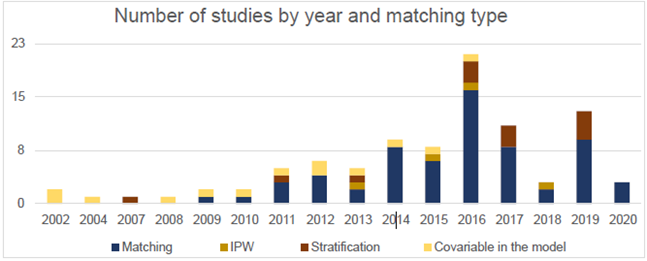
| 2002 |
Ravindra L. |
The American Journal of Medicine |
United States |
Cohort |
Timing of nephrology consults in acute renal failure (early vs. late). |
Age, sex, urinary output, liver failure, hematological insufficiency, heart rate, and serum creatinine and BUN |
Covariable in one model |
Not reported |
ROC values |
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2002 |
Mehta RL |
JAMA |
United States |
Cohort |
Association of diuretics with adverse or favorable outcomes in critically ill patients with acute renal failure |
Age, nephrotoxic etiology of acute renal failure, BUN, acute respiratory failure and congestive heart failure. |
Covariable in one model |
Not reported |
ROC values |
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2004 |
Uchino, S. |
Crit Care Med |
Australia |
Cohort |
Determination of the impact of diuretics on mortality rate in critically ill patients with acute renal failure |
Patient age, simplified acute physiology score II, creatinine on ICU admissions, need for renal replacement therapy, time between ICU admission and inclusion in the study, central venous pressure, Glasgow coma score, vasopressor use, urine volume during 6 hours prior to inclusion, platelet count, creatinine, arterial pH, septic etiology, low cardiac output etiology and other etiologies |
Covariable in one model |
Not reported |
C statistic |
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2006 |
Cho, K. C. |
J Am Soc Nephrol |
United States |
Cohort |
Survival by dialysis modality (continuous vs. intermittent) in critically ill patients with acute renal injury |
Age, liver failure, sepsis, thrombocytopenia, blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine |
Not reported |
Not reported |
ROC values |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Survival |
| 2006 |
Liu, K. D. |
Clin J Am Soc Nephrol |
United States |
Cohort |
Association between dialysis initiation (early vs. late) and mortality. |
Age, liver failure, sepsis, thrombocytopenia, and serum creatinine and stratification by site and modality of initial dialysis |
Not reported |
Not reported |
ROC values |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Mortality |
| 2007 |
S. Uchino |
The International Journal of Artificial Organs |
United States |
Cohort |
Renal replacement therapy (continuous vs. intermittent) to assess impact on survival and renal recovery |
ATrterial pH, furosemide dose, creatinine, gastrointestinal medical admission, immunomodulation, use of pulmonary artery catheter, hepatorenal syndrome, mechanical ventilation, mean arterial pressure and Glasgow coma score |
Stratification |
Not reported |
P Value |
Logistic regression |
Survival |
| 2008 |
Schortgen, F. |
Intensive Care Med |
France |
Cohort |
The risk of renal adverse events in patients with shock resuscitated with hypo-oncotic colloids, artificial hyperoncotic colloids, hyperoncotic albumin or crystalloids |
Demographic characteristics, admission category (i.e., planned or unplanned medical, surgical, with the type of surgery), potentially life-threatening underlying disease, immunodeficiency, risk factors for acute renal failure and use of nephrotoxic drugs. Simplified acute physiology score (SAPS II) and the number of organ dysfunction |
Covariable in one model |
Not reported |
P Value |
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2009 |
Bagshaw, S. M. |
Intensive Care Med |
Canada |
Cohort |
In patients with septic shock, describe the association between time of onset of hypotension and effective antimicrobial therapy and onset and severity of early acute renal failure |
Age, sex, comorbidity, source of infection, surgical status, need for mechanical ventilation, need for vasopressors, APACHE II score, hospital setting and study year |
Covariable in one model |
Not reported |
ROC values |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Renal failure |
| 2009 |
Benedetto, U. |
The Annals of thoracic surgery |
Italy |
Cohort |
Association between on-pump coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) vs. mini cardiopulmonary bypass systems (mini-CPB) and reduced incidence of acute renal failure |
Age, sex, body mass index (BMI), preoperative GFR, diabetes mellitus, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease requiring treatment, hypertension, peripheral vascular disease, NYHA class III/IV, left ventricular ejection fraction, prior percutaneous coronary intervention, myocardial infarction within 30 days, emergency surgery, preoperative medications including blockers, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers, aspirin and clopidogrel within 5 days after surgery; primary surgeon, number of grafts per patient and CPB time; postoperative variables including red blood cell transfusions and low cardiac output incidence |
Coincidence matching |
Coincidence matching Nearest neighbor |
C statistic |
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2010 |
Billings |
Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia |
United States |
Cohort |
Pre- and postoperative use of statins and incidence of acute renal failure in patients taken to cardiac surgery |
Preoperative treatment with statins, baseline creatinine, age, sex, history of diabetes,history of hypertensive disease, BMI, baseline left ventricular ejection fraction,preoperative diuretic, preoperative use of ACEi, valve surgery, use of CBP, time on CBP, aortic cross-clamping time, intraoperative inotropic support, intraoperative coronary catheterization, postoperative surgical re-exploration, postoperative diuretic, and extubation time |
Stratification y Covariable in one model |
Not reported |
P Value |
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2010 |
Chamchad, D. |
J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth |
United States |
Cohort |
Immediate extubation in the operating room after cardiac surgery associated with intensive care and hospital length |
Age, sex, BMI, ethnicity, preoperative serum creatinine, NYHA, reoperation, CABG, valve procedure, DM, hypertension, COPD, use ofBB, angina, reintubation, bleeding, postoperative renal failure, postoperative atrial fibrillation, time on CPB, priority of the surgery, off-pump operation, surgical priority |
Coincidence matching |
Greedy matching |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Estancia |
| 2010 |
Engoren, M. |
Anesthesiology |
United States |
Cohort |
Red blood cell transfusion vs. no transfusion in patients with acute pulmonary injury for the development of acute renal failure |
Not described |
Not reported |
Not reported |
Not reported |
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2011 |
Chou, Y. H. |
Crit Care |
Taiwán |
Cohort |
Impact of early or late initiation of renal replacement therapy in patients with acute renal failure of septic origin |
Demographics, comorbidities, septic AKI development after surgery (or not), and indications for TSR. Biochemical data such as complete red blood cell count, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), serum creatinine (sCr), serum glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase (GOT), total serum bilirubin, serum albumin and serum potassium (sK+) were documented on admission to the ICU and initiation of RRT. Clinical parameters included heart rate, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, central venous pressure (CVP), partial oxygen pressure in arterial blood gases and inspired oxygen fraction. Severity scores included Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), acute physiology score and chronic health evaluation II (APACHE II), sequence organ failure assessment (SOFA) and simplified acute physiology score III (SOFA III). The use of mechanical ventilation was documented and inotropic equivalent dose was calculated. |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Mortality |
| 2011 |
Kawar, E. |
Jaapa |
United States |
Cohort |
Comparison of clinical outcomes between pages admitted to an intensive care unit managed by residents vs. medical assistant |
Age, sex, admission diagnoses, patient origin before admission to the ICU and insurance status, tachycardia (heart rate 150 beats per minute), arrhythmia, hypotension, stroke, coma, intracranial mass, gastrointestinal bleeding and need for mechanical ventilation, cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) within 24 hours before admission, liver cirrhosis, serum creatinine or metastatic cancer, readmission to the ICU. |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Length of stay and mortality |
| 2011 |
Le Manach, Y. |
Anesthesiology |
France |
Cohort |
Chronic statin treatment compared to no statin treatment in terms of the main postoperative adverse events in patients undergoing vascular surgery |
Age, sex, admission diagnoses, patient origin before admission to the ICU and insurance status, tachycardia (heart rate 150 beats per minute), arrhythmia, hypotension, stroke, coma, intracranial mass, gastrointestinal bleeding and need for mechanical ventilation, cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) within 24 hours before admission, liver cirrhosis, high serum creatinine levels (< 2 mg/dL) or metastatic cancer. Physician and staff names and whether the patients was being readmitted to the ICU |
Covariable in one model |
Not reported |
C statistic |
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2011 |
Lee, E. H. |
J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth |
Korea |
Cohort |
Immediate postoperative hypoalbuminemia value as a marker of outcome after off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting (OPCABG) |
Sex, age, body mass index (BMI), diabetes mellitus, hypertension, chronic pulmonary disease, renal failure, prior stroke, preoperative ejection fraction, preoperative hematocrit, preoperative albumin, European System for Cardiac Operative Risk (EuroSCORE) and EuroSCORE logistic additive |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value |
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2011 |
Shahin, J. |
Crit Care |
Canada |
Cohort |
Relationship between inotrope use and hospital mortality and renal dysfunction in patients undergoing cardiac surgery |
Parsonnet score and low left ventricular ejection fraction, age, sex, bypass time, procedure type, CABG only or other procedures and the perioperative use of intra-aortic balloon pump |
Stratification |
Greedy matching |
P Value |
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2012 |
Attaran |
European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery |
UK |
Cohort |
Radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery in relation to a better outcome and postoperative survival rate |
Age, BMI, female gender,class IV angina, recent acute MI, current smoker, DM, hypercholesterolemia, hypertension, respiratory disease, cerebrovascular disease, renal dysfunction, three-vessel disease, priority surgery, rheumatic valve disease, euroSCORE, LVEF < 30% |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value |
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2012 |
Azuma, N. |
Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg |
Japan |
Cohort |
Determination of factors that affect ischemic wound healing and the role of angiosome in bypass surgery |
Diabetes, end-stage renal disease, heel ulcer, Rutherford classification, serum albumin and CRP |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value |
Logistic regression |
Survival |
| 2012 |
Clec'h, C. |
Crit Care |
France |
Cohort |
Association of renal replacement therapy with in-hospital mortality in ICU patients with acute renal failure |
Increase in creatinine reflected by the RIFLE score, oliguria reflecte in 24-hour urine output and SAPS II score, blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine and potassium (before RRT initiation), fluid accumulation (reflected by the difference in patient weight when reaching maximum RIFLE class as compared to weight on admission to the ICU) and SAPS II score |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value |
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2012 |
Lee, E. H. |
Intensive Care Med |
Korea |
Cohort |
Association between preoperative low levels of serum albumin and acute renal injury after offpump coronary artery bypass |
Age, body mass index, baseline renal function, left ventricular ejection fraction, liver disease, diabetes mellitus, occlusive peripheral vascular disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
Coincidence matching |
Greedy matching |
C statistic |
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2012 |
Vaara, S. T. |
Acta Anaesthesiol Scand |
Finland |
Cohort |
Volume of annual cases in an intensive care unit of patients treated with renal replacement therapy due to acute renal injury and its association with inhospital mortality |
Gender, age, BMI, elective surgery, intra-aortic balloon, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, comorbidities, systemic organ failure, among others |
Covariable in one model |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2012 |
Wu, V. C. |
PLoS One |
Taiwan |
Cohort |
Impact of diuretic use and dose on mortality in critically ill patients with acute renal injury 30 days after dialysis |
Gender, age, BMI, elective surgery, intra-aortic balloon, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, comorbidities, systemic organ failure, among others |
Covariable in one model |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Mortality |
| 2013 |
Apel, M. |
Crit Care |
Germany |
Cohort |
End-stage renal disease is independently associated with a higher risk of death following major surgical procedures |
Age, sex, comorbidities, SAPS II, surgery type and SOFA subitems on admission to the ICU |
Coincidence matching |
Greedy matching |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2013 |
Bayer, O. |
Critical Care Medicine |
Germany |
Cohort |
Comparison of perioperative fluid management in cardiac surgery patients using colloids vs. crystalloids with dialysis, cardiovascular stabilization, fluid balance and mortality |
Age, hypertension, DM, cirrhosis, NYHA IV, acute MI, pulmonary hypertension, bypass time, serum creatinine, use of noradrenaline or adrenaline, NSAIDs, diuretics, ACEi, aminoglycosides, glycopeptides, antifungals, iodinated contrast media, septic shock, SAPSII score |
Stratification |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2013 |
Ehrmann |
Critical Care Medicine |
France |
Cohort |
Use vs. non use of iodinated contrast medium as related to an increase in the incidence of acute renal injury in ICU patients . |
Age, hypertension, creatinine levels, chronic renal failure, diabetes, respiratory failure, coma, trauma, fluid use 12 h before inclusion, use of mechanical ventilation, shock, lactate, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) and sepsis. |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2013 |
Leite, T. T. |
Crit Care |
Brazil |
Cohort |
Determination of the association between early vs. late initiation of dyalisis after AKIN stage 3 classification and in-hospital mortality in critically ill patients |
Demographic, clinical and laboratory data on ICU admission and on the day of renal replacement therapy initiation |
IPW (weighting) |
Not reported |
Standardized measurements + significance |
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2013 |
Verônica Torres Costa e Silva |
PLOS ONE |
Brazil |
Cohort |
Time of early vs. late nephrology consult and association with prognosis in patients with acute renal failure in the ICU |
Late consult: Diuresis, serum creatinine levels, surgical AKI and mechanical ventilation Nephrology consult: SAPS 3, CSA score, diuresis, serum creatinine levels, potassium and bicarbonate levels |
Covariable in one model |
Not reported |
ROC values |
Logistic regression |
Mortality and Renal failure |
| 2014 |
Brewer, R. |
Ann Thorac Surg |
United States |
Cohort |
Comparison between on-pump and off-pump coronary revascularization surgery |
Age, gender, race, mortality risk, body surface area, smoker, preoperative creatinine, hypertension, DM, dyslipidemia, dialysis, chronic pulmonary diseases, peripheral vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, prior stroke, prior acute MI, heart failure, type of surgery, number of compromised vessels, VEF <40%, left trunk stenosis >50%, preoperative intra-aortic balloon |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2014 |
Elmiste-kawy, E |
Ann Thorac Surg |
Canada |
Cohort |
Incidence and associated risk factors in mild renal failure and determination of clinical impact following cardiovascular surgery |
Acute myocardial infarction, age, angina class, atrial fibrillation, cardiopulmonary bypass, CARE score, central nervous system complications, left ventricular functional class, coronary artery disease, endocarditis, sex, hypertension, intraoperative blood transfusion, hospital length of stay, length ofICU stay, time on ventilation, surgical priority, peripheral vascular disease, preoperative creatinine, preoperative hemoglobin, preoperative intra-aortic balloon pump, pulmonary edema, repeat cardiac surgery, shock, smoking |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2014 |
Iwagami, M. |
Crit Care Med |
Japan |
Cohort |
Effect of postoperative polymyxin B hemoperfusion on mortality in patients with abdominal septic shock |
Age, sex, surgery-related findings; use of noradrenaline, dopamine and dobutamine; previously defined organ dysfunctions (6), hospital volumes and hospital type (teaching or non-teaching hospital) |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor |
C statistic |
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2014 |
Raghunathan |
Critical Care Medicine |
United States |
Cohort |
Association between the use of crystalloids and in-hospital mortality in critically ill adult patients with sepsis |
Not described |
Coincidence matching |
Greedy matching |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2014 |
Linder, A. |
Am J Respir Crit Care Med |
Canada |
Cohort |
At least one episode of mild acute renal failure (stage 1) vs. absence of renal failure associated with long-term survival after recovery from critical disease |
Sex, age, diabetes, MAP (lower baseline), noradrenaline treatment, lactate level on day 1, chronic heart failure, COPD, chronic liver failure, chronic steroid treatment, malignancy and HIV |
Coincidence matching |
Caliper |
P Value
|
Regresión |
Survival |
| 2014 |
Oh, H. J. |
Crit Care |
Korea |
Cohort |
Benefit of a team that specializes in acute renal injury patients undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy |
Age, gender, mean arterial pressure, APACHE II, organ failure, age-adjusted Charlson comorbidity index, RIFLE scale, contributing factors, use of anticoagulation, use of diuretics, laboratory tests (hemoglobin, leukocytes, creatinine, bicarbonate, BUN, total cholesterol, albumin, CRP, arterial pH and total bilirubin) |
Coincidence matching |
Greedy matching |
P Value
|
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Survival |
| 2014 |
Picard, W |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother |
France |
Cohort |
Determine the nephrotoxicity risk associated with aminoglycoside treatment |
Age, gender, nosocomial sepsis, sepsis origin, sepsis severity, organ failure, rhabdomyolysis, renal graft of single functional kidney, DM, cirrhosis, pre-existing renal failure, nephrotoxic treatments, ACE inhibitors/ARBs, use of diuretics, high osmolarity contrast medium, use of hydoxyethyl starches, NSAIDs, antibiotics |
Covariable in one model |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Cox regression |
Renal failure |
| 2014 |
Vaara, S. T. |
Crit Care Med |
Finland |
Cohort |
Excess mortality attributable to acute renal injury |
Excess mortality attributable to acute renal injury |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
Standardized measurements + significance |
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2014 |
Wald, R. |
Crit Care Med |
Canada |
Cohort |
Intermittent vs. continuous dialysis associated with the risk of chronic dialysis |
Age, sex, hospitalization year, number of admissions and emergency room visits, number of visits to family physician, nephrologist, internist, cardiologist, geriatrician and psychiatrist; coronary artery, carotid or peripheral artery revascularization, heart valve surgery, coronary angiography, cardiac stress test, echocardiography, 12-lead individual electrocardiography or outpatient 24-hour electrocardiography, pacemaker insertion or carotid Doppler ultrasound within the 5 years prior to hospitalization and ARI diagnosis, major infection, alcoholism, chronic renal disease, liver dysfunction, heart failure, myocardial infarction, diabetes mellitus, cancer, cerebrovascular disease, myocardial infarction or angina and peripheral artery disease within 5 years prior to the date of hospital admission, Charlson comorbidity index, sepsis, non-ruptured aortic aneurysm repair, heart surgery, mechanical ventilation and initiation of dialysis in a teaching hospital |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Renal failure |
| 2015 |
Chiang, Y. |
J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth |
United States |
Cohort |
Effect of pulmonary artery catheterization on clinical outcomes after cardiac surgery in high risk patients |
Demographic characteristics, preoperative characteristics (hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes mellitus, obesity, prior stroke, coronary heart disease, endocarditis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary hypertension, peripheral vascular disease, chronic renal failure, dialysis, liver disease, substance abuse, previous CABG, prior valve surgery), elective surgery, type of cardiac surgery, CABG, single valve CABG surgery, double or triple CABG surgery |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2015 |
Ding, W. |
Cardiology |
China |
Cohort |
Intra-aortic balloon pump in relation to early clinical outcome in high risk patients taken to elective off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting (OPCABG) |
Age, sex, body mass index, smoker, DM, hypertension, dyslipidemia, renal dysfunction, prior stroke, prior acute MI, prior cardiac surgery, number of compromised coronary arteries, SYNTAX, BNO, euroSOCRE, LVEF, distal anastomosis |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2015 |
Horkan, C. M. |
Crit Care Med |
United States |
Cohort |
Acute renal injury in patients who survived critical care and association of post-discharge outcomes (readmission beyond 30 days after discharge, postdischarge mortality and progression to endstage renal disease) |
Age, sex, race, Deyo-Charlson index, type of patient and risk classification, injury, failure, loss of renal function or end-stage renal disease |
Covariable in one model |
Caliper |
P Value |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Mortality and Renal failure |
| 2015 |
Leite, T. T. |
Clin J Am Soc Nephrol |
Brazil |
Cohort |
Renal outcomes in critically ill patients receiving propofol or midazolam |
Sex, age, non-renal admission, simplified acute physiology score I and sequential organ failure evaluation, main comorbidities, type of ICU admission (medical, surgical or coronary), sepsis diagnosis, admission, Glasgow Coma Scale score, renal function on admission to the ICU (first serum creatinine measurement available), need for vasoactive drugs during the first 48 hours in the ICU and mean arterial pressure median in the first 48 hours in the ICU |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor |
Standardized measurements + significance |
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2015 |
Alexandre Liborio |
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation |
United States |
Cohort |
Propofol vs. midazolam. |
Sex, age, non-renal admission, simplified acute physiology score I and sequential organ failure evaluation, main comorbidities, type of ICU admission (medical, surgical or coronary), sepsis diagnosis, admission, Glasgow Coma Scale score, renal function on admission to the ICU (first serum creatinine measurement available), need for vasoactive drugs during the first 48 hours in the ICU and mean arterial pressure median in the first 48 hours in the ICU |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor + caliper |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2015 |
Liborio, A. B. |
Clin J Am Soc Nephrol |
Brazil |
Cohort |
Complications of renal failure in critically ill patients associated with mortality and dialysis rates |
Age, SAPS-I/SOFA scores on admission, maximum BUN, cumulative fluid balance, minimum bicarbonate, maximum serum potassium and main comorbidities, including heart failure |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Mortality and Renal failure |
| 2015 |
Sang, B. H. |
Crit Care Med |
Korea |
Cohort |
Influence of postoperative albumin level on the prevalence of acute renal injury after live donor liver transplant |
Age, sex, BMI, diabetes, hypertension, mean arterial pressure, CHILD PUGH score, model for end-stage liver diseasescore, hemoglobin, platelets, albumin, sodium, total bilirubin, creatinine, prothrombin time and intraoperative data |
IPW (weighting) |
Not reported |
C statistic |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Renal failure |
| 2015 |
Shaw, A. D. |
Crit Care |
United States |
Cohort |
Type of intravenous fluid administered to patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome and association with outcome |
Age, sex, race, admission source, admission type, urban, comorbidities |
Coincidence matching |
Greedy matching |
P Value |
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2015 |
Shen, T. C. |
Medicine (Baltimore) |
Japan |
Cohort |
Risk of septicemia in patients with endstage renal disease with or without renal transplant |
Age, sex, index date, comorbidities (hepatitis B, hepatitis C, Charlson comorbidity index score) and medications (steroids and immunosuppressors [cyclosporine, azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil and tacrolimus]). |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Mortality |
| 2016 |
Allen, C. J. |
Mil Med |
United States |
Cohort |
Risk of acute renal failure or death in patients with penetrating trauma receiving a single bolus of hydroxyethyl starch during initial fluid resuscitation |
Age and sex, injury characteristics (injury severity score, initial systolic blood pressure, heart rate, Glasgow scale), excess base, hematocrit, need for blood transfusion, ICU admission and surgery |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Mortality and Renal failure |
| 2016 |
Bonnet, V. |
Medicine (Baltimore) |
France |
Cohort |
Comparison of postoperative complications of mitral valve repair taking into account age under and over 80 years and comorbidities |
Age over and under 80 years, sex, BMI, comorbidities, NYHA >=2, LVEF <45%, pulmonary hypertension, type of surgery, surgical time |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
C statistic |
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2016 |
Carmona, p |
Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg |
Spain |
Cohort |
On or offpump coronary revascularization surgery comparing intraoperative and 30-day postoperative outcomes |
Age, sex, EuroSCORE logistic, smoking, obesity BMI >30, hypertension under treatment, dislipidemia under treatment, diabetes mellitus under with insulin treatment, past medical history of stroke (stroke or transient ischemic attack), chronic pulmonary disease: pulmonary disease under treatment with bronchodilators or steroids, clinical symptoms of stable or unstable angina, past history of percutaneous coronary intervention, history of acute coronary syndrome within the previous 6 months. Surgery, intra-aortic balloon pump implantation before surgery. Chronic renal disease: defined as preoperative creatinine >2 mg/dL or need for renal replacement therapy, peripheral artery disease with intermittent clinical symptoms. Lower limb claudication, more than 50% carotid artery occlusion, amputation of any limb due to arterial disease, prior aortic or lower limb artery surgery, priority of the surgery: if the case was intervened within the first 24 hours after indication of surgery or later |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
ROC values |
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2016 |
Chao, p. W. |
Crit Care Med |
Taiwan |
Cohort |
Long-term results in critically ill septic patients who received cardiopulmonary resuscitation vs. those who did not receive resuscitation |
Age, year of onset, month of onset, sex, urbanization level, hospital level, Charlson comorbidity idex score, infection site, use of inotropic agents, dialysis, ventilation, days in the ICU, comorbidities, concomitant medications |
Stratification |
Nearest neighbor |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Survival |
| 2016 |
Charat Thongprayoon |
BMC Nephrology |
United States |
Cohort |
Effect of several measurement methods to determine baseline creatinine levels on the accuracy of acute renal injury diagnosis in critically ill patients |
Age, race, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, coronary heart disease, stroke, peripheral vascular disease, congestive heart failure and APACHE III on admission to the ICU |
Not reported |
Not reported |
C statistic |
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2016 |
Cipolle, M. D. |
J Trauma Acute Care Surg |
United States |
Cohort |
Differences in results between trauma patients who received care in the trauma hospital program and patients with similar medical complexity trauma who did not receive care in the trauma program |
Age, injury severity score and pre-existing diabetes mellitus conditions requiring insulin therapy, hypertension, congestive heart failure and stroke |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2016 |
Clark, E. |
Intensive Care Med |
Canada |
Cohort |
Clinical characteristics and in-hospital mortality in patients with end-stage chronic renal failure o chronic dialysis with septic shock as compared to patients with septic shock not on chronic dialysis |
Age, sex, comorbidities (cancer, immune compromise, ICC, coronary artery disease, elective or emergency surgery, COPD, dibetes) and APACHE II score |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor |
Standardized measurements and C statistic |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Mortality |
| 2016 |
Hammond, D. A. |
Pharmacotherapy |
United States |
Cohort |
Comparison of the incidence of acute renal failure development in critically ill patients who received concomittant vancomycin with piperacillin-tazobactam or cefepime |
Age, sex, BMI, initial creatinine, creatinine at the time of antibiotic initiation, SOFA, APACHE IV, septic shock, number of concomitant antibiotics, initial vancomycin levels, number of nephrotoxic medications, length of stay, admission unit, infection-associated length of stay, comorbidities |
IPW (weighting) |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2016 |
Henriikka Mildh |
Mildh et al. Ann. Intensive Care |
Finland |
Cohort |
Three-year mortality in survivors of 30 days of critical care with acute renal injury |
Age, comorbidities and ICU admission and treatment characteristics |
Coincidence matching |
Caliper |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Mortality |
| 2016 |
J. Latour-Péreza |
Med Intensiva |
Spain |
Cohort |
Assessment of the use and effectiveness of the routine invasive strategy in patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome with renal dysfunction |
Age, sex, mode of access, transport, delays and access to the center, cardiac catheterization availability, coronary risk factors, prior cardiovascular disease, prior treatments (pharmacological and coronary) and baseline clinical status (blood pressure, heart rate, initial EKG, initial Killip, TIMI score, GRACE and CRUSADE). |
Stratification |
Not reported |
Standardized measurements |
Not reported |
Mortality |
| 2016 |
Joung, K. W. |
Medicine (Baltimore) |
Korea |
Cohort |
Comparison of postoperative acute renal injury in ileal conduit and urinary shunting of the neobladder following radical cystectomy |
Sex, years, height, weight, body mass index, history of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, coronary heart disease or cerebrovascular disease, cancer stage and grade, application of neoadjuvant chemotherapy, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor II blocker or diuretic medications, albumin, hematocrit, creatinine, uric acid and placement of ureteral stent |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2016 |
Jun, I. G. |
Liver Transpl |
Korea |
Cohort |
Incidence of acute renal failure in patients with live donor liver transplant with and without ABO compatibility |
ABO compatibility, sex, age, body weight, height, body mass index (BMI), ABO type and end-stage liver disease score model (MELD); comorbidities such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension and coronary artery disease and preoperative laboratory values such as platelet count, prothrombin time, normalized international proportion and hemoglobin, glucose, serum albumin, serum sodium, total serum bilirubin, sCr, serum aspartate aminotransferase, serum alanine aminotransferase, and the highest intraoperative IA titre. |
Stratification |
Nearest neighbor |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Survival |
| 2016 |
Karamanos, E. |
World J Surg |
United States |
Cohort |
Impact of diabetes mellitus on outcomes of patients undergoing emergency laparotomy due to small bowel adhesive obstruction |
Age, gender, BMI, comorbidities, wound classification, Charlson index, inflammatory status at the time of admission. |
Not reported |
Not reported |
C statistic |
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2016 |
Kerry C. Cho |
Clinical Science Articles |
United States |
Cohort |
|
Age, liver failure, sepsis, thrombocytopenia, blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine |
Covariable in one model |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Survival |
| 2016 |
Lai, W. H. |
Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med |
Taiwan |
Cross-sectional |
Incidence and clinical presentation of post-traumatic acute renal failure in hospitalized adult patients and its association with shock |
Sex, years, comorbidity, Glasgow scale, head/neck, chest, abdomen or limb injury according to severity on the abbreviated injury scale for each body region and injury severity score (ISS). |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Mortality and Renal failure |
| 2016 |
Lin, C. Y. |
Medicine (Baltimore) |
Taiwàn |
Cohort |
Correlation of preoperative renal failure with mortality and morbidity after aortic valve replacement vs. patients without renal failure. |
Preoperative demographics, associated comorbidities, surgical procedures and hospital recovery were compared between groups. In-hospital mortality was defined as death occurring during hospitalization. Emergency operations included hemodynamically unstable patients requiring a high dose of inotropic agents, endotracheal intubation or mechanical circulatory support, including intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) before the surgery. |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2016 |
Mazzeffi, M. |
J Anesth |
United States |
Cohort |
Preoperative use of aspirin associated with cardiac surgery patients with massive transfusion. |
Type of surgery, urgency of the surgery, year of the surgery, cardiopulmonary bypass time, use of antifibrinolytics, age, sex, weight, height, preoperative platelet count, preoperative hematocrit, preoperative INR, baseline hemodialysis, baseline creatinine, chronic pulmonary disease, hypertension, diabetes, dislipidemia, peripheral vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, infectious endocarditis, prior myocardial infarction, prior cardiac intervention, congestive heart failure within the 2 weeks following surgery, use of betablockers, use of statins and use of warfarin |
Coincidence matching |
Greedy matching |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2016 |
Moise, p. A. |
J Anesth Clin Ther |
United States |
Cohort |
Comparing the results of early treatment with daptomycin vs. vancomycin for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia |
Variables identified for matching were: age (<60 vs. >60), disease severity (ICU status) and type of infection (intravascular, extravascular or catheter). Bacteremia clearing was used to validate the hierarchy for the type of infection. |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2016 |
Oscar Peñuelas |
Journal of Intensive Care Medicine |
Spain |
Cross-sectional |
Assessment of predictors for ICU-acquired paresis and associated short-term outcomes |
Age, SAPS II, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sepsis (leading to mechanical ventilation or as a complication during mechanical ventilation), use of neuromuscular blockade, cardiovascular failure, renal failure, hematological insufficiency and days on mechanical ventilation before weaning |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor y Caliper |
Standardized measurements y ROC values |
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2016 |
Park, J. Y. |
Crit Care |
South Korea |
Cohort |
Results of early vs. late initiation of renal replacement therapy |
Age, sex, CCI, systolic arterial pressure, prothrombin time and total bilirubin level |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor y Caliper |
Standardized measurements +significance |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Survival |
| 2016 |
Ruan, S. Y. |
Crit Care |
Taiwan |
Cohort |
Risk of acute renal failure associated with inhaled nitric oxide therapy in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome |
Age, sex, year of entry to the cohort, height, body weight, ARDS etiology, simplified acute physiology score II (SAPS II) 15, lung injury score 16, comorbidities, ventilator settings, vital signs, arterial blood gases, complete blood count, creatinine and bilirubin levels, urine output, radiological pattern, and use of vasopressors on the first ARDS day. Creatinine clearance was estimated using the Cockcroft-Gault. |
Stratification |
Caliper |
P Value
|
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Renal failure |
| 2016 |
Thongprayoon, C. |
J Am Soc Nephrol |
United States |
Cohort |
Assessing the risk of acute renal failure in patients taken to transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) vs. surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) |
STS risk score, eGFR, sex, body mass index, type of surgery (elective vs. urgent/emergent), presence of anemia, history of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, congestive heart failure, peripheral vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, chronic pulmonary disease, NYHA (classes 1 and 2 vs. 3 and 4), preoperative use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker, prior percutaneous cardiac intervention, prior coronary bypass grafting, prior aortic valve surgery, cardiac rhythm during surgery (normal vs other) and aortic valve regurgitation (none or trivial vs, mild, moderate or severe) |
Coincidence matching |
Caliper |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2017 |
Bentzer, p. |
Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med |
Sweden |
Cohort |
Effect of dextran-70 on outcomes in patients with severe sepsis |
Age, sex, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), renal failure, diabetes, outcome variables (except mortality) and fluid administration data. |
Coincidence matching |
Greedy matching |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression |
Mortality and Renal failure |
| 2017 |
Chan, M. J. |
Medicine (Baltimore) |
Taiwàn |
Cross-sectional |
Effects of 3 different surgical methods for coronary revascularization in renal injury |
Age, sex, preoperative creatinine level, cardiac ejection fraction, emergent/ urgent intervention, use of intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP), preoperative ventilator use, diabetes mellitus, recent myocardial infarction, shock and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2017 |
Dos Santos, T. O. C. |
PLoS One |
Brazil |
Cross-sectional |
Mortality-related factors in patients admitted to the ICU with acute renal failure requiring dialysis who underwent continuous veno-venous hemodiafiltration (CVVHDF) |
Age, comorbidities, severity of the disease that caused AKI, metabolic disorders, organ dysfunction and weight gain during the resuscitation phase. Other factors that appear to influence prognosis in these patients are those related with the therapy itself, including type of dialysis modality, time of initiation of the procedure, administered dialysis dose, metabolic control and volume status obtained over the course of treatment |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Survival |
| 2017 |
Dou, L. |
Nephron |
United States |
Cohort |
Obstructive sleep apnea associated with the risk of acute renal failure in the intensive care unit |
Age, BMI, history of CHF, CKD, CPD, hypertension, diabetes, high risk surgery, exposure to nephrotoxins, mechanical ventilation and APACHE III score |
Coincidence matching |
Caliper |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2017 |
Hoi-Ping SHUM |
Nephrology |
China |
Cross-sectional |
Impact ofrenal replacement therapy on 90-day mortality in critically ill patients with KDIGO stage 3 renal failure |
Age, baseline GFR, worse creatinine/potassium/ bilirubin/platelet count level, pH within the first 24 hours of admission to the ICU and APACHE IV score |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor y Caliper |
C statistic |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Mortality |
| 2017 |
Jennifer S. McDonald |
Intensive Care Med |
United States |
Cohort |
Association between intravenous iodinated contrast material administration and later development of post-contrast AKI, emergent dialysis and short-term mortality |
Age, serum creatinine before CT (sCr), changes in sCr prior to exploration and SOFA score, comorbidities, use of nephrotoxic drugs, IV fluids used, stability prior to CT |
Stratification |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Mortality and Renal failure |
| 2017 |
Kianoush Kashan |
PLOS ONE |
United States |
Cohort |
Effect of bicarbonate concentration in the replacement solution on patients in the ICU that required CRRT for AKI. |
pH, bicarbonate, interaction between pH and bicarbonate, presence of sepsis, use of mechanical ventilation, vasopressor administration, intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) and Charlson comorbidity index |
Coincidence matching |
Caliper |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Mortality |
| 2017 |
Kovacheva, V. p. |
Neurosurgery |
United States |
Cohort |
Determine ifAKI in patients after craniectomy is associated with higher 30-day mortality |
Age, sex, race (white vs. non-white), Deyo-Charlson index, sepsis and chronic renal disease covariables, severity of the disease, intracranial bleeding, subarachnoid hemorrhage, acute respiratory failure and trauma |
Coincidence matching |
Caliper |
P Value
|
Logistic regression y Cox |
Mortality |
| 2017 |
Latour-Perez, J |
Med Intensiva |
Spain |
Cohort |
Assess the use an effectiveness of the routine invasive strategy in patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome with renal dysfunction |
Age, sex, clinics, mode of access, transportation and delay in accessing the center, availability of cardiac catheterization, coronary risk factors, prior cardiovascular disease, previous treatments (pharmacological and coronary) and baseline clinical status (blood pressure, heart rate, initial EKG, initial Killip, TIMI 24, GRACE and CRUSADE scores |
Stratification |
Not reported |
Standardized measurements + significance |
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2017 |
Legouis, D. |
Anesthesiology |
France |
Cohort |
Impact of acute renal injury in patients who experience reversible acute renal injury after cardiac surgery |
Age, body mass index, preoperative eGFR, clamping and bypass time, European logistic system for assessing the cardiac surgery risk, left ventricular ejection fraction and type of surgery |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor y Caliper |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Renal failure |
| 2017 |
Marik, p. E. |
Chest |
United States |
Cohort |
Hydrocortisone, vitamin C and thiamine for the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock |
Age, sex, diagnosis on admission, comorbidities, need for mechanical ventilation, use of vasopressors, daily urine output, fluid balance after 24 and 72 hours, length of stay in the ICU and laboratory values, Immunocompromised patients if they received cytotoxic therapy or if diagnoses with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Serum creatinine levels, leukocyte counts (WB), platelet count, total bilirubin, PCT and lactate. Acute renal injury (AKI), APACHE II and APACHE IV scores on admission, including foreseen in-hospital mortality in APACHE IV |
Not reported |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Survival |
| 2017 |
Shou-Chun Yu, |
World Neurosurgery |
Tai wan |
Cohort |
One-year mortality rate in patients with spinal cord injury with CKDandTRDand comparison in patients with spinal cord injury without CKD |
Age, sex, comorbidities, length of stay in the intensive care unit and total length of stay |
Stratification |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Cox regression |
Mortality |
| 218 |
Etienne Gayat |
Intensive Care Med |
France |
Cohort |
Association between the use of ACEi and ARA II in patients with acute renal failure in the ICU with mortality within 1 year |
Age, Charlson score, CKD, diabetes mellitus, chronic heart failure, ACEi/ARB administration before ICU admission, vasopressor administration while in the ICU, RRT during ICU stay, systolic blood pressure at discharge from the ICU |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor |
Standardized measurements |
Cox regression |
Mortality |
| 2018 |
Buyun Wu |
Scientific Reports |
China |
Cohort |
Impact of low AKI recognition (more than 3 days after onset) on short-term prognosis |
Sex, age, setting in which AKI occurred, eGFR on admission, oliguria, history of malignant neoplasm, APACHE II score, SOFA score, risk factors for AKI (hypovolemia, heart failure, sepsis, surgery), AKI stage, blood urea nitrogen and whether RRT was used |
IPW (weighting) y Stratification |
Caliper |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2018 |
Shih-Ting Huang_ nuevo |
CMAJ |
Tai wan |
Cohort |
Renal outcomes in patients with no preexisting renal disease who were admitted due to critical acute disease |
Age (5-year periods), sex and index year with control patients, comorbidities |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Mortality and Renal failure |
| 2019 |
AMANDA Y WANG |
Nephrology |
Australia |
Cohort |
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) and acute renal injury |
Age, sex, sepsis, mechanical ventilation and APACHE III scores at the time of randomization |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Cox regression |
Renal failure |
| 2019 |
Ana p. A |
ccmjournal |
Brazil |
Cohort |
Assessment of inhospital mortality and mortality risk factors in patients with cancer discharged from the ICU after the decision to refuse vital support therapies |
SAPS 3 and SOFA on admission to the ICU, setting prior to admission to the ICU, infection on admission to de ICU, use of non-invasive mechanical ventilation, acute renal injury and delirium during while in the ICU |
Coincidence matching |
Caliper |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2019 |
Ian E. McCoy, |
Crit Care Expl |
United States |
Cohort |
Estimation of the effects of diuretic use in the first 24 hours in the ICU |
Age, sex, race, comorbidities, type of admission, ICU type, serum creatinine on admission, mechanical ventilation and each of the SOFA score items on admission, out of six ICU items |
Coincidence matching |
Greedy matching |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2019 |
Muhammad Zeeshan |
American Association for the Surgery of Trauma |
United States |
Cohort |
Four-factor prothrombin complex plus fresh frozen plasma vs. fresh frozen plasma alone in patients with trauma-related bleeding |
Age, sex, race, body mass index, vital signs (systolic blood pressure, heart rate, Glasgow scale), time to therapy initiation, injury mechanisms, injury severity score, abbreviated injury scale (AIS), Head-AIS, chest-AIS,abdominal-AIS, spine-AIS, limb-AIS, comorbidities, use of anti-platelet agents before injury, and trauma center level |
Stratification |
Nearest neighbor |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Mortality and Renal failure |
| 2019 |
Philippe Gaudard |
BMC Infectious Diseases |
France |
Cohort |
Acute renal injury during treatment with daptomycin vs. vacomycin in critically ill cardiovascular patients |
Severity score such as simplified acute physiology (SAPS II) on admission to the ICU and sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) upon initiation of treatment, history of chronic renal failure (creatinine clearance under 50 mL/min), creatinine and AKI before initiation of treatment (defined as baseline), sepsis-related or heart-failure related circulatory shock (defined as systolic blood pressure undere 90 mmHg and resistant to fluid challenge, with evidence of end-organ hypoperfusion such as oliguria, altered mentation or high plasma lactate level), need for cardiopulmonary bypass for surgery (within 48 h of antibiotic initiation), use of other nephrotoxic agents (iodine contrast, aminoglycosides, cyclosporin), bacteremia documented by CPG |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2019 |
Raphael Donadio Pitta |
European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases |
Brazil |
Cross-sectional |
Comparison of the incidence of AKI in critically ill patients treated with aminoglycosides or meropenem in the intensive care setting |
Age, sex and use of vancomycin, polymyxin, diuretic and amphotericin |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor y Caliper |
P Value
|
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2019 |
Sarah A. Schubert |
The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery |
United States |
Cohort |
Determine the influence of perioperative administration of betablockers before aortic valve replacement |
Rates of hypertension, anemia, coronary artery disease, preoperative atrial fibrillation or heart failure, among others |
Stratification |
Greedy matching |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression |
Mortality |
| 2019 |
Wuhua Jiang |
Braz J Cardiovasc Surg |
China |
Cohort |
Discover potentially modifiable perioperative predictors for renal replacement therapy (RRT) in patients with cardiac surgery-associated acute renal injury |
Age, comorbidities, history of contrast media exposure, preoperative cardiac function status (NYHA classification), baseline eGFR (CKD-EPI), creatinine levels surgery-related factors (proceduresk urgency, time on cardiopulmonary bypass, red blood cell transfusion) and operative characteristics of central venous pressure and red blood cell transfusion. If >1 cardiac surgery procedures were performed during the same admission, only the data for the first surgery were considered |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value |
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2019 |
Yanfei Shen |
Critical Care BMC |
China |
Cohort |
Relationship between the use of loop diuretics and in-hospital mortality in critically ill patients with vasopressor support |
Age, weight, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, heart disease, AKI, SOFA score on admission to the ICU, white count, fluid volume intake and proportions of various vasopressors |
Stratification |
Nearest neighbor y Caliper |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression |
Mortality and Renal failure |
| 2019 |
Yoshihisa Miyamoto |
Intensive Care Med |
Japan |
Cohort |
Examine the association between the use of intravenous contrast and no recovery from acute renal injury requiring dialysis (AKI-D) and hospital in-hospital mortality in patients with sepsis |
Age, sex, CCI, congestive heart failure, diabetic nephropathy, CKD, consciousness level with JCS, discharge year, source of infection, emergency surgery due to infectious source, hispital volume and treatments performed within the next 2 days after discharge |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor |
Standardized measurements and C statistic |
Logistic regression |
Mortality and Renal failure |
| 2019 |
Yu Hsiang Chou |
Journal of Nephrology |
Taiwan |
Cohort |
Preoperative continuation of renin-angiotensin system inhibitor and cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury |
Age, sex, CKD, DM, decompensated heart failure, coronary heart disease, occlusive peripheral artery disease, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cirrhosis, hyperuricemia, metastatic cancer, smoking, hemoglobin, baseline creatinine, albumin, urinary protein, surgery type, antihypertensives and statins |
Coincidence matching |
Caliper |
P Value |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Renal failure |
| 2019 |
Yuya Goto |
Goto et al. Critical Care |
Japan |
Cohort |
Assess the effect of contrast media on renal function and mortality in patients with sepsis who already had AKI |
Age, sex, infection site, history of chronic kidney disease, diabetes mellitus, septic shock, immune compromise, use of aminoglycosides or vancomycin, laboratory data (hemoglobin, Cr, total bilirubin, platelets, lactate), partial oxygen pressure/ inspired oxygen fraction ratio, and Glasgow coma scale on admission to the ICU |
Coincidence matching |
Not reported |
P Value |
Logistic regression |
Mortality and Renal failure |
| 2019 |
Lisa-Mae |
Chest |
United States |
Cohort |
Association between contrast and acute renal injury in critically ill patients with normal renal function |
Age, gender, comorbidities, use of contrast, race, obesity, primary diagnosis, APACHE |
Stratification |
Nearest neighbor y Caliper |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression |
Renal failure |
| 2020 |
Ala Abudayyeh |
American Journal of Hospice |
United States |
Cohort |
Determine the impact of dialysis on survival of patients admitted to the ICU with stage IV cancer and renal failure |
Age, sex, race/ethnicity and vital status (alive vs. dead). Clinical data included type of malignant neoplasm, peripheral vascular disease and/or dementia diagnosis, and consults for dialysis and palliative care. Dementia, peripheral vascular diseases and reduced albumin, length of stay in the ICU, SOFA score and disposition. First albumin level obtained in the first 3 days in the ICU |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Renal failure |
| 2020 |
Guangju Zhao |
Zhao et al. Critical Care BMC |
United States |
Cohort |
Administración de furosemida y los resultados en pacientes críticos con lesión renal aguda. |
Edad, género, etnia, tipo de admisión, comorbilidades, puntuación simplificada de fisiología aguda II (SAPSII), puntuación de evaluación de falla orgànica secuencial (SOFA), presión arterial media (MAP), nivel de creatinina en suero, uso de vasopresores e inotrópicos, entrada diaria de líquidos, fluido equilibrio, tipos de líquidos, cirugía cardiaca, TSR y ventilación mecànica. |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor y Caliper |
Standardized measurements |
Logistic regression and Cox regression |
Renal failure |
| 2020 |
Gustavo A.Ospina-Tascón |
Critical care |
Colombia |
Cohort |
Effects of very early initiation of noradrenaline in patients with septic shock |
Age, APACHE II, comorbidities and patient origin (emergency room, general ward or intensive care unit) were documented. Heart rate and blood pressure were also documented and at 2, 4, 6, 8 and 24 h after vasopressor administration. Multiple organ dysfunction was assessed using the sequential organ failure assessment score (SOFA). Days off ventilation, renal replacement therapy requirement and days without RRT were also calculated. Finally, ICU and hospital length of stay were recorded together with ICU, in-hospital and 28-day mortality |
Coincidence matching |
Nearest neighbor |
P Value
|
Cox regression |
Mortality and Renal failure |


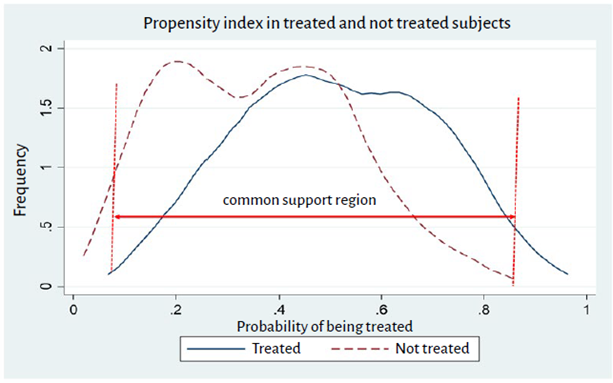











 text in
text in