Introduction
Gait is defined as the bipedal motion of humans, with low effort and minimal energy consumption. In the elderly gait is associated with independence and interaction with the environment, as well as the potential to conduct the activities of daily living (ADL). When free ambulation declines, these activ ities become limited.1,2 Functional alterations of the joints in the lower extremities may affect the ability to walk, particularly when the dynamic and static stability of the knee joint is interrupted due to structural changes such as osteoarthritis (OA), a degenerative disease associated with aging, and affecting the functionality of the affected individuals.3)-(5
Knee OA is a musculoskeletal disease which could be idiopathic but is associated with the interaction of biological factors such as genetic predisposition, gender, age and race, or factors of the joint mechanics, of which the most relevant are overweight, previous injuries, the level of physical activity and the adduction and abduction moments of the joint.1),(6)-(8) Hence, knee OA may affect between 7 and 17% of the population, with a trend to increase with aging; this factor increases the cost for healthcare systems.1,9
Individuals with OA of the medial or lateral compartment exhibit more varus or valgus alignment, respectively, as com pared to controls.10)-(13 Likewise, varus alignment is greater in the most severe cases of OA.14)-(16 During the stance phase of gait in people with this condition and varus deformity, there is an increased external moment of knee adduction, which increases the medial compartment forces which is more prone to develop OA.4,17
The forces that cross the knee during the stance phase of gait may be internal or external. The former are produced by muscles, ligaments, and soft tissues, while the latter are produced by the ground reaction and gravity forces. The external forces are applied medially with respect to the center of articulation of the knee and tend to cause a medial rotation of the tibia with respect to the femur in the coronal plane.17 This phenomenon is called the external adduction moment-of relevance for the elderly population since the higher it is, the more the compressive forces increase in the medial compartment of the knee, and this is associated with the development of degenerative disease.9),(17)-(19 The literature describes that this moment presents a peak at the 20% of the gait stance phase,9 called maximum peak moment (MPM), measured in Nm/kg. However, to accurately access such data, the gold stan dard should be motion analysis laboratories20,21 that have their own reference parameters.22
Hence, in order to establish the MPM deviations in the Colombian population, international references are used but this may bias the interpretation of the data.22 It is important for each laboratory to have its own reference parameters, since the anthropometric and demographic characteristics, as well the individual life styles, change according to their nationality. Moreover, the elderly population is growing leading to an increasing demand for healthcare, particularly from practitioners working in the area of human body motion. This highlights the need to procure reference parameters for intervention of the Colombian elderly population.23 Until now, no studies had been conducted in Colombia - specifically at the motion analysis laboratory of CES University on the knee joint moments in the coronal plain during walking of asymptomatic elderly individuals. Consequently, this research project is intended to describe the knee joint movements in the coronal plane, during gait in asymptomatic elderly individuals, residents of the Valle de Aburrá, Antioquia, Colombia.
Materials and methods
Study type and design
A descriptive, cross-sectional study was conducted intended to describe the knee joint moments in the coronal plane during gait of asymptomatic elderly individuals, residents of the Valle de Aburrá.
Population and sample
The reference population for this study was Colombian elderly individuals, aged 60 years and older, residents of the Valle de Aburrá. The inclusion criteria were: both males and females who accepted to voluntarily participate, able to follow instructions and to walk with no external walking aids. The exclusion criteria were: fractures or surgeries of the lower extremities during the past two years; neurological disease, cardiopulmonary instability or experiencing pain at the time of the assessment; uncorrected visual impairment; hearing or sensory limitations; allergies to the instruments used for assessment, such as allergy to double-sided tape. The data from 50 elderly individuals were analyzed, who were selected in a non-probabilistic and convenience mode.
Data collection
Following the signature of the informed consent, each elderly individual was asked to dress in comfortable clothing provided by the team of investigators, suitable for data capture. The measurements were taken using an anthropometer (Lafayette 60) and ergonomic measuring tape (SECA model 201), the del Full Body PiG model, measuring each item on both sides of the body. The measurements were: length of lower limbs, ankle width, knee width, elbow width, wrist with, hand width and shoulder displacement, height and body mass. Subsequently, the 39 markers were entered, including 4 head markers and markers at C7, T10, posterosuperior and anterosuperior iliac spines, acromion, arm, lateral humeral epicondyle, forearm, styloid process of the ulna and radius, head of the second metacarpal, manubrium of the sternum, xyphoid process, thigh, lateral femoral condyle, leg, external malleolus, heel bone, and head of the second metatarsal.24
The participant was asked to walk back and forth over a 6-meter walkway and complete four runs. Two force platforms (AMTI-OR6-7-1000) were placed in the middle and 8 previously calibrated optoelectrical cameras surrounding the area Bonita 10 (VICON, Oxford, UK). The participant was instructed to "walk as you normally do, and at your normal speed". No records were made while the participant adapted to the laboratory environment and the markers; then at least 7 valid captures were recorded. This was done when the participant made full contact with a different foot on each of the platforms. Once the data were captured, the information was processed and the appropriateness of the tests was checked using the Polygon 4.3.3 software. Then the data were exported onto an Excel spreadsheet to create the database for analysis using the SPSS V.20 software.
Statistical analysis
In order to describe the sociodemographic characteristics and assess the knee joint moments in the coronal plane, the qualitative variables were presented using frequencies and percentages; the quantitative variables were expressed as means and standard deviation or medians and interquartile ranges, according to distribution. Pearson or Spearman were used to assess the relationship of the MPM to the anthropo-metric variables (size, mass and BMI), spatial temporal (gait speed, length of step, length of stride, step rate, stance phase) based on distribution.
Ethical considerations
The study was conducted under the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, the ethical standards for research in humans of the World Health Organization (WHO), Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), the Council of International Organizations of Medical Sciences (CIOMS) and Resolution 8430 of 1993 of the Colombian Ministry of Health, keeping in mind good research practices favoring the participants and respecting intellectual property during the development of the project. The participation was voluntary and those who accepted to be part of the study, previously signed the informed consent.
Results
Sample data
50 asymptomatic elderly individuals with a mean age of 66 years (64-72) were studied; 52% were females (n = 26). Only the anthropometric variables showed a normal distribution: height 1.60 (±0.087) m, mass 66.07 (±13.54) kg, BMI 26.34 kg/m2. The median MPM of the knee in the coronal plane was 0.26 (±0.67) Nm/kg.
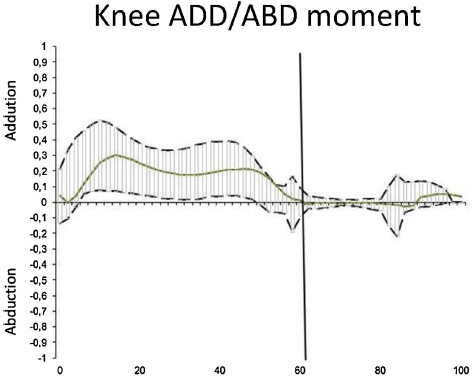
Fig. 1 illustrates the behavior of the knee joint moment in the coronal plane during the gait cycle: the vertical shows the positive and negative adduction moments, whilst the hori zontal axis shows the percentage of the gait cycle where the stance phase had a duration of 60.42%. The moments were mostly adduction and exhibited a curve with two peaks. The MPM occurred at approximately 17% of the gait cycle, and the second lower intensity peak at 40 60%.
Table 1 shows the references of the time, spatial and spatial temporal values which presented a non-normal behavior; each variable was reported in terms of the median and its corresponding IQR.
Table 2 shows the correlations between MPM and the anthropometric and spatial temporal aspects; no statistically significant values or strong correlations were identified among the variables assessed.
Table 1 Univariate analysis of the spatial-temporal variables.
| Spatial-temporal variables | Median | IQR |
|---|---|---|
| Length of step (m) | 0,55 | (0,53-0,59) |
| Length of stride (m) | 1,12 | (1,06-1,19) |
| Step cadence (steps/min) | 108,79 | (100,43-114,42) |
| Gait speed (m/s) | 1,01 | (0,93-1,07) |
| Stance phase (%) | 60,42 | (59,20-62,05) |
| IQR: interquartile range. |
Table 2 Correlation between MPM and anthropometric/spatial-temporal variables.
| Variables | Stance phase maximum peak | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rho | P | 95% CI | |
| Size | -0,13* | 0,17 | (158,7-1618,9) |
| Mass | -0,18* | 0,07 | (63,06-68,43) |
| BMI | -0,17* | 0,87 | (25,31-27,11) |
| Length of step | 0,09** | 0,36 | (0,54-0,59) |
| Length of stride | 0,07** | 0,48 | (1,08-1,13) |
| Stance pase | 0,06** | 0,55 | (58,57-61-18) |
| Cadense of step | 0,15** | 0,11 | (107,39-127,74) |
| Gait speed | 0,16** | 0,10 | (0,98-1,04) |
| CI: confidence interval; BMI: body mass index. ∗ Pearson correlation test. | ∗∗ Spearman correlation test. | ||
Discussion
This preliminary study shows the value of the knee joint moments in the coronal plane, identifying the highest peak in the stance phase; however, no associations were found between each variable associated with gait of the asymptomatic elderly individuals studied. Until this date, there are no data available in Colombia reporting the values for the coronal knee joint moments during gate in this population. The data herein collected may be interpreted as an initial description which could be the foundation for future studies on knee joint moments and how these may affect the occurrence of musculoskeletal diseases.
The graphical representation of the external knee joint moment in the subjects studied showed a curve with two adduction peaks in the stance phase. The MPM was identified at 17% of the gait cycle, indicating a similar pattern to what Foroughi et al.25 described in their systematic review about coronal knee joint moments, in patients with OA. Despite the consistency of the general morphology of the curves, the MOM in this study was 0.26 Nm/kg in asymptomatic subjects, while in the systematic review the MOM was reported between 0.25 and 0.71 Nm/kg in patients with OA, and a narrower range, but with lower peaks, between 0.33 and 0.55 Nm/kg for con trols. According to these data, MPM could be related to the severity and the OA symptoms.25 Moreover, this evidences a significant variation among the various nationalities, which further emphasizes the need to establish population-specific parameters according to symptomatology.
The adduction MPM herein described refers to the maxi mum force per kilogram that results in the tendency of the tibia to rotate medially with respect to the femur, which actually happens during the stance phase of gait. This rotational force may account for the maximum compression on the medial compartment of the knee. Hence, several authors argue that elevated MPMs are associated with radiographic changes and degeneration of the knee cartilage,26'27 due to increased medial contact force which is presumed to be the deleterious mechanical effect for the cartilage.28 Moreover, the adduction MPM, the peak of the maximum moment in the sagittal plane (flexor moment peak) is also considered a significant contributor to the force of the medial contact of the knee,29) hence showing the importance of the three-dimensional com-ponents in the analysis of motion and the need to study these components in populations at increased risk for OA.
Furthermore, the body mass index (BMI) of the participants indicates overweight (BMI = 26.34 kg/m1), a factor which depending on the magnitude, may increase the risk for OA up to four-fold, in contrast to normal weight individuals.30) However, this study failed to show an association with MPM, probably because the participants were asymptomatic. Similarly, Verlaan et al.30 studied the relationship of the adduction moment while going up and down the stairs in patients with knee OA, with and without obesity, and they found no differences in the adduction moment among these participants. The authors believe that their findings are due to the fact that obese individuals slow down their walking speed as an effective strategy to reduce the adduction moment during stair negotiation.
Over time, humans have experienced aged-related musculoskeletal changes that may lead to gait impairment, with a subsequent reduction in gait cadence, length of stride, and speed by 20%.31 In this particular study the speed was 1.01 m/s, and although participants were allowed to walk at their preferred speed and were given some time to adapt, the speed was below the reference values according to several authors, with asymptomatic populations of various age groups22),(32),(33 and of elderly individuals, such as the Mündermann et al. trial.15) The authors observed a group of subjects with OA and a con trol group; their speeds were 1.25 and 1.23 m/s, respectively. It may be argued that the differences among these studies are due to the assessment environment in the laboratory and the length of the walkway. However, the speed apparently did not affect the MPM, but considering that in this study the MPM and the gait speed were lower than the numbers reported by other authors, it is possible to conclude that reducing the speed increases the duration of the stance phase, which may con tribute to reducing the ground reaction force30 and hence the moment.
The limitations of this study may be related to the number of participants; nevertheless, the kinetics of both knees was analyzed and totaled 100 data points. Moreover, it may valuable to include the analyses of other complementary tests in future studies, to establish the correlation between any exist-ing symptoms and structural changes, including the static load alignment test, as well as the behavior of joint kinematics of the lower extremity, since as already mentioned, it is associated with several factors affecting the progression of OA and the joint moment. Another limitation was that the assessment model failed to consider the muscle activation factor involved in generating the moments in the coronal plane. This value is important to determine the involvement of muscles and other soft tissues for potential therapies to strengthen these structures and their impact on the loads that are injurious to the knee. It should be noted however, that the available bibliography is not very extensive for the analysis of the population studied, since most published articles discuss the behavior of joint moments on each plane in individuals with musculoskeletal pathologies, but not in asymptomatic populations.
Conclusion
This study analyzed the coronal knee joint moments during the stance phase of gait, in 50 asymptomatic elderly subjects, using a 3D analytical system. The behavior curve of the external adduction moment is similar to the findings reported by researchers in other countries, but with an adduction MPM of 0.26 Nm/kg, which in general is less that the figures reported in the population with OA. However, this MPM was not associated with other anthropometric or spatial temporal variables.
Further studies are needed to expand the reference parameters used by motion analysis laboratories and healthcare professionals, to contribute to making accurate, timely, quantitative and objective diagnoses in gait disorders and to make headway in physiotherapy intervention. Although these technological tools are not always available, this study provides an initial reference on behavior of the knee joint moment in asymptomatic elderly subjects.











 text in
text in