INTRODUCTION
The end of the political armed conflict between the State and the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC) 1 has given a period of peace between these two actors. It is possible that this new situation has indirectly generated some changes in the epidemiological profiles of the population groups that inhabit the rural areas that were the scenario of the violence in the country 1. Perhaps, one way to approach this hypothesis, would be to assess the changes in the incidence of malaria in these areas 2.
Violence has caused changes in habitat, lifestyles, economic production, and the displacement of rural populations. All these factors have affected the social determinants of health of these populations 3. Therefore, as the social cause (violence) disappears, it would be expected that these communities could return to their previous habits, or modify them in a positive way, improving their health status by incorporating new living conditions. Especially considering that in the signed peace agreement between the Colombian state and FARC, it was established that the victims of the conflict should get repairations, economically and socially 4.
The Department of Nariño, and, in particular, its municipalities close to the Pacific coast, were one of the territories most affected by the scourge of violence between FARC and the Colombian state. These areas have been the most affected by the war. Therefore, the peace agreement would be expected to 5 be an advantage for the improvements in the well-being and health of their population 1.
However, in these rural territories, despite the signing of the peace agreement, violence has continued, maybe due to the social an economic factors characteristic of this area. Social factors such as: high incidence of poverty; illiteracy; discrimination against ethnic populations, such as indigenous and Afro descendants; the absence of the State, expressed in poor road and port infrastructure; education; and health, among others. Moreover, economical factors such as high rates of unemployment and informality; the existence of economies based on illegal mineral exploitations; coca crops, for the production of narcotics; and the prospecting of oil farms are highlighted 6.
From the epidemiological context, malaria is a multifactorial disease that affects populations in rural areas, where not only exposure to the causal agent determines its development, but also various factors of an environmental, social, and personal nature, interacting with each other, allowing the presence of this disease. The main factors that promote its transmission include: 1) displacement of susceptible or disease-carrying populations to endemic areas, due to armed conflict, or the expansion of the agricultural border used for the cultivation of illicit narcotic plants and illegal mining, especially in flood areas; 2) the underdevelopment of healthcare infrastructure and the low effectiveness and coverage of operational actions in the healthcare sector, and government agencies in general 7.
If you add different factors, such as: 1) the weak presence of the state; 2) that the inhabitants of this region, even if they have access to certain measures to prevent and treat the disease, they do not properly use of them; 3) the type of housing design and construction: mainly pile-dwelling, without any physical barriers that prevent the entry of the vector to the room area of the families; 4) its location, near mangroves swamp, jungle areas, pools for shrimp farming, areas of legal and illegal mining excavations and cultivation of coca, banana, corn, among others increase the risk of transmission, and, therefore, the disease is multiplied 7.
Specifically, from the 64 municipalities of Nariño, 44 had an BNI index higher than the department average, including nine of the ten municipalities that compose the PCN. Negatively highlighting Magüí Payán (96.6%), La Tola (91.46%9), and Roberto Payán (90.3%) with indicators above 90%, followed by Mosquera (84.32%), El Charco (81%), Santa Barbara (74.2%), Barbacoas (73.87%), Francisco Pizarro (71.31%), Olaya Herrera (65.56%); there is one that is not above the departmental average: Tumaco (48.7%) 7) (8) (9. See Figure 1.
Source: Author's design.
Figure 1 Geographical location of Nariño Department on the Colombian Pacific coast. From: Own design. Understanding the phenomenon of malaria as an exponent of the social, economic, and political factors on the Pacific coast of Nariño - Colombia
In addition, the report "Consequences of the Armed Conflict on Health in Colombia" highlights that the municipalities that were most impacted by the war have worse health indicators than those of the rest of the country. As a result, the ten municipalities of the PCN are the most health affected by diverse pathologies, being malaria the one with the greatest incidence in these territories 10. Malaria morbidity and mortality in Colombia had been showing a declining trend including the Nariño department, but now, it has varied towards a worrying increase, judging by statistics from the Public Health Surveillance (SIVIGILA). In the municipalities of the PCN, this increase could be associated with the resurgence of violence, and the constant presence of illegal mining and illicit coca crops, rather than the cycles associated with climatic conditions typical of this territory 11) (10.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A multi-group ecological 12 study was conducted, with a secondary source of information, on the frequency of malaria cases in the PCN population, and its relationship to the armed conflict in the region between 2003 and 2017.
The Public Health Surveillance (SIVIGILA) 11, and Individual Health Service Delivery Records (RIPS) of the Ministry of Health and Social Protection, MSPS 13, were used as sources of information for malaria cases, because they contain information of the morbidity of the country, and the information was analyzed through the Comprehensive Social Protection Information System (SISPRO) 14.
The data related to the armed conflict was obtained from the records of the Observatory of Memory and Colombian Conflict 15. he selected variables were: victims of anti-personnel mines and forced recruitment for the period of 2003 to 2017, as all these situations affect the population that live in the rural areas, and are coincident with the places where the anopheline vector circulates.
The analysis of the data was conducted in three stages: 1) a descriptive analysis, in which malaria cases were analyzed from an epidemiological approach (specifically, incidences and prevalence of the disease in the area of study); 2) the search for a link between the occurrence of malaria cases and the victims of anti-personnel mines and forced recruitment. For this stage, a simple linear regression model was developed, taking the cases of malaria as a dependent variable, and the victims of the armed conflict by anti-personnel mines and forced recruitment as an independent variable; 3) an explanation from the social context of the behavior of this pathology in the PCN was generated. For this purpose, a multiple linear regression model that analyzed the relationship that malaria can have with the social variables of the region and the victims of armed conflict was designed. These variables were constant during the study period, and interacted with the dynamics of the disease, conflict, and the general internal problem that still affects this region. We considered the Human Development Index (HDI), Basic Needs Index (NBI), and the statistics of winter-affected people as data sources for the social variables. All this information was obtained from the National Bureau of Statistics (DANE) 16.
The data was analyzed in a matrix, taking the geographical location of both malaria cases and victims of the armed conflict as a reference. he analysis of the information was performed with the statistical program Stata Version 14.
This study was submitted for evaluation to the Ethics Committee of the Jorge Tadeo Lozano University, being approved by Act 001 of February 6, 2019.
RESULTS
Descriptive Analysis of Malaria and the Social Conditions of the PCN Population
During the study period, the frequency of the disease had a seasonal behavior (R2 x 0.5193), having its highest peaks in 2007, 2016, and 2017, as presented in Table 1.
Table 1 Malaria Cases, Armed Conflict, and Social Variables, 2003-2017

Source: Colombian National Institute of Health, calculations were made by the authors
The municipalities of the PCN that recorded the most cases of Malaria during the 2003-07 period were the municipalities of Tumaco, Olaya Herrera, and Roberto Payán. For the year 2017 (see Figure 2), these municipalities were listed as the ones with the most transporting cases of Malaria to the national notification system, only surpassed by the municipality of Quibdó (Chocó Department).

Source: Colombian National Institute of Health (NIH) - Sivigila.
Figure 2 Accumulated malaria cases in the Pacific coast municipality of the Department of Nariño, 2003-17
The geographical location of the PCN gives this region a large volume of rainfall for most of the year, resulting in a considerable number of people affected by winter, trend that was not very variable (R2=0.59). The natural phenomenon produces slurry water, an ideal place for the location of anopheles hatcheries. As a result, the population is affected, because they do not have any physical barrier of protection against the vector in these rural areas. It leads to the confluence of the eco characteristics that enhance the likelihood of the malaria disease.
To evaluate the social aspects, the Human Development Index (HDI) was used, an arithmetic average of the standardized indices of each of the three dimensions that assessed such as health, education, and standard of living. See Figure 3.
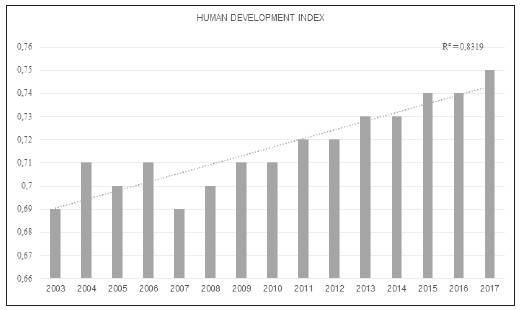
Source: Dane 2003-17.
Figure 3 Human Development Index for 2003-17 in the Pacific coast of the Nariño Department.
The health dimension is evaluated according to life expectancy at birth; education is measured by the average school years of adults aged 25 and over, and by the expected school-age years of school-age children; the standard of living is measured according to the unsatisfied basic needs index.
Thus, in the social sphere, a slightly incremental trend in HDI was evident (R2=0.8319), indicating that, despite adverse situations, life expectancy of its inhabitants has increased.
On the other hand, there has been a decline in the Basic Needs Index for the PCN, situation that indicates that the most critical deficiencies of the inhabitants of this region have had some improvement in housing, health services, basic education, and minimum income, which correspond to the indicators related to people's basic needs. See Figure 4.
Malaria's Relationship with the Armed Conflict
The behavior of the armed conflict in the region of PCN at the time of this study presented a stable trend (R2 = 0.0044). During 2011 and 2012, most anti-personnel mines victims also reported forced recruitment. All these factors affected this rural population, and made them more likely to be sick with malaria.
In a simple linear regression model, taking malaria cases as a dependent variable and victims of the armed conflict as an independent variable (result of the aggregate of the two variables: anti-personnel mines and forced recruitment), it was found that the armed conflict would only be related to 1.04% of malaria cases. However, it is important to notice that the relationship between cases of malaria and armed conflict is inversely proportional, suggesting that greater conflict presents less malaria. See Table 2.
This finding could suggest that in the areas and regions where armed conflict is accentuated and have suffered abandonment from institutions of the Colombian government, there is a masking of malaria cases. This means that the decrease in cases is not real, but the violence difficults the diagnosis, report, and treatment of this disease; for example, the armed conflict become a barrier to access to healthcare services.
Explanation of the relationship between malaria, armed conflict, and social variables
To explain the behavior of malaria in the PCN, a multiple regression model was performed, including social and environmental variables, in order to contextualize the dynamics of the disease in this population group. See Table 3.
Table 3 Multiple regression to analyze relationship between malaria, armed conflict, and social variables

Source: by the authors.
The HDI, BNI, victims of the armed conflict, and those affected by winter, are variables present in the PCN. The interaction between these variables could explain 68.6% of malaria cases, being the model statistically significant (p= 0.013). See Table 3.
From the independent variables (HDI, BNI, victims of armed conflict, and those affected by winter) only the victims of the armed conflict variable is significantly related to malaria cases (p= 0.03), being this an inversely proportional ratio. This finding matched with the one found when the aforementioned simple linear regression model was performed.
DISCUSSION
Situations of war or conflict have shown to increase the incidence of some communicable diseases. Malaria presents a close relationship with the isolation suffered by the population that have been a victim to war, as well as the cessation of activities in the environmental control, healthcare, sanitation, and other programs aimed at controling this disease 3) (10.
In periods of armed conflict, health services aimed at caring for the general population and malaria sufferers are affected, because of the reduction of healthcare personnel, the bad conservation of vaccines and medicines, and the inability to do preventive activities in conflict territories due to violations to the medical mission. All these factors, combined with the low or absence of the Colombian government in the PCN, and the displacement of the population to areas where is easy to find the malaria vector, possibly affected the population to get them sick 3) (10) (17.
In contrast, this study found an inversely proportional relationship between the frequency of malaria cases and armed conflict, a situation that seemed to show that the presence of conflict would "control" malaria. Perhaps, this finding is only masking the reality of the PCN, because the situation of the armed conflict in this region maybe hinders the access to malaria prevention programs and healthcare services in general, slowing down, or even preventing, timely diagnosis, treatment, and reporting to public health systems of said cases. All these aspects could lead to a decrease in malaria cases in times of armed conflict and an increase of these cases in the absence of it.
The transmission of malaria in the Nariño Department of Colombia focuses on the rural areas of the municipalities of the department, such as: Barbacoas, El Charco, Francisco Pizarro, La Tola, Magüi Payan, Mosquera, Olaya Herrera, Roberto Payán, Santa Bárbara, and Tumaco. Previous studies have found the same situation in this Colombian region 18) (19) (11. Since historical times, armed groups have made presence outside the law in Colombia, and this scenario of violence, poverty, where there are killings of social leaders, where there is a presence of illicit crops, illegal mining, is the ideal ecological and social scenario for the presence of the malaria disease 5) (15) (20.
CONCLUSIONS
The epidemiological behavior of malaria in the PCN has an inversely proportional relationship with the armed conflict that has occurred in this Colombian region. This does not mean that war is a protective factor against the disease, but perhaps masks the incidence of cases by making it difficult to report in a timely manner.
Likewise, these findings make it possible to conclude that, in spaces such as the PCN, it is essential to think of social solutions and clinical interventions that transform the living conditions of these communities, which have always been forgotten, marginalized, discriminated against by Colombian society and the government. It is also necessary that the young population that was the most affected by malaria in the PCN, and decide to remain in the area, can be provided with strategies that reorient their life project. This is why the policies for replacing illegal crops, the technology of agricultural production, the improvement of housing, access to education, the strengthening of the local healthcare system, and the construction of roads that allow merchants to take their agricultural products to outside markets are part of the peace agreement signed between the Colombian government and FARC.
Therefore, the peace consolidation, understood as social development, well-being, and quality of life for all the inhabitants of these rural territories, becomes the main factor that can reduce the presence of malaria.

















