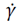1. INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, the use of mineral additions is paramount in reducing energy consumption, emissions of polluting gases and the production costs of both cement and concrete. Nonetheless, it can not be forgotten that all additions will have an impact on the performance of both fresh and hardened cement mixtures. Depending on characteristics such as shape and size of particles, reactivity and percentage of substitution of the cement, the rheological properties (yield stress and viscosity), the mechanical strength (at initial and final ages) and the self-compacting capacity of the mixtures will be modified.
1.1. Rheology
The rheology of concrete is an issue of interest both for its influence on the placement of the material as well as for the mechanical response when it reaches the hardened state [1]. The yield stress and the plastic viscosity are two of the parameters that define the rheology of a mixture, where a low yield stress and a moderate viscosity lead to consolidation and increase fluidity without segregation between the cementing material and the aggregates [2].
In recent years there has been growing interest in research on the issue of industrial waste as mineral additions to cement and concrete, such is the case of Fly Ash (FA) and Silica Fume (SF) [3,4].
Some researchers have determined that the inclusion of FA in the cement pastes reduces both yield stress and viscosity, due to its spherical shape and its wide particle size distribution that promotes the fluidity of the mixture; thus functioning as “filling” and increasing the packing factor [4,5]. Regarding compressive strength, FA reduces it at early ages (7-14 days), due to its low reactivity with respect to other additions [4,6].
In the case of SF, due to its purity and its average size of up to four times less than that of the cement, it offers high reactivity, accelerates the hardening of the mixture and at the moment of flow increases the particle to particle interaction; thus generating a high friction and restricting workability [7]. In the same sense, as asserted by Park and col. [3], SF reactivity is also reflected in the final resistance, reaching resistance in some cases over those achieved with pure OPC [8].
In simple additons of OPC plus FA, as stated by Lee and col. [9], the ash itself promotes fluidity by its spherical shape as it sets in the flocs in formation of the OPC and water, but before high replacement percentages, due to its low reactivity derived from both its size and composition; good resistance are not reached at early ages of hardening, this condition is compensated with the addition of SF that in the early ages of the mixture improves the workability and later, compensates for the compressive strength deficiencies with its ability to improve the mechanical strength due to its high reactivity [8], this is the reason why it is sometimes more convenient to think about composite additions rather than simple ones [3,10].
The rheological model used in this study is the Bingham equation (Equation 1), which is widely used for cement-based mixtures, because it describes its behaviour as a viscoplastic fluid in which there is a conversely stress (τ 0 ) and the rest of the behaviour is similar to a Newtonian fluid [11,12], a necessary condition to be able to apply this model is that the values of shear rate ( 𝛾 ) must be bellow 300 s-1 , this is because research has shown that for higher values the system is distorted and the stress value (𝜏) increases in an uncontrolled manner [3,13].
Where:
1.2. Self-compacting
Self-compacting mixtures can be defined as those that can easily flow by their own weight and self-consolidate without the help of a mechanical vibration system, reaching high deformation capacity and volumetric stability as well [14]. Self-compacting concrete has high fluidity and its implementation allows placement in complicated forms without vibration or without segregation [15]. For self-compacting concrete, insufficient compaction causes the increase of air bubbles which leads to a reduction in concrete strength and durability [16]. Self-compacting cements have provided a promising vision of the concrete industry with respect to environmental impact and cost reduction; however, the use of cement mixtures with mineral mixtures has not developed sufficient applications for the production of these cements [17].
This is the case of Fly Ash (FA) and Silica Fume (SF) [2-4], they have found that these additions affect significantly both the performance and placement of self-compacting cement mixtures.
1.3. Influence of mineral additions
1.3.1. Influence of particle size
Generally, with a smaller particle size of the addition, the packing factor increased by reducing the vacuum ratios per unit volume. As the packing factor increases, fluidity is promoted, because the deformation capacity increases due to the compactness of the mixture, this condition has a certain range of efficiency since the greater number of particles per unit volumen also increase the particle to particle interaction, which at the moment of flow increases the friction among particles, which restricts the movement of the mixture; for this reason the particle size distribution should be as wide as possible so that finer materials improve both the lubrication and packing of the mixture while thicker materials reduce the particle to particle interaction [13,18,7].
1.3.2. Influence of flocculant capacity
The flocculation processes of the cement-based mixtures obey a Brownian movement due to their particle size, variety of electric charges, the flocculation capacity itself and the hydration process. The additions of SF and FA affect the flocculation processes in different ways, with respect to the presence of SF, its great purity and fine size makes it a quite reactive addition, which permits the formation of flocs with cement, accelerating hydration and reducing the workability of the mixture. With regard to FA, its low reactivity interrupts the flocs in formation and its wide particle size distribution reduces the particle to particle interaction; moreover, due to its low reactivity at early ages, the focculation energies of the cement are reduced, inducing a plasticizing effect, this phenomenon is reflected in the self-compacting capacity since there is a direct relationship between low fluidity effort and viscosity and high fluidity as well [13,4,5].
1.3.3. Influence on compressive strength
Mohamed in 2011 reported that the higher the FA percentage the higher the compressive strength values up to 30%; instead for SF the highest values were found only at 15% of addition; and for ternary mixtures the highest compressive strength values were found with 10% of FA and 10% of SF [19]. Turk in 2012 found that the compressive stress improved with the presence of FA in binary mixtures and with all the ternary mixtures of FA and SF [18]. Jadhav and Chavarekar in 2013 found that mixtures of cement with FA and microsilica increased by 12.9% the compression effort compared to the control sample for 2.5% of each of the additions [20]. Raharjo and col., in 2013 reported a statistical equation to determine the compression strength of cement mixtures with FA, SF and steel slag; however, they warned that the accuracy of the equation depends on the ambient temperature, air humidity, measurement materials and others [21,29].
1.3.4. Influence on self-compacting
To measure the self-compacting, the evacuation time measurements of samples in V funnel are taken [14], the smaller the evacuation times of the cone, the more self-compacting the mixture will be [22,23]. Gesoğlu and col., in 2009, manufactured cement mixtures with SF, FA and steel slag, finding that all samples were 5 s below the flow time under the upper limit of EFNARC [17]. Siddique in 2011 mixed self-compacting cement with FA type F and determined a time between 4 and 10 s for the tests in the V funnel [24]. Turk in 2012 obtained a reduction of time in the tests in the V-funnel with the increase in the content of SF, and an increase in the time with the increase of FA in the content; it also determined that ternary mixtures increase more viscosity compared to binary mixtures [18]. Contrary to this, Kennouche and collaborators in 2013 mixed 15% of FA with two types of cement, finding high fluidity and absence of segregation in all tests [26]. All of the above shows that there are still contradictions in the results and that this is still an issue under discussion [30-33].
In conclusion, a more in depth-study of the influence of mineral addition such as FA and SF is necessary to find the conditions where self-compacting, rheology and compressive strength of a mixture are simultaneously improved, seeking to establish correlations between these three performance parameters in portland cement pastes in binary (OPC + SF and OPC + FA) and ternary (OPC + SF + FA) mixtures [28,30-33].
2. EXPERIMENTAL PHASE
All the mixtures studied were manufactured with the following raw materials: Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC), manufactured by a Colombian Company; Fly Ash (FA) type F (ASTM C 618 - 99), obtained from a Colombian garment factory; Silica Fume (SF) (ASTM 1240) which was imported. For the characterization of the components, the chemical composition was determined by means of X-ray fluorescence (XRF) in PANalytical AXIOS equipment; the particle size distribution (PSD) using laser diffraction in a Mastersizer 3000 from Malvern Instruments and the morphology was evaluated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) in an EVO MA10, by Carl Zeiss. The rheological evaluation was carried out in a rotational Kinexus Pro rheometer from Malvern Instruments. The tests of compressive strength were carried out complying with norms ASTM C-109 and ASTM C-305-11, the materials for the manufacture and failure of cubes of cement paste were mixed to 7 and 28 days of curing with a water/cementing material ratio (w/cm) of 0.5 constant for all samples. As a self-compacting measure of the mixtures, the emptying time in the V funnel was determined, according to the recommendations recorded in EFNARC [14,27,28].
2.1. Characterization of materials
The results obtained by XRF of both cement and mineral additions are provided in Table 1. The OPC has low contents of limestone, this due to both low losses on ignition and high content of CaO. The FA is an ash class F, because the sum of its main oxides (SiO2 + Al2O3 + Fe2O3) is greater than 75% [27]. Regarding SF, a high purity material with high SiO2 content and low contents of other oxides is observed [28].
The result of the PSD is featured in Fig. 1, where it can be seen that the OPC is the finest material and the FA the thickest one in comparison with other materials;
Table 2 shows the passing size (in microns) that has a certain amount of material: d10, d50 and d90 for 10%, 50% and 90%, respectively. In this table it is confirmed that the fine material is the OPC and the thickest one is the FA.
The micrographs for each component of the manufactured mixtures are displayed in Figs 2, 3 and 4. Fig. 2 shows a wide distribution of particle size, in addition that each particle in general has irregular shapes and ridges, which agrees with what is expected from dry cement without hydration. I
The red arrows show the spherical shapes of the FA of various sizes, some irregular shapes indicated by the blue arrows obey to the unburned ones, which are of the order of 4.37%, measured on the FA by the ASTM D3174 standard. Figure 4 shows SF particles of different sizes and many on the nanometric scale with spherical shapes, this shows that a good part of what is being measured in PSD are agglomerations of SF.
2.1. Preparation of mixtures
15 mixtures and a control mixture, composed of cement and water only, were prepared. The mixtures manufactured with simple additions (OPC + one addition) and composite (OPC + two additions) in certain percentages are shown in Table 3; the name of the simple addition has the following nomenclature: the letter or letters of the material used and on its right side the amount present in percentages (OPC = C).
The red arrows show the spherical shapes of the FA of various sizes, some irregular shapes indicated by the blue arrows obey to the unburned ones, which are of the order of 4.37%, measured on the FA by the ASTM D3174 standard. Figure 4 shows SF particles of different sizes and many on the nanometric scale with spherical shapes, this shows that a good part of what is being measured in PSD are agglomerations of SF.
2.2. Preparation of the mixtures for the rheological analysis
The pastes were prepared in a conventional agitator for 1.5 min at 700 rpm before they were taken to the rheometer. The scheme of the rheological test can be seen in Fig. 5. The mixtures were subjected to a pre-shear for 1 minute at a shear rate of 300 s-1 and afterwards were left to rest for 1 minute before starting the rheological measurements.
3. RESULTS
3.1. Yield stress
Fig. 6 shows that for simple additions, yield stress values are lower for samples added with FA than for samples with SF; thus making clear that FA contributes more to the workability of the mixture, with a decrease in the fluidity stress up to 20% on average with respect to the addition of SF. Both for the additions of FA as well as for SF as their amount increases in the mixtures the yield stress increases and only the samples with FA additions of 10% and 20% show values below the control sample. For composite additions it can be noticed that three mixtures are below the value of the control sample, with 20% and 30 % of FA, which corroborates that the presence of FA decreases yield stress in some cases.
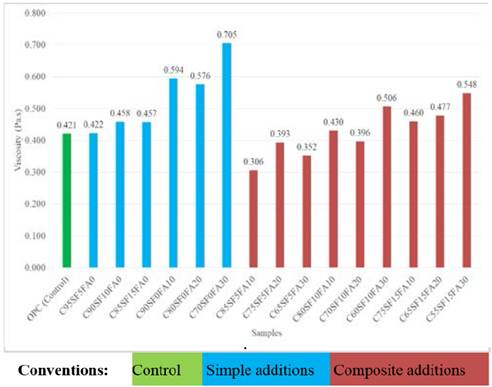
Regarding the composite additions, in Fig. 7 the influence of the addition of SF in a mixture with 10% constant FA is observed; a direct proportional relation between the yield stress with the presence of SF is determined, this behaviour can be due to the reactivity and fineness of the material that accelerates the formation of flocs; the beginning of a flow with individual particles demands higher energy compared to the start of flow for flocs, which have sizes larger than the particles. It is noteworthy that with only 10% of FA, in the combined or ternary samples, it is possible to decrease the yield stress for all the evaluated SF percentages, making the yield stress with 5 and 10% of SF very close to the one found for the control sample.
Source: the authors
Figure 7 Trend of yield stress for mixtures with 0 to 15% SF and 10% constant FA.
Fig. 8 displays the positive influence on FA variation from 0 to 30% in a mixture with 15% of SF, which shows an inverse relationship between the addition of FA with the yield stress, which is due to the fact that the particles of FA of spherical shape set in among the flocs in formation of the cement and perform a plasticizing work which reduces such yield stress.
3.2. Viscosity
Fig. 9 shows the viscosity value (calculated with the Binghan model) of the analyzed mixtures. In general, it can be noticed that the viscosity of the mixtures increases for all simple additions; however, there is a more pronounced viscosity increase for additions with FA and lower for additions of SF; probably this is because the particle size of the FA is more than 5 times the size of the cement, while the size of the SF is of the order of the size of the OPC and smaller. Regarding the composite additions it can be seen that there are some mixtures with lower viscosity values with respect to the control sample; such mixtures have additions in few proportions, this behaviour is due to the phenomena of rolling and lubrication by small particles and packing phenomena, up to a certain number of particles where energy is spent in moving all the particles present. This again corroborates a complementary effect between these two mineral additions.
3.3. Compressive strength
Fig. 10 summarizes the results obtained for the compressive strength of the mixtures, at 7 and 28 days of curing. Carrying out an analysis first for 7 days of curing, it can be noticed that only greater strength than that of control sample are obtained with simple additions of SF, as the amount of FA increases the compressive strength in relation to the control sample decreases; this evidences the reactive nature of each of these mineral additions. For all composite mixtures the compressive strength decreases as the amount of FA additions increases. For 28 days of curing no mixture, either simple or composite, clearly exceeds the compressive strength of the control sample. Nonetheless, many of the mixtures with percentages of substitution of cement in high percentages have mechanical resistance values similar to control sample, as is the case of the mortars with all SF percentages, with 5% SF + 20% FA; with 10% SF + 10% FA and with 15% SF + 10% FA.
3.4. Self-compacting
Fig. 11 displays the evaluation time for the V -funnel test for each prepared mixture. Regarding simple additions, a direct relationship appears for SF, since as the quantity increases, so does the evaluation time. Conversely, for mixtures with FA the relation is inverse, the evaluation time decreases as its concentration increases. This is due to the fact that SF is quite reactive and it reduces the workability of the mixture, while the FA being less reactive interrupts the formation of flocs serving a plasticizing function. No ternary mixture showed a significantly shorter evacuation time than that of the evacuation time of the control mixture; thus the reactivity of the SF is possibly more decisive than the plasticizing that the FA delivers to the mixture.
3.5. Correlations
In order to perform the correlations among variables, the areas where the additions have desirable behaviours were determined by graphical analysis: low yield stress, high compressive strength, low viscosity and short evacuation time (self-compacting test); the objective was to establish areas in which these conditions were met thanks to the presence of mineral additions, that is why these graphs were made:
Compressive strength vs. yield stress.
Compressive strength vs. viscosity.
Yield stress vs. self-compacting cone
Self-compacting cone vs. viscosity
Compressive strength vs. self-compacting cone.
Each of the graphs shows a median value of the mixtures in a red line and a blue line, for the two properties plotted, and an area of optimal values in green boxes for the mixture that meets the ideal properties simultaneously thanks to the presence of mineral additions.
3.5.1. Compressive strength vs. Yield stress
In Fig. 12 the red line defines the mean value for the compressive strength at 49.51 MPa and the blue line defines the mean value for the yield stress at 32.21 Pa. The green box shows the mixture having a compressive strength avobe average and the yield stress below the mean value. For the present case a single mixture meets the optimal conditions: 10% SF and 20% FA.
3.5.2. Compressive strength vs. viscosity
In Fig. 13 the red line defines the mean for the compressive strength at 49.51 MPa and the blue line defines the mean value for the viscosity at 0.4575 Pa·s. The green boxes show six mixtures that meet the ideal conditions; for this case, all simple mixtures with SF, and composite mixtures with 5% SF + 20% FA; 10% SF with 10% and 20% FA.
3.5.3. Yield stress vs. Self-compacting cone
In Fig. 14 the blue line is the median for the yield stress at 32.21 Pa and the red line defines the median for the self-compacting V funnel test at 5.77 s. The green boxes show 4 mixtures with ideal conditions: two mixtures with simple additions: 10% and 20% FA; and two mixtures with composite additions: 5% SF + 30% FA and 10% SF and 20% FA.
3.5.4 Self-compacting cone vs. viscosity.
In Fig. 15 the red line defines the median for the self-compacting V funnel test at 5.77 s and the blue line defines the mean for the viscosity at 0.4575 Pa∙s. The green boxes display 3 compound mixtures with ideal conditions: 5% SF + 30% FA and 10% SF with 10% and 20% FA.
3.5.5. Compressive strength vs. Self-compacting cone
In Fig. 16 the blue line defines the median for the compressive strength at 49.51 MPa and the red lines defines the median for the self-compacting V funnel test at 5.77 s. The green boxes feature 2 compound mixtures with ideal conditions: 10% SF with 10% and 20% FA.
4. FINAL DISCUSSION
Throughout the research it has been possible to determine that during the plastic state of the mixture not only the yield stress, but also the viscosity and the evacuation time increase.
For instance, as the SF increases from 5% to 10% the yield stress increases by about 20%, the viscosity by 10% and the evacuation time by 17%; this due to its particle size and its reactivity that allows it to act as nucleation centers and promotes particle to particle interaction to increase friction among them as well as the formation of flocs. Otherwise happens with the FA, which, due to its larger particle size less reactivity and spherical shape interrupts the formation of flocs and acts as plasticizer or lubricant and also decreases the compressive strength. It can also be established that by mixing these two additions their effects combine and interact, allowing to look for a mixture that meets the parameters of low yield stress, high compressive strength, low viscosity and short evacuation time (self-compacting).
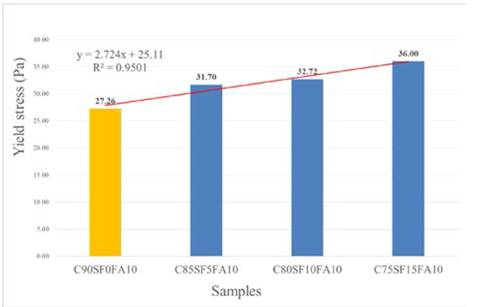
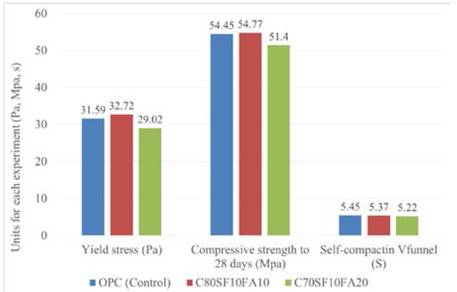
When analyzing the results featured in Figs. 12 to 16, it can be asserted that the composite additions are more efficient than the simple additions, because in the excecuted tests the samples C80SF10FA10 and C70SF10FA20 are the ones that presented the best behaviour; these data are summarized in Table 4 and Fig. 17.
Source: the authors
Figure 17 Comparison between control sample and samples selected as optimal in the correlations.
In agreement with several researchers, in the correlation graphs it is observed how when combining the additions, the influence of one addition with the other is compensated, that is, the reductions in compressive strength that could be had with the presence of FA regulates with the reactivity of the SF and on the other hand, the loss of fluidity due to the presence of SF is regulated by the plasticizing effect of the FA [3][4][2][28].
In Table 4 and Fig. 17 it can be seen that the values obtained for these three mixtures are very similar; nonetheless, the recommended mixture is C70SF10FA20; since, although some compressive strength is sacrificed, it improves both in rheology and self-compacting and a very significant aspect is that the percentage of cement replacement is maximized, which, as already mentioned, has paramount effects on environmental as well as economic aspects.
5. CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results found throughout this research it can be concluded that:
Both SF and FA have opposite effects on yield stress, viscosity, evacuation times (self-compacting capacity) and compressive strength. This is due to its difference in particle size, reactivity and chemical composition as well.
The SF in the mixture in fresh state promotes more particle to particle interaction and acts as a nucleation center, increasing the friction among them and facilitating the formation of flocs and this results in an increase in yield stress, viscosity and evacuation time. In the mixtures in hardened state and thanks to its chemical composition and pozzolanic activity the compressive strength is increased.
In the mixtures in fresh state, the FA, thanks to its larger particle size and spherical shape, interrups the formation of flocs and acts as a plasticizer or lubricant. In the mixtures in the hardened state the compressive strength decreases due to its lower reactivity and pozzolanic activity as well.
By mixing these two additions their effects combine and interact allowing finding dosages that are efficient in all measured variables, that is, with good peformance in both fresh and hardened state.
In this study the samples that comply with the proposed variables are C80SF10FA10 and C70SF10FA20, nonetheless, the chosen one is C70SF10FA20 since it allows maximizing the percentage of replaced cement with the corresponding additional benefits, in terms of environmental and economic aspects.