Introduction
Localized scleroderma (LS) is an autoimmune disease characterized by fibrosis of the skin and the underlying tissue.1) Scleroderma in «coup de sabre» is a groove-shaped type of LS that affects the frontoparietal area, like a sclerotic band with atrophy and thinning of the outer layers of the skin. It can rarely be associated with lesions in the central nervous system,2 although in recent years different neurological manifestations have been described, ranging from sensory disturbances to epileptic seizures or neuropsychiatric man-ifestations.3),(4 An increased incidence of lesions in the white matter has been demonstrated in the complementary tests.5)-(7) Their clinical significance is uncertain since in most cases they are subclinical. Even though the pathophysiology is unknown, their presence may have therapeutic implications.5)-(7 To date, no cases of stroke-mimic related to LS have been described.
Clinical case
It is a 30-year-old Caucasian woman, without toxic habits or associated cardiovascular risk factors. As relevant antecedents, she had episodic migraine without auras and scoliosis. The patient was diagnosed with right frontal LS in «coup de sabre» (Fig. 1) in 2012. For this, she had received several treatments, including methotrexate with a maximum dose of 7.5 mg weekly which was suspended due to digestive intolerance, even subcutaneously, and prednisone at doses of 5mg/every 24h. Treatment with mycophenolic acid 180 mg was started in 2016, with good tolerance and control of the cutaneous symptoms.
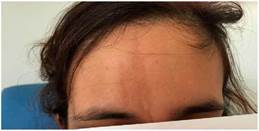
Fig. 1 Image with hyperpigmented lesion in the right hemiforehead corresponding to scleroderma in "coup de sabre".
In October 2017, the patient went to the hospital for a sudden clinical picture of paresthesia and corking of the left extremities (distal left lower limb and ascending progression to the arm and hemiface) and sensation of weakness (she limped, the arm was heavy), which was interpreted as a vascular profile, and was referred to the stroke reference hospital and treated with intravenous fibrinolysis. The neurological symptoms were improving in the following days, with full improvement at present.
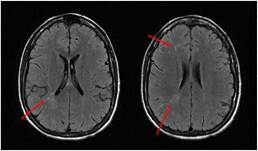
The vascular study, the electroencephalogram and the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) were normal. The nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed hyperintense lesions in T2 in the white matter of the right hemisphere without restriction in contrast diffusion or uptake (Fig. 2). Analytically, CRP 13.3 mg/dl, ANA 1/160 speckled pattern and negativity of other antibodies stood out.
Evolution
The patient was treated with methylprednisolone 1 mg/kg/day/for 3 days and then with prednisone 1 mg/kg/day in a descending pattern and increase of mycophenolate to 180 mg/every 12 h. She has remained asymptomatic and the MRI has not changed after 18 months of follow-up.
Discussion
Scleroderma is an immune-mediated disease characterized by inflammation, vascular damage and fibrosis. The term scleroderma encompasses different subtypes of diseases, from the LS, with predominantly cutaneous involvement, to systemic scleroderma (SS), with a higher frequency of internal organ involvement.8 The estimated incidence of LS is between 0.4 and 2.7 cases per 100,000 inhabitants/year. It is predominant in women (2-3:1) and in Caucasian patients.3
Considered as a cutaneous form with a benign prognosis, neurological complications such as focal neurological deficits, epileptic seizures, trigeminal neuralgia, extrapyramidal symptoms, headaches and neuropsychiatric disorders have been described in recent years.3),(4 Seen in perspective, this could have been related to the headaches that the patient had previously.
The time of development of the neurological symptoms ranges between 2 and 24 years since the onset of the cutaneous lesion.4
In the complementary tests, images with abnormal findings stand out in 83% of the cranial computed tomography (CT) scans and in 84% of the MRI scans.6 In these cases, the MRI shows calcifications, atrophy or hyperintensities on T2 in the subcortical white matter, corpus callosum, basal ganglia, and trunk, usually ipsilateral to the cutaneous lesion, often sub-clinical. The lesions were generally unilateral and ipsilateral to the cutaneous lesion; however, cases with bilateral lesions in the image have been reported.7 No modifications of the lesions have been described over time with these imaging tech-niques.9 The electroencephalogram was abnormal in 67.7% of the cases.6 It has been described the pathological anatomy of a case which required lobectomy due to poor control of the epileptic activity.10 Complement-mediated microvascular endothelial damage is described in the samples, although its pathophysiology has not been determined.5)-(7
There is no consensus on the treatment or on the need for immunosuppression in these cases. In previous publications, most patients were treated with corticosteroids, methotrexate, azathioprine, mycophenolate or tocilizumab, with favorable outcomes.3),(9),(10
In summary, neurologic involvement in scleroderma is more frequent than what can be expected. Therefore, it is convenient to take it into account in view of the onset of symptoms that would alert us since its existence could condition a different treatment.











 text in
text in