The power flow solution is a classical problem in electrical engineering which has been studied for more than 60 years 1. One of the most widely used methods corresponds to the Newton-Raphson approach, which is currently employed for analyzing power systems with meshed configurations and multiple generation sources, i.e., it is typically employed for power systems at high-voltage levels 2. In the case of medium- and low-voltage levels, power flow analysis is performed with graph-based approaches that consider the radial topology of the network in order to propose derivative-free solution methods 3), (4. Said graph-based approaches reduce the processing times required to obtain the power flow solution because they do not use recursive matrix inversions during the iterative solution process, unlike derivative-based power flow methods 5.
Two of the most widely known power flow solution methodologies for radial distribution networks in medium-voltage levels are the backward/forward power flow 4 and the triangular-based power flow 3. Both methods are based on the tree structure that represents radial distribution networks. The main characteristic of both methods is that they are formulated using the branch-to-node (Ad) and the triangular (T) matrices. However, both solution methods are mathematically different. The power flow method based on the triangular matrix is only applicable to strictly radial electrical distribution networks. Still, it is possible to find an analytical relation between both matrices, as demonstrated in this editorial note.
Theorem 1. The branch-to-node incidence matrix A and the upper-triangular matrix T are related through a negative inverse, including a transposed operation, i.e.,
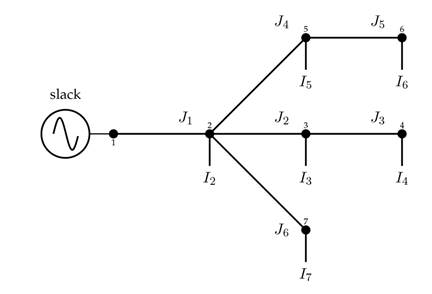
Proof. To demonstrate Equation (1), let us recur to the distribution grid presented in Fig. 1. Note that Jb represents the current flowing through line b, and Ik corresponds to the net demanded current at node k.
It is worth mentioning that the branch and nodal currents can be related using a matricial operation, as presented in Equation (2):
where
 is the vector that contains all the branch currents, and
is the vector that contains all the branch currents, and
 contains all the demanded currents, respectively.
contains all the demanded currents, respectively.
Now, if the Kirchhoff’s first law is applied to each node of the network, except to the substation node, i.e., node 1, as illustrated in Figure 1, the relation between nodal injected currents and branch currents is reached as presented in (3).
For more details regarding the construction of the branch-to-node incidence matrix, please refer to 6. Now, in order to demonstrate that Equation (1) is true, if (3) is substituted into (2), then (4) is obtained:
which clearly shows that
where l is the number of distribution lines in the distribution grid under analysis, i.e., for Figure 1 l = 6.
In addition, if the operation in (5) is made for matrices T and A⊤ d in (2) and (3), the following result is reached.
which confirms that
thus completing the proof.
Remark 1. The result in Equation (1) is particularly important for power flow studies since it demonstrates that, for strictly radial distribution grids, the branch-to-node incidence matrix Ad and the upper-triangular matrix T are related. This is, it will be possible to demonstrate that the upper-triangular power flow method is indeed a particular case of the classical and well-known backward/forward power flow method 7.