Introduction
According to the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD),1 chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common, preventable, and treatable condition characterized by airflow limitation and respiratory symptoms such as dyspnea, cough, expectoration, chest tightness, fatigue, and exercise restriction, which usually persist over time and affect the quality of life of patients.2,3
Multiple studies on the prevalence of COPD have been carried out, showing that this condition varies depending on the population. In a study that included patients from 12 countries, Landis et al.4 established that the overall prevalence of this disease is between 7% and 12%, with estimates ranging from 7% to 9%. Likewise, in a systematic review conducted in 28 countries and included 62 studies, Halbert et al.5 found that the prevalence of COPD determined based on physiological characteristics in adults over 40 years of age varies between 9% and 10%. In Latin America, in a study on COPD prevalence carried out in 5 cities (São Paulo, Santiago de Chile, Mexico, Montevideo, and Caracas) with 5 315 participants, Menezes et al.6 found that this value fluctuated between 7.8% and 19.7%, while in Colombia, in a cross-sectional study carried out in 5 539 patients over 40 years of age, Caballero et al.7 estimated an overall prevalence of COPD of 8-9% using spirometry, ranging from 6.2% in Barranquilla to 13.5% in Medellín.
According to a SEPAR-ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of COPD by Peces-Barba et al.,8 airflow obstruction is considered to be present when the forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEVi) after bronchodilator administration is <0.7. Although this paper establishes that this value is the best indicator of the severity of the obstruction (and therefore of COPD), given the heterogeneous and systemic nature of the disease, it is advisable to consider other variables such as the clinical assessment of patients, gas exchange, lung volumes, perception of symptoms, exercise capacity, frequency of exacerbations, presence of nutritional alterations (unintentional weight loss), among others.8
The GOLD initiative also states that, in the assessment of COPD, the determination of the severity of airflow limitation and its impact on the patient's health status, as well as the risk of future exacerbations, is essential for proper management of the disease as it allows for the establishment of appropriate treatment guidelines.1
Also referring to the complex and heterogeneous nature of this disease, Lopez-Varela & Montes-de Oca stated that COPD has "an important interpersonal variability in its biological characteristics and clinical, functional and radiological presentation, as well as in its progression".9, p105 Furthermore, there are publications that analyze symptom variability during the day and, specifically, the perception of symptoms during the first hours of the day.10,u
In Colombia there is no research on the subject. Therefore, the objectives of this study were to describe symptom variability in COPD patients throughout the day and night for four weeks using a patient diary, and to validate a questionnaire developed for this purpose (Colombian Self-administered Instrument of Symptom Variability in COPD: EPOC-CoVaSy).
Materials and methods
Study type and population
Cohort study conducted in adult COPD patients treated at the Centro de Atención Pulmonar - CAP (Pulmonary Care Center), in Barranquilla, Colombia, between June and December 2016.
Sample size was estimated following the criteria established for finite populations. On the one hand, according to the PREPOCOL study, carried out by Caballero et al.7 between February 2003 and May 2004, the prevalence of COPD confirmed through spirometry in Barranquilla in adults over 40 years of age was 6.2%. On the other hand, the population over 40 years of age projected for 2014 in Barranquilla, according to the National Administrative Department of Statistics (DANE by its acronym in Spanish), was 417 436 people.12 Thus, taking into accounta 95% confidence interval for a z (alpha)=1.96 and an accuracy of 5%, the sample size obtained was 90 participants to be included in a 6-month period. In addition, the lost to follow-up was estimated at 5%, so the final sample size was 95 patients.
Patients over 40 years of age who had been diagnosed with COPD by spirometry (FEV1 values<0.7 after bronchodilator administration) within six months prior to the date of enrollment in the study, were receiving outpatient care, and had not had their treatment modified at least one month prior to the start of the study, were included. All patients agreed to participate voluntarily in the study.
On the other hand, patients who experienced exacerbation of COPD symptoms according to the GOLD 20141 criteria within three months prior to the start of the study; those with a history of asthma, allergic rhinitis, lung cancer, bronchiectasis, interstitial lung disease, tuberculosis, and sarcoidosis; and those who had participated in an investigational drug intervention study within 30 days prior to the start of the study were excluded. The final sample was made up of 96 patients.
Instruments
In addition to the patient's diary (Annex 1), which was to be used to record symptoms, performance in activities of daily living, adherence to therapy, and the occurrence of adverse events, the EPOC-CoVaSy instrument, designed by the authors for that purpose, was used to assess symptom variability.
The EPOC-CoVaSy (Annex 2) is a questionnaire of 8 questions: 6 Likert questions about symptom intensity during the day and night and when performing activities of daily living with scores from 0 to 9 (0: not at all; 10: unbearable), and 2 closed questions on sleep quality and the use of medication for the treatment of the disease.
Procedures
Once the instrument was designed, a pilot test was conducted in November 2015 on a sample of 10 patients diagnosed with COPD at the CAP. During individual sessions, the researchers asked patients to sign an informed consent to participate in the pilot test, provided them with the EPOC-CoVaSy instrument for completion, and recorded, on a form designed for this purpose, the start and end times, as well as questions, concerns, observations, and comments made by each patient.
The age range of the participants in the pilot was between 54 and 73 years, the average response time was 6.9±3.8 minutes, and 50% of patients expressed concerns about how to answer (check) each question. Once the results of this test were analyzed, the relevant changes were implemented in the instrument and the resulting version, which was submitted for review and approval of the Research Ethics Committee of the Fundación del Caribe para la Investigación Biomédica - BIOS (Caribbean Foundation for Biomedical Research), was used in the study.
The study protocol stated that once the eligibility criteria had been verified and written informed consent had been obtained, the demographic and baseline characteristics of the participant's disease (COPD severity, treatments, medical history, etc.) should be documented in the medical record. Patients were then instructed on how to fill the diary (during the next four weeks, every day at the same time) in which they should report information on their COPD symptoms; performance in activities of daily living such as bathing, drying off, dressing, eating, and walking; adherence to treatment; and any adverse events. At a second visit to the center, four weeks later and prior to the clinical evaluation and follow-up visit with the investigator, patients were required to submit the diary and complete the EPOC-CoVaSy instrument.
Symptom variability and the ability to perform activities during the day were assessed, both in the diary and in the EPOC-CoVaSy instrument, using visual analogue scales (VAS) with scores ranging from 0 to 10, with "0" being the least discomfort or difficulty and "10" being the maximum discomfort or difficulty.
Variables
The patient diary was designed to assess four domains: global symptoms, ability to perform activities, administration of COPD medications, and quality of sleep at night:
I. Global symptoms during the day and night: shortness of breath, cough, expectoration, wheezing, and chest tightness.
II. Ability to perform activities during the day: bathing, drying off, dressing, eating main meals, and walking.
III. Administration of COPD medications: time of administration (morning, afternoon, night).
IV. Assessment of sleep satisfaction in relation to disease symptoms: general sleep assessment, and sleep and wake-up times.
The diary also included the recording of discomfort or symptoms that could be classified as adverse events and serious adverse events to meet pharmacovigilance requirements.
Instrument validation
The EPOC-CoVaSy instrument was validated by comparing the data recorded in the patient's diary with those obtained with the self-administered questionnaire during the second visit. Therefore, by means of a multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA), the relationship between the patient's assessment of the diary questions and the cross-sectional evaluation of the instrument was established. In other words, it was intended to establish that there were no statistically significant variations between the responses recorded over the four weeks in the diary and the immediate responses documented in the EPOC-CoVaSy.
The MANOVA allowed comparing each variable in both instruments, at three times of the day (morning, afternoon, and night). In this special case, the aim was to contrast the system of hypothesis H a : "There is no similarity between the results of the diary and those of the EPOC-CoVaSy" with H 0 : "There is a similarity between diary results and those of EPOC-CoVaSy." The purpose of this analysis was to find statistically significant differences between the responses of both instruments using a linear regression analysis with the Pillai's trace statistics.
Statistical information concerning MANOVA is described in detail in the sub-section "Statistical analysis".
Instrument applicability
Principal component analysis (PCA) was used to assess the applicability of the EPOC-CoVaSy instrument. In the first component (Dim1), symptoms in general and symptoms when performing activities throughout the day were considered together, while general symptoms and symptoms when performing activities at each of the 3 times of the day (morning, afternoon, and night) were analyzed in the second (Dim2).
Statistical analysis
For the descriptive analysis of the data, measures of central tendency (mean and median) and dispersion (standard deviation and interquartile range) were used for continuous variables, and absolute frequencies and percentages for categorical variables. On the other hand, independence and frequency comparison of categorical and continuous variables were established using the chi-squared test and Fisher's exact test and the Pearson correlation coefficient, respectively.
Finally, a MANOVA was performed to determine the correlations between patient diary and EPOC-CoVaSy scores using linear regression models that were tested with Pillai's trace. All statistical analyzes were carried out using the R software and a significance level of p<0.05 was considered for all analyses.
Ethical considerations
The study took into account the ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects established by the Declaration of Helsinki13 and the technical, administrative and scientific standards for health research of Resolution 8430 of 1993 of the Colombian Ministry of Health.14
Furthermore, the research protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of BIOS through Minutes No. 0127 of July 31, 2015, and informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Results
The average age of the participants was 73.3±8.3 years (range 55-89) and the majority were male (71.87%). Table 1 shows the summary of the demographic characteristics and clinical evaluation results.
Table 1 Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of patients (visit 1, n=96).

WHO: World Health Organization.
Source: Own elaboration.
For the combined assessment of COPD, the classification of the GOLD 2014 guidelines1 (effective at the time of patient enrollment in the study) was used and information on other diagnostic tests was obtained (Table 2).
Table 2 Assessment of COPD and risk factors (visit 1, n=96).

COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Source: Own elaboration.
When analyzing comorbidities and risk factors, two patients who responded being on bronchodilator therapy were found to have severe obstruction and an unspecific history of respiratory allergies and smoking (20 and 15 packages/year, respectively).
Evaluation of the patient's diary
In general, mean scores were higher in the morning (mean scores between 1.5 and 2.5) than in the afternoon and night (mean scores between 0.5 and 1.5) for all symptoms and for the performance of activities assessed in the patient's diary, demonstrating that there was variability of symptoms over the course of the day, although this variability was minimal (Figure 1).
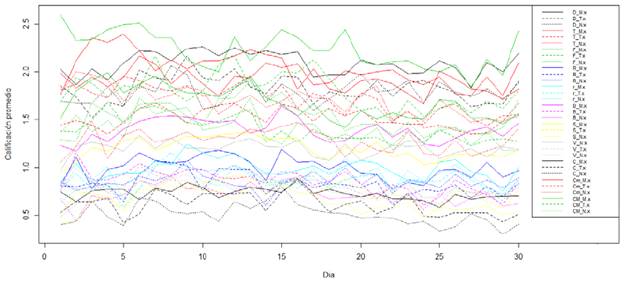
Solid line: morning results; dashed line: afternoon results; dotted line: night results; Mx: Morning; Tx: Afternoon; Nx: Night; D: shortness of breath; T: cough; F: phlegm; R: breath sounds; r: chest tightness sensation; B: bathing; S: drying off; V: dressing; C: eating; Cm: walking less than one block; CM: walking more than one block.
Source: Own elaboration.
Figure 1 Combined result of symptom variability and activities in patient diaries.
When the Pearson correlation coefficient was applied, a statistically significant correlation (p<0.05) between the perception of activity variables in the morning and in the afternoon and night was found.
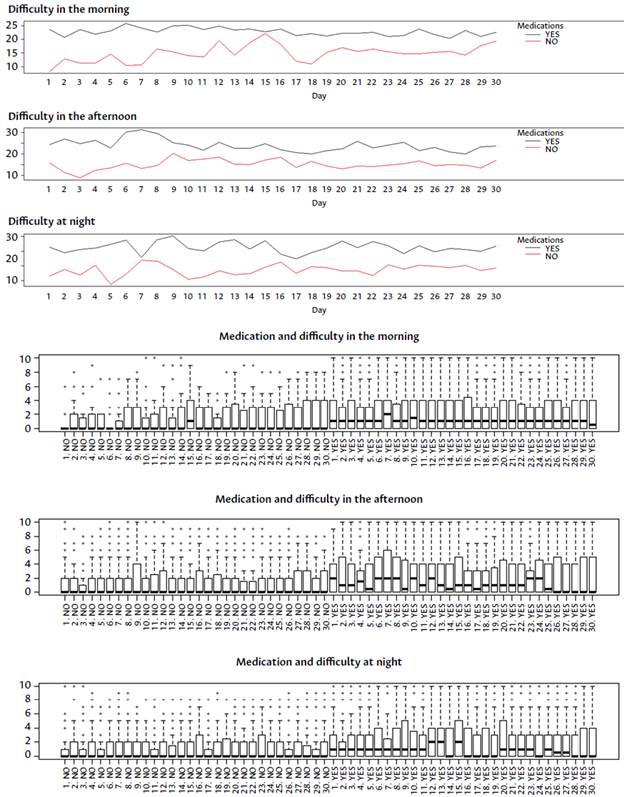
The GOLD 20141 classification did not influence symptom variability. The results also showed that there is a small variation in the mean score between the variable taking or not the drug versus the mean score obtained in the symptom assessment. This variation was positive in some cases and negative in others, which could be due to the perception of symptom severity versus the need to use the indicated drug, i.e., the worse the symptoms, the greater the use of the medication (Annex 3). On the other hand, it was found that those who rated their symptoms negatively had greater difficulty sleeping (Annex 4).
Regarding adherence to treatment, it was found that this variable had a positive rating in 87% of the evaluations.
Validation of the EPOC-CoVaSy instrument
When MANOVA was performed to determine the correlations between the data collected in the patients' diaries and the results obtained using the EPOC-CoVaSy, it was found that there was a similarity between the two instruments for each of the symptoms and activities evaluated according to the time of day assessed (Table 3).
Table 3 Multivariate analysis of the variance of the variables of the patient's diary versus the variables of the instrument EPOC-CoVaSy according to the time of day assessed.

D: difficulty breathing; T: cough; F: phlegm; R: breath sounds; r: chest tightness sensation; B: bathing; S: drying off; V: dressing; C: eating; Cm: walking less than one block; CM: walking more than one block; M: morning; T: afternoon; N: night.
* Each variable is expressed with respect to the time of day, so D_M means difficulty breathing in the morning; D_T, difficulty breathing in the afternoon, etc. Three degrees of freedom in the numerator and 88 degrees of freedom in the denominator were considered.
Source: Own elaboration.
However, according to the MANOVA, the p-values for testing the H 0 hypothesis were significant, which made it possible to reject the H a hypothesis, thus, the comparison between the two data capture instruments could be statistically validated and a univocal association between both instruments was demonstrated. Therefore, it can be stated that the EPOC-CoVaSy instrument reflects the variability of symptoms over the last four weeks (Table 4).
Table 4 Multivariate analysis of variance of the variables of the patient's diary versus the variables of the instrument EP -OC-CoVaSy.
| Variables * | Pillai's trace | F approach | p -value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Difficulty breathing | 0.011088 | 0.69143 | 0.5583 |
| Cough | 0.011769 | 0.7344 | 0.5327 | |
| Phlegm | 0.016018 | 1.0038 | 0.3924 | |
| Breath sounds | 0.027655 | 1.7539 | 0.1576 | |
| Chest tightness sensation | 0.019189 | 1.2065 | 0.3088 | |
| Activities | Bathing | 0.024567 | 1.5531 | 0.2023 |
| Drying off | 0.0095919 | 0.59723 | 0.6176 | |
| Dressing | 0.0020585 | 0.1272 | 0.9439 | |
| Eating | 0.024331 | 1.5378 | 0.2062 | |
| Walking less than a block | 0.014545 | 0.91017 | 0.4372 | |
| Walking more than a block | 0.0070652 | 0.43879 | 0.7255 | |
* 3 degrees of freedom in the numerator and 185 degrees of freedom in the denominator were considered.
Source: Own elaboration.
Applicability of the EPOC-CoVaSy instrument
PCA found that in both components (joint information from the three times of the day and morning only, afternoon only, and night only) about 70% of the variability of the information obtained was captured, including all the characteristics of interest. Likewise, it was shown that the higher the score, the more "symptomatic" the patient tended to be in most of the variables analyzed throughout the day, and when the analysis was performed independently in the morning, afternoon and night, the same findings were observed. Figure 2 shows the unit circle with the same characteristics of the instrument in the morning, afternoon, and night with all the variables directly correlated.

Dim 1: dimension 1= component 1; Dim 2: dimension 2= component 2.
Source: Own elaboration.
Figure 2 Analysis of major components.
After PCA was developed, a classification analysis was performed on three data sets: low scores (low-risk group), intermediate scores (medium-risk group), and high scores (high-risk group). Figure 3 shows low-scoring data set in black, intermediate-scoring data set in red, and high-scoring data set in green.

Dim 1: dimension 1= component 1; Dim 2: dimension 2= component 2.
Source: Own elaboration.
Figure 3 Score Group analysis.
According to the above, if a person were to score each variable with 10 points, a total of 110 points in each period of the day (morning, afternoon, and night) would be obtained and, therefore, the overall score would be 330 points, a score that represents the worst scenario for COPD.
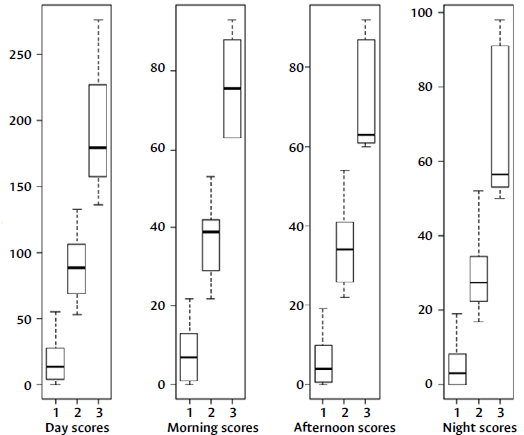
These results were summarized in the box plots shown in Figure 4. The diagram on the left shows the total symptom score of the day (morning, afternoon, and night): a score <50 represents mild symptoms; between 51 and 140, moderate symptoms; and >141, severe symptoms. The following three plots correspond to the morning, afternoon, and night scores, respectively: a score <20 at each of the three times of the day represents mild symptoms ; between 21 and 5 5, moderate symptoms ; and > 5 6, severe symptoms.
Source: Own elaboration.
Figure 4 EPOC-CoVaSy instrument score cut-off points for the day and the three moments of the day.
Table 5 describes the cut-off points for the EPOC-CoVaSy instrument scores to determine the severity of symptoms at each of the three times of the day (morning, afternoon, and night). The difference between the scores obtained for two moments allowed to establish the variability of the same symptoms during the day.
Discussion
The ECLIPSE study "Evaluation of COPD longitudinally to Identify Predictive Surrogate Endpoints" showed that individuals with airflow limitation have a significant variability in their symptoms, exercise capacity, exacerbations, and quality of life, implying different prognosis and treatment.15
The present study confirmed that there is variability in COPD symptoms in the morning, afternoon and night, and that, while this variability is minimal, the perception of COPD remains the same throughout the day, meaning that, although there is an improvement in the perception of symptom severity at any of these three times, this perception tends to be the same throughout the day. In this sense, it was found that if the patient had a good score in the morning, this trend was maintained throughout the day with mild positive variations, and vice versa. This finding is supported by the high correlation between the three periods analyzed.
The variability of COPD symptoms can be attributed to three important factors that explain the greater difficulty in breathing during the first hours of the day: i) bronchial muscle tone is higher in the morning, ii) secretions accumulate after several hours in a decubitus position, and iii) the patient performs more physical activity in the first hours of the day, such as waking up, eating breakfast, washing up, bathing, drying off, dressing, etc.16 Moreover, it is known that the respiratory system has a circadian rhythm that would explain the worsening of lung function at night and its improvement during the day, a fact that has been demonstrated in the relevant literature on COPD, although with a weak correlation to the perception of symptoms.17-19 In addition, it should be noted that in COPD, contrary to what happens in asthma, symptom variability has not been studied extensively.20,21
With regard to adherence to treatment, the results of the present study show that there is a small variation between the variable taking the drug or not and the mean score obtained in the symptom assessment. In some cases, this variation is positive and in others it is negative, which may be due to the perceived severity of the symptom versus the need to use the indicated medication. In other words, the greater the exacerbation of symptoms, the greater the use of the medication. It was also established that symptom variability significantly impacts sleep quality since the higher the score (worsening of symptoms), the greater the difficulty to sleep.
The purpose of studying symptoms in COPD patients over time is to evaluate, among other factors, changes in their intensity, their impact on activities of daily living, adherence to drug therapy, and impairment of sleep quality; it is worth clarifying that the exacerbation of symptoms in COPD corresponds to a change in intensity that goes beyond normal daily variation. Although there is no data to indicate how the daily variation in COPD symptoms occurs,22 the most direct way to measure the impact of symptoms on activities of daily living is to include questions to evaluate this aspect in the usual anamnesis.
In this regard, two symptom assessment questionnaires have been developed: the Capacity of Daily Living during the Morning (CDLM) and the Global Chest Symptoms Questionnaire (GCSQ).23 The Saint George Respiratory Questionnaire, designed to assess quality of life in COPD and asthma patients, is also available.21 All these tools combine symptom perception with quality of life.
However, as stated above, there is no instrument that evaluates symptom variability throughout the day because, even though the CDLM instrument assesses the development of activities in the morning, it does not include the perception of all symptoms and only the day on which it is administered is evaluated. On the other hand, although the GCSQ questionnaire is quite complete and includes perception of symptoms and quality of life, it is very extensive and does not evaluate variability during the day, but rather the period corresponding to the previous year, which can generate patient memory biases.
In contrast, the EPOC-CoVaSy instrument developed for this study offers some advantages in routine clinical practice since it evaluates three essential factors: i) symptoms and activities throughout the day, ii) sleep quality, and iii) adherence to therapy; in addition, it does so over a four-week period, which minimizes memory bias and facilitates the patient's usage of a VAS.
Finally, the high correlation between the patient diary and the cross-sectional evaluation with the EPOC-CoVaSy instrument allows validating this tool and recommending the single evaluation of symptom variability in patients with COPD to determine objectively, through scores, how that variability has been in the last four weeks, without having to resort to a diary or more complex assessments.
Conclusions
Based on the findings of the present study, it can be concluded that there is slight variability in COPD symptoms over the course of the day, which should be considered when establishing treatment schemes for this disease. It was also established that the EPOC-CoVaSy is a valid instrument for measuring this variability in the Colombian population.