INTRODUCTION
Lemon balm (Melissa officinalis L) is a medicinal plant belonging to the Lamiaceae family and one of the main aromatic species traded worldwide. It contains secondary metabolites such as unsaturated sterols, triterpenes, phenylpropanoids, catechins, tannins, polyphenols, flavonoids, glycosides, and alkaloids in its essential oil (Moradkhani et al., 2010; Vélez et al., 2018). Recent studies have demonstrated that lemon balm extract exhibits antitumor properties (Jahanban-Esfahlan et al., 2017) and antimicrobial activity against human disease-causing microorganisms such as Escherichia coli and Listeria monocytogenes (Vélez et al., 2018; Carvalho et al., 2023). Due to these properties, it is considered a promising crop globally, especially in developing countries. However, it is highly affected by water stress, which leads to reduced yield and a decrease in essential oil production (Ahmadi et al., 2019; Mohasseli et al., 2020).
The use of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) offers an alternative to excessive chemical fertilizer usage, as it enhances the quality and yield of crops and horticultural products. For instance, PGPR has been shown to improve the drought tolerance of medicinal plants (Eshaghi-Gorgi et al., 2022) and restore plant growth under biotic and abiotic stress by reducing ethylene levels, increasing auxin biosynthesis, and promoting nitrogen fixation in the roots (Glick et al., 2007; Zahir et al., 2008). The concept of induced systemic tolerance has been proposed, referring to the physical and chemical changes induced by microorganisms in plants that result in enhanced tolerance to abiotic stress (Yang et al., 2009).
Holbrook (2015) described how drought stress reduces water content in plants, causing loss of turgor and stomatal closure, resulting in decreased growth. Additionally, excessive reactive oxygen species are generated, causing lipid peroxidation of the cell membrane and damage to enzymes, proteins, and nucleic acids (Ahmadi et al., 2019). Plants respond to drought stress by developing various strategies, including maintaining high tissue water potential, growing a deeper root system to optimize water absorption, increasing cell wall flexibility, and osmotic adjustment (Tardieu et al., 2017; Polle et al., 2019; Leuschner et al., 2019). Abiotic stress has been found to increase the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites in plants, with recent studies showing an increase in the production and accumulation of phenolic compounds, anthocyanins, and flavonoids in lettuce and pea plants subjected to water stress (Kumar & Sharma, 2018; Xu et al., 2019; Sharma et al., 2022).
PGPR-induced tolerance to water stress has been reported in several plant species. The mechanisms of drought resistance in plants induced by rhizobacteria involve several physiological and biochemical changes, such as alterations in plant hormone levels, enhanced antioxidant defense, and metabolic adjustments involving the accumulation of organic solutes such as sugars, amino acids, polyamines, and volatile organic compounds. These mechanisms have been observed as action strategies in PGPR-mediated tolerance to salinity and drought (Kaushal & Wani, 2016).
Among the most widely used PGPR genera around the world is Bacillus, known for its ability to form endospores, providing resistance to adverse environmental conditions such as water stress; in addition, this genus has great potential to stimulate plant growth through the synthesis of plant hormones such as indoleacetic acid and gibberellins, the solubilization of phosphates and the production of different metabolites with antagonistic activity, such as lipopeptides including phengyzine and surfactin, which stimulate induced systemic resistance (Xie et al., 2017).
Based on the above, this study is aimed to determine the effect of PGPR on physiological variables of growth, stomatal conductance (Gs), and efficiency of the photosystem PSII in Melissa officinalis plants subjected to water stress, elucidating its potential use as biofertilizers.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Experiment Location
The experiment was conducted in the greenhouse of the Biological Control Laboratory at the Pedagogical and Technological University of Colombia, located at 5°33'15'' N and 73°21'30'' W, with an average temperature of 12°C.
Plant Material
Lemon balm seeds were disinfected in a 70% ethanol solution for one minute. Germination was carried out in peat moss, and the seedlings were irrigated with distilled water until they were transplanted into 1-liter pots 60 days after sowing. One lemon balm seedling was planted per pot and watered to field capacity for 85 days. Afterward, the treatments with plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR), previously isolated and cultivated in a Nutrient Agar medium, were applied.
Experimental design. The PGPR were applied directly to the plant roots at concentrations of 1x106 CFU. In a completely randomized design with four replicates per treatment and the following six treatments:
Treatment 1: Bacillus cereus without water stress (BCW).
Treatment 2: Bacillus cereus with water stress (BCD).
Treatment 3: Bacillus amyloliquefaciens without water stress (BAW).
Treatment 4: Bacillus amyloliquefaciens with water stress (BAD).
Treatment 5: Without bacterial inoculation and without water stress (absolute control) - SBW.
Treatment 6: Without bacterial inoculation and with water stress (relative control) - SBD.
Application of Water Stress
After applying plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR), the plants were subjected to drought stress at two levels: field capacity and 50% of field capacity, following the methodology of Eshaghi-Gorgi et al. (2022). The pots were weighed daily to measure water lost through leaching and evapotranspiration, and this water was replaced accordingly. The plants were fertilized once with Nutriponic® at a dose of 5 cc L⁻¹. The water stress treatments lasted for 90 days, after which the plants were harvested.
Measurement of Growth and Stress Parameters
At the end of the experiment, growth variables such as plant height, root length (cm), and fresh and dry weights of shoots and roots were measured according to the methodology of Ghorbani et al. (2011). Physiological variables were also assessed. Chlorophyll content was measured using a SPAD-502 Plus chlorophyll meter (SPAD units), a portable, non-destructive device for determining leaf chlorophyll content. Stomatal conductance (gs) was measured using a Decagon Devices SC-1 porometer. The equipment was calibrated before use, and one leaf per plant was selected and placed in the porometer, ensuring a proper seal to avoid leaks.
Fluorescence Measurements
Chlorophyll fluorescence is a valuable tool for assessing the physiological status of plants and determining the impact of stress on their photosynthetic apparatus (Jiménez-Suancha et al., 2015). Fluorescence measurements were taken from the upper third of the leaves between 10:00 and 11:00 AM using a JUNIOR-PAM fluorometer (WALZ Photosynthesis Instruments, Germany). Maximum photochemical efficiency (Fv/Fm) was calculated as the ratio of variable fluorescence (Fv) to maximum fluorescence (Fm), following Equation 1 (Baker, 2008). Additionally, the quantum yield of photochemical energy conversion (Y(II) = (Fm’ - Fs’)/Fm’), regulated quantum yield of non-photochemical energy dissipation (Y(NPQ) = 1 - (Y(II) + Y(NO))), and non-regulated quantum yield of non-photochemical energy dissipation (Y(NO) = 1 / (NPQ + 1 + qL(Fm/Fo - 1))) were calculated as stress indicators.
Statistical Analyses
The data were analyzed using R software version 4.3.0. A Shapiro-Wilk normality test and Bartlett’s test for homogeneity of variances were performed. Following these tests, an Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) was conducted, and a Tukey test was applied when significance was observed (p < 0.05).
RESULTS AND DISCUSION
Plant Growth. "The height of lemon balm plants did not differ significantly between the control treatment and the treatment that was subjected to water stress (50% field capacity). This contrasts with the findings of Eshaghi-Gorgi et al. (2022), who reported a 28.9% reduction in height in lemon balm plants subjected to water stress. However, the present study found higher average numbers of leaves than those reported by Eshaghi-Gorgi et al. (2022), who found a 24.1% reduction in the number of leaves under water stress compared to non-stressed plants."
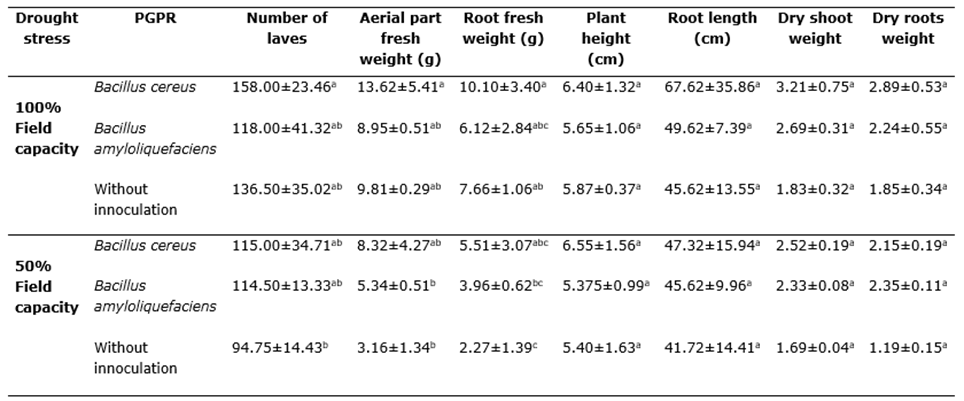
"Drought stress (50% field capacity) reduced the number of leaves (P<0.05), fresh shoot weight, and fresh root weight in plants without inoculation of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) (Table 1). In plants not subjected to water stress, the use of Bacillus cereus significantly increased the number of leaves, fresh root weight, and shoot weight compared to plants without PGPR inoculation and those treated with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (ANOVA, P<0.05). Although there was no statistically significant difference in root length between the treatments (t-test, P ≥ 0.05), plants treated with Bacillus cereus showed the highest value. Similarly, plant height was not affected by any of the analyzed treatments, but its values were higher in plants with Bacillus cereus inoculation.
Table 1 Effect of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) on Physiological Growth Parameters in Lemon Balm Plants Subjected to Drought Stress.
The values represent the mean of 4 replicates ± SD. Values with different letters indicate a significant difference (Tukey, P<0.05).
The application of PGPR restored both shoot and root fresh weight compared to non-inoculated and water-stressed plants (Table 1). In plants not subjected to water stress, the shoot fresh weight increased by 28% with the application of B. cereus and 34.3% with B. amyloliquefaciens, compared to non-inoculated plants. The number of leaves showed a significant decrease (P<0.05) in water-stressed plants without PGPR application, while water-stressed plants with PGPR inoculation did not show a significant difference compared to non-water-stressed plants (Table 1).
The inoculation of B. cereus significantly increased root fresh weight, shoot fresh weight, and the number of leaves in plants grown at field capacity (Table 1). Plants treated with B. cereus also showed higher values for these variables than plants treated with B. amyloliquefaciens or without PGPR inoculation. In plants subjected to water stress, B. cereus and B. amyloliquefaciens both had a positive effect on root fresh weight, shoot fresh weight, and the number of leaves (Table 1). Root characteristics are important indicators of plant adaptation to environmental conditions, including water stress. However, research on root characteristics is lacking for many cultivated species (Bardgett et al., 2014).
The decrease in growth observed in lemon balm under drought stress can be explained by the alteration of several physiological aspects of the plant under water stress conditions, such as reduced water potential, water uptake, and stomatal closure (Blankenship, 2015). All these changes represent the plant's attempt to cope with the unfavorable period of low water availability (Kapoor et al., 2020). Medicinal plants have been reported to show growth and dry weight reductions similar to those found in this study (Saheri et al., 2020; Abbaszadeh et al., 2020; Eshaghi-Gorgi et al., 2022).
The decrease in the number of leaves is a common physiological response of plants to water stress conditions (Bhargavi et al., 2017). Leaves are the primary organs for photosynthesis, and under water scarcity, the production of various photosynthetic products, including triose phosphates, sugars, and amino acids, decreases. This reduction in photosynthetic output can ultimately lead to the shedding of leaves to conserve resources.
Additionally, reducing leaf area is a strategy to mitigate the impact of drought, as a decrease in leaf area results in less water loss through transpiration. This reduction in leaf area is due to cell expansion inhibition, which is a consequence of cellular turgor loss (Bangar et al., 2019).
The reduction in the water stress effect on plants due to PGPR application can be explained by various physiological responses at the cellular level, such as increased activity of ACC (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid) deaminase enzymes, leading to a decrease in ethylene levels in the plant (Glick et al., 2007). Specifically, the Bacillus genus has been used for its ability to form endospores, providing tolerance to adverse conditions such as water stress. Its application is associated with the synthesis of plant hormones and the production of metabolites such as lipopeptides, including fengycin and surfactin, which stimulate plant resistance to both biotic and abiotic stresses (Xie et al., 2017).
Similar results to those found in this study have been reported in other works (Ganjeali et al., 2018; Mutumbam et al., 2018; Zakerian et al., 2020; Eshaghi-Gorgi et al., 2022; Salazar-Garcia et al., 2022). These studies have indicated that inoculation with PGPR, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, or a combination of these, can improve the growth and biomass of medicinal plants subjected to water stress. For example, Zhang et al. (2019) reported that Glycyrrhiza uralensis subjected to drought stress and inoculated with Bacillus pumulis showed enhanced drought tolerance due to improved integrity of chloroplast and mitochondrial cellular structure, leading to increased chlorophyll content, more efficient photosynthetic rate, and better relative water content.
Various mechanisms of inducing drought and salinity stress tolerance in plants regulated by PGPR action have been reported, including increased production of plant hormones such as indoleacetic acid and gibberellins, accumulation of osmolytes such as proline and glycine, and accumulation of total soluble solids in plants (Etesami et al., 2018). All these physiological processes at the cellular and organ levels in plants inoculated with PGPR can explain the improvement in growth parameters of lemon balm subjected to water stress and inoculated with B. cereus and B. amyloliquefaciens in the present study.
Stomatal Conductance. Drought stress reduced stomatal conductance (gs) (Figure 1). The treatment that showed the greatest decrease in gs was the treatment without PGPR inoculation and with water stress (SBD), while the treatment with water stress but inoculated with B. amyloliquefaciens (BAD) exhibited stomatal opening behavior similar to the treatment without water stress and inoculated with B. cereus (BCW). The treatments with the highest average gs values were the treatments without water stress, inoculation (SBW), and without water stress but with inoculation of B. amyloliquefaciens (BAW). The application of B. amyloliquefaciens prevented stomatal closure in lemon balm plants subjected to water stress, explaining why the gs values were similar to those of plants at 100% of field capacity.
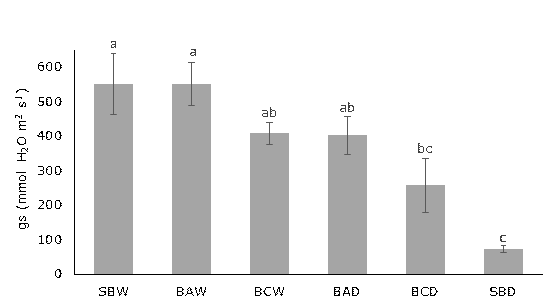
Figure 1 Stomatal conductance of M. officinalis under drought conditions and PGPR inoculation. Averages with different letters show statistically significant differences according to Tukey test (P≤ 0.05). Vertical bars on each average indicate standard error (n=4). Abbreviations of treatments explained in Materials and Methods.
Drought stress causes stomatal closure, reduced leaf area, and suppression of photosynthesis (Zare et al., 2011; Nezhadahmadi et al., 2013). Among these physiological changes in the plant, the decrease in CO2 conductance due to stomatal closure under drought conditions is a major factor contributing to reduced photosynthesis (Singh et al., 2018). This reduction in photosynthesis explains the observed decrease in fresh weight, number of leaves, and gs in non-inoculated plants subjected to water stress.
The treatment with water stress but inoculated with B. amyloliquefaciens showed statistically similar stomatal conductance values to the treatments without water stress (Figure 1). This indicates that bacteria of the Bacillus genus can help plants to activate resistance mechanisms to water stress conditions. Studies conducted on pepper plants inoculated with Bacillus butanolivorans and subjected to water stress have shown similar behavior to the present study (Kim et al., 2022).
Stomatal closure during water stress requires signaling by the hormone ABA. It has been found that some rhizobacteria regulate the ABA status in the plant (Karadeniz et al., 2006), B. amyloliquefaciens can alter the plant's endogenous ABA signaling, preventing a reduction in stomatal conductance (gs).
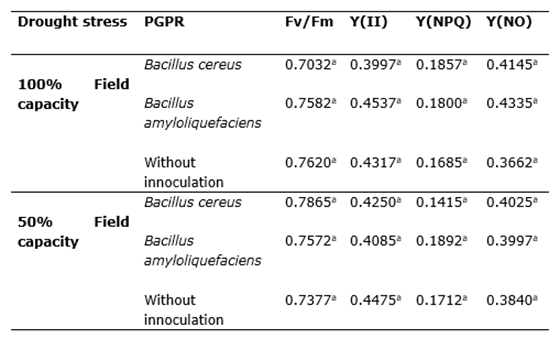
Maximum quantum efficiency of photosystem II. The maximum quantum efficiency of photosystem II (Fv/Fm) (equation 1) did not show significant differences between treatments (Table 2). This parameter indicates the maximum potential efficiency with which the light absorbed by the PSII antenna is converted into chemical energy in the first electron acceptor (QA) (Blankenship, 2015). When Fv/Fm decreases, the excitation rate of the PSII reaction centers is affected, which in turn affects the production of NADPH and ATP.
All evaluated treatments presented fluorescence values of chlorophyll below 0.8, which could indicate abiotic stress (Jeyakumar et al., 2005) even on control plants. The fact that all treatments including the control, had a Fv/Fm values lower than 0.8 might indicate that leaves were starting the senescence process, in which case the maximum potential efficiency of photosystem II also decreases (Bresson et al., 2018).
The Fv/Fm values of chlorophyll found in this study were lower than those reported by Pellegrini et al. (2011) in lemon balm plants subjected to ozone stress (0.806-0.817) but higher than those reported by Rodriguez et al. (2014) in papaya plants subjected to water stress due to flooding (0.48-0.55 for treatments with 48 hours or more of inundation). These comparisons suggest that the Fv/Fm values observed in this study are within the expected range for plants subjected to stress conditions.
Quantum yield Y(II), Y(NPQ), and Y(NO). The parameters for non-photochemical quenching quantum yield Y(NPQ) and Y(NO) complement the quantum yield of photochemical energy conversion Y(II), and the sum of these is equivalent to unity: Y(II) + Y(NPQ) + Y(NO) = 1. These parameters provide insight into the plant’s capacity to cope with excess excitation energy (Baker, 2008). Thus, a reduction in Y(II) indicates a decrease in quantum efficiency and closure of the reaction centers, accompanied by an increase in the quantum yield of non-regulated non-photochemical energy loss Y(NO) (Mathur et al., 2021).
In the present study, the parameters Y(II), Y(NPQ), and Y(NO) did not show significant differences between treatments, but rather showed a similar trend to that reported by Mathur et al. (2021), whereby Y(NO) increased when Y(II) decreased (Table 2).
In addition to photochemical adjustments, plants manifest other mechanisms to cope with water deficit, especially under mild water stress. For example, stomatal closing (Figure 1) and photorespiration increase are earlier responses than photochemical or enzyme changes (Flexas et al., 2012). The above might mean that stressed plants irrigated until 50% field capacity might have undergone mild and not sever water deficit.
CONCLUSIONS
Growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) alleviate the effects of water stress in lemon balm plants at 50% of field capacity, improving growth and development parameters such as number of leaves, shoot fresh weight, root fresh weight, and stomatal conductance. PGPR application prevented stomatal closure in plants subjected to water stress. The maximum quantum yield of PSII (Fv/Fm) showed similar values in plants with PGPR application plus water stress and in plants without water stress, which may indicate that the rhizobacteria prevent damage to the photosystem caused by water absence in the plant. Native strains of Bacillus cereus and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens are viable alternatives to be used in areas facing water stress issues in medicinal plants such as lemon balm.