INTRODUCTION
The most common intraocular tumor diagnosed in children is retinoblastoma (RB). Each year, this condition affects about 8 000 eyes, and survival rates vary significantly between developing and developed countries 1. The retinal tissue is the exact location of the histopathological origin of RB, and it can manifest as either a hereditary or nonhereditary form 2. In 98% of cases, the RB is caused by an allelic inactivation of the RB1 tumor suppressor gene localized on chromosome 13q14 3. The most common signs, which indicate late stages, include leukocoria and strabismus 4.
The employed therapeutic modalities include chemotherapy, radiotherapy, brachytherapy, and surgery. One of the most efficient approaches, at the moment, is selective intraarterial chemotherapy, which may be utilized at different phases 5.
In Colombia, some other groups have published previous epidemiological data in a 2021 report on the clinical management of RB 6. This study also concludes that significant socioeconomic differences lead to significant variations in healthcare availability among states and regions. Due to all these factors, it is essential to supplement the available epidemiological data on RB with information regarding the sociodemographic, clinical, pathological, and therapeutic characteristics of the patients in the Colombian Caribbean region.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Design, study population, and study sample: A retrospective case series of patients with RB was conducted. Potential medical records were electronically identified, from 2016 to 2021, at a referral ophthalmology center located on the northern coast of Colombia, using ICD-10 codes, keywords "Retinoblastoma" or reasons for admission to chemotherapeutic treatment, and, then, these records were manually reviewed to confirm the pertinence of its inclusion, which applies to all patients with RB admitted to the referral center on the study date; excluding those patients with previous ophthalmologic treatment outside the institution, and who do not comply with the established follow-up protocol.
Institutional protocol: The initial diagnostic parameters included pediatric, hemato-oncology, genetic, and ophthalmologic evaluation through biochemical laboratory tests, orbits, and brain magnetic resonance imaging, both simple and contrasted with gadolinium, ocular ultrasound. The examination was performed under anesthesia. The ocular treatment was defined, monthly, at medical board meetings, and applied in accordance with the RB stage, based on the International Classification of Retinoblastoma. The different treatments-chemotherapy (intravitreous, intraarterial, and systemic), laser photocoagulation, transpupillary thermotherapy, cryotherapy, and enucleation-were not exclusive. They were combined to obtain the greatest outcomes.
Data: sociodemographic characterization included the general variable collection. The clinical variables used included signs, tumor laterality, growth and staging patterns, genetic tests, and family history of RB. Finally, treatment (type and quantity of drugs), outcomes (enucleation, extension, evolution), and complications were registered.
Statistical analysis: a descriptive analysis was performed using frequency distributions, proportions, means, and standard deviations. For the data analysis the R software (R Core Team (2021) was used.
Ethical considerations: This research was designed and conducted complying with national law. The research protocol (003-2021) was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Universidad de Cartagena.
RESULTS
A total of 21 eyes, corresponding to 16 patients, were diagnosed with RB in the ophthalmologic center during the 6 years of the study. The average age was 17.7 months [range=5; 49], 68.8% (n=11) had low socioeconomic status and some lived in rural areas 68.8% (n=11). See Table 1.
With regards to clinical findings, RB was bilateral in 66.7% (n=14) of the eyes, and 76.2% (n=16) presented leukocoria as a predominant clinical finding (Table 1). The tumor was classified as endophytic in 61.9% (n=13) of the eyes, and type D was the predominant stage of diagnosis (42.9%). In four (19%) eyes, genetic tests were reported, and three of them had a mutation in the RB1 gene.
Table 1 Sociodemographic characteristics of patients with RB were included in the research and Clinical characteristics of patients with RB included in the research.
| Sociodemographic aspect | Number of patients (N=16) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Male | 8 (50%) |
| Female | 8 (50%) |
| Social Stratum | |
| 1 | 11 (68.8%) |
| 2 | 3 (18.75) |
| 3 | 1 (6.25%) |
| 4 | 1 (6.25%) |
| Affiliation Regime | |
| Subsidized | 11 (68.8%) |
| Contributory | 5 (31.25%) |
| Residence Area | |
| Rural | 11 (68.8%) |
| Urban | 5 (31.25%) |
| Clinic aspect | Total (N=21 eyes) |
| Laterality | |
| Bilateral | 14 (66.7%) |
| Unilateral | 7 (33.3%) |
| Eye treated | |
| Right | 14 (66.7%) |
| Left | 7 (33.3%) |
| Clinical signs | |
| Leukocoria | 16 (76.2%) |
| Strabismus | 5 (23.8%) |
| Tumor growth pattern | |
| Endophytic | 13 (61.9%) |
| Combined (endophytic and exophytic) | 6 (28.6%) |
| Diffuse | 1 (4.8%) |
| Retinoma | 1 (4.8%) |
| Tumoral staging | |
| a | 3 (14.3%) |
| B | 3 (14.3%) |
| C | 3 (14.3%) |
| D | 9 (42.9%) |
| E | 3 (14.3%) |
| Genetic test | 4 (19%) |
| Genetic test results | |
| rb1 mutation | 3 (14.3%) |
| Normal rb1 alleles | 1 (4.8%) |
| Extraocular commitment | |
| Optic nerve | 2 (9.5%) |
| Enucleation requirement | 6 (28.6%) |
| Enucleation cause | |
| Progression of the disease | 4 (19%) |
| Initial extraocular commitment | 1 (4.8%) |
| Retinal detachment | 1 (4.8%) |
Regarding treatments, intraarterial chemotherapy was applied (36%), requiring an average of five sessions per eye [range = 1; 15], followed by photocoagulation (14.4%), intravitreous chemotherapy (15.6%), transpupillary thermotherapy (8.4%), cryotherapy (11.6%), and systemic chemotherapy (14%). The most frequently used drug for intravitreous treatment was Melphalan® (64.7%). After treatments, the data showed that 71.4% (n=15) of the examined eyes achieved remission. Table 2 summarizes the evolution of the eyes included in the study, and Figure 1 shows some images of particular cases of RB and their treatment.
Table 2 Detailed evolution of the eyes of patients with RB included in the study.
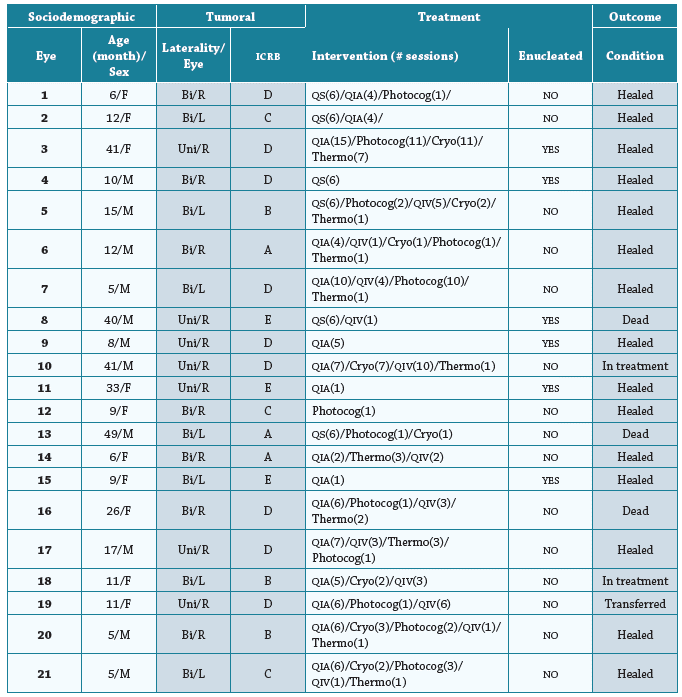
Abbreviations. M: male; F: female; Bi: bilateral; Uni: unilateral; R: right; I: left; ICRB: Intraocular Classification of Retinoblastoma; QIA: intraarterial chemotherapy; QIV: intravitreous chemotherapy; QS: systemic chemotherapy; Cryo: Cryotherapy; Photocog: Photocoagulation; Thermo: Thermotherapy.
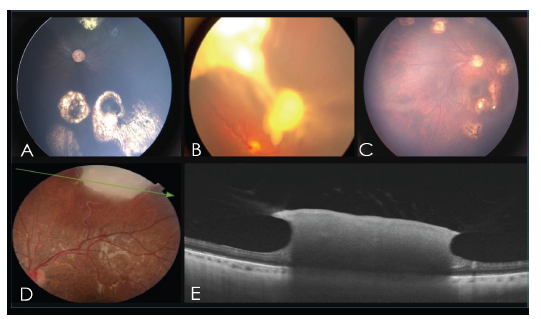
Figure 1 Representative of study cases of RB and treatments. A) RB group B with varied resolution (calcification, atrophy of retinal pigment epithelium-RPE. B) Diffuse RB with high vitreous seeding. C) Complete resolution of retinoblastoma with multiple vitreous seeding after intravitreous and intraarterial chemotherapy and transpupillary thermotherapy. D) RB group B with image similar to fish-flesh. E) Optical Coherence Tomography of the eye shown in D.
DISCUSSION
Retinoblastoma is a disease that requires timely diagnosis and effective treatment to improve its prognosis 7. In this study, the characterization of 21 eyes of 16 patients revealed an average age of diagnosis of 17.7 months, similar to what was reported by Fabian et al. 6.
Regarding disease distribution by sex, the data obtained from our study proved to be similar to those reported by other studies 5,6. Fabian et al. 6 also described that 70% of cases were unilateral, and the remaining 30% were bilateral. Bilateral presentation is associated with a better prognosis when the retinoblastoma is diagnosed at an older age 1,8. In our study, unilateral involvement was 33.3% of total eyes included, while bilateral was 66.7%.
In our research, only 19% of the patients had access to genetic testing, showing barriers to access to this kind of diagnostic test. This situation can occur due to the high cost of the tests 7 and low availability in our context. An additional essential aspect during the diagnosis of RB is the disease staging, because it potentially impacts prognosis and cure rates. In a study on 14 eyes conducted by Liu et al. 9, 57% of the patients had an RB in advanced stages (D or E group), and at least 93% received intra-arterial chemotherapy as secondary therapy after previous failed treatments. In another report performed in Medellin by González et al. 10, the RB cases in D and E stages was 66%, with secondary treatment of 67%. These results are similar to what we found in our research (57.2% in these stages) and with secondary interventions in 76%.
Another critical aspect of RB is choosing an optimal treatment. Current treatment of RB focuses on the preservation of the eyeball, and the use of intraarterial and intravitreal chemotherapy.
This research has various strengths. It is the first case series of the Colombian Caribbean region. It is also essential to mention that most patients received intraarterial chemotherapy, which brings valuable information on the evolution of the patients that used this treatment approach. Nevertheless, it is not possible to directly extrapolate the results to other populations because of its specific context. We believe that these results could, however, be useful for policy formulation within countries and regions with similar contexts.
CONCLUSION
The results of this study showed some particularities concerning RB patients' diagnostic and treatment process in the Caribbean Colombian region that needs to be addressed and thoroughly investigated. Another critical aspect of RB is choosing an optimal treatment. Current treatment of RB focuses on the preservation of the eyeball, and the use of intraarterial and intravitreal chemotherapy. As a multidisciplinary group, we followed this concept and adopted this patient management guide for the last 5 years. Additionally, these results may suggest that the Colombian health system exhibits problems with healthcare access that can affect the prognosis of these patients, and this must be investigated further.















