitted to three water deficit periods.

Making an analogy with physiological variables, the descending order of growth variables would be stem diameter, height and dry leaf mass. In R. rospigliossi there was a faster physiological response to water deficit, in comparison to growth. While in the rest of the species, there were both a growth reduction and a physiological response. However, C. sulcatum showed an opposite response: there was a physiological change but without a growth decrease.
Considering the reduction of growth as well as of stomatal conductance, growth reduction might have been caused by one of these reasons: i) cell growth reduction, which is one of the most sensitive processes to water deficit (Czaja et al., 2020) or ii) a fall in photosynthesis, transpiration and mesophyll conductance due to stomatal close (Flexas et al., 2012), which was also proved by Cordero (2016) in one of the evaluated species (C. spinosa ). Since some species did not show a relationship between instantaneous physiological variables and growth parameters, it is important to use growth variables to evaluate water deficit. However, it should be also considered physiological variables that indicate some degree of water deficit adaptation or response, even if those variables do not translate into growth reductions.
C. sulcatum and R. rospligiosii showed certain tolerance to water deficit possibly because of their conservative strategy (low growth rate and transpiration): both species had a slower rate of water consumption (Figure 1), low growth and in the case of R. rospigliosii the lowest gS rate (Table 2). Mitchell et al. (2012) propose that a conservative strategy reduces the risk of hydraulic failure, and decreases the rate of carbon depletion, which in turn extend the tree's lifespan under drought conditions, which would explain the tolerance of C. sulcatum to all treatments and of R. rospigliosii to T15.
The tolerance of R. rospigliosii to water deficit might be also due to its wood anatomy. Having narrow tracheids (25.2-54.6 µm) and a high frequency of these (740-128 tracheids mm-2) (Vásquez Correa et al., 2010), this species has less vulnerability to high vapour pressure deficit, embolism and drought (Aroca, 2012). By contrast, some species of Citharexylum genus like Citharexylum myrianthum (Marcati et al., 2014) and Inga genus (María Martín-Seijo et al., 2021) have ring-porous wood, whose vessels are wider and less frequent. Additionally, I. edulis with rapid growth and high transpiration usually is more vulnerable to drought (Mitchell et al., 2012).
Trees that keep their growth rate and show certain tolerance to water deficit are desirable for urban trees since they will reach their final size faster than those that will not, which means to rapidly provide services like shade, temperature reduction, rainwater interception and pollution removal (Eisenman et al., 2021). Additionally, tolerance to water deficit is an advantage for trees growing under an urban environment, since temperature and water deficit are more frequent in urban than in rural areas (Czaja et al., 2020).
CONCLUSIONS
i) The water consumption, in descending order, was I. edulis, C. montanum, C. spinosa, C sulcatum and R rospigliosii, ii) A volumetric water content of 20% is enough to guarantee all species growth, iii) Stem water potential is the best variable for using as a water deficit marker for these species. Because this study was carried out on young trees, there would be important to assess the water requirements of each species in several phenological stages under the urban landscape. Neither basal stem diameter nor height alone should be considered to plan irrigation but any variable related to potential transpiration like the leaf area of trees.

















