Introduction
The purpose of the research is to carry out a perception study through the results obtained in the Saber Pro tests of students of the bachelor's degree in Basic Education with an emphasis on Mathematics, Humanities, and Spanish Language in 2019. This dissertation establishes a relationship of results with the program, the institution, and the national average as a strategy of systematic comparison. In addition, it addresses the reference comparison between the years 2016 and 2019. Called Saber Pro Tests, they constitute one of the graduation requirements that students aspiring to receive their professional degree should take, according to the provisions of the Ministry of National Education of Colombia. The administration of Saber Pro Test results is the responsibility of the Colombian Institute for the Evaluation of Education.
Therefore, students must take the Saber Pro Test almost at the end of their professional training. This based on Decree 3963 of 2009. The main objective of this test is checking the level of development of students' competences who are about to obtain their diploma as professionals.
In addition, the results allow the production of value-added indicators and serve as a source of information for the construction of indicators for evaluating the quality of higher education programs and institutions (ICFES, 2021); this is how ICFES defines a conceptual and theoretical foundation for the tests construction. It is supported by the educational community to which they are addressed. The instruments of the test must include the references set forth in the theoretical framework in such a way that the generic competences expected in all professional undergraduate programs are harmonized. Meanwhile, the specific competencies are determined by the profession being evaluated; thus, the professionals object of study of this research are framed in the field of education.
Analyses such as those presented in this research allow university administrative in Colombia to identify the level of educational quality in which the programs are located and, therefore, undergraduate students. In addition, the results obtained constitute a point of reference against the academic competence of other institutions that measure students' educational performance with the same level. In this sense, the research purpose is to diagnose the state of undergraduate programs. Specifically, this case addresses the training of teachers in Basic Education. It is also meant that the results could help to establish Improvement Plans that allow mitigating the challenges that the current training demands. In addition, to generate opportunities for change that strengthen methodologies, curricular plans, and evaluation within the program, to respond with quality to the standardized measurement.
State of the Art
At the beginning of the epistemological debate about standardized tests in Colombia, and the case of the Saber Pro tests aimed at students of undergraduate professional programs of the different institutions of Higher Education -IES. It is advisable to develop a theoretical foundation for standardized tests of the homogeneous connotation that aim to measure students and HEIs. These institutions have a heterogeneous population in certain conditions of accessibility, coverage, and quality of education, far from the ideals outlined in the government plans and the norms issued by the Ministry of National Education.
Standardized Tests and the University
Conceptualizing standardized tests is not an easy assignment because of the different perspectives the discussion can be presented. For Harvey and Green (1993) standardized tests constitute a set of tasks under standard conditions designed to measure some aspect of a person knowledge, skills, or personality. While for Ahumada etal. (2019), standardized tests are considered, as evaluation instruments that allow recognizing population groups with specific educational needs, determining the factors that impact students' performance and verifying how an educational system develops or evolves. This process leads to identifying different aspects that characterize the purpose of standardizing tests to measure education.
Hughey (2018) states that standardized tests have been endemic to the academic culture for the last century. They are still woefully entangled at all levels of our educational institutions. Therefore, signs came-up suggesting that perhaps the practice has reached the limit of its usefulness as an assessment tool. This process leads us to rethink the sense of standardized tests as an objective for measuring educational quality, with objectivity being an element in this discussion. In this sense, Tristán-López and Pedraza-Corpus (2017) define objectivity as a necessary attribute that must be clearly detailed to satisfy the scientific purposes of any evaluation project in health sciences, social sciences, and education; as well as in each of the stages of production and use of standardized tests.
Based on the given debates, standardized tests are evaluation instruments that aim to measure the strengths and weaknesses of the academic competencies acquired by students at certain stages of their training process. As a result, standardized test results also serve as an instrument for categorizing the educational quality provided by institutions. These results are the critical item of analysis by international organizations that do not see with objectivity the conditions and scope of tests in contexts with more vulnerability of access to knowledge.
It should be noted that standardized tests, carried out around the world, are promoted by international organizations, for example, the main tests that are known internationally are among others: The program for International Student Assessment (PISA), the Study of Trends in Mathematics and Science (TIMMS), the Evaluation of Adult Competencies (PIAAC), the Third Regional Comparative and Explanatory Study (TERCE). At the national level, the National Plan for the Evaluation of Learning (PLANEA) tests in Mexico or SABER in Colombia can be found.
In many educational scenarios, there is a latent discussion that analyzes the effectiveness of standardized tests to measure the quality of education offered in Colombian institutions. Meanwhile, there is concern about subgroup differences in standardized tests and, during this situation, it is suggested that these tests should be replaced by holistic evaluations of unstructured application materials, which according to their proponents show less bias (Dalal etal., 2022).
According to Tristán-López and Pedraza-Corpus (2017), there are five fundamental and distinctive properties noticed in interpreting the results, eliminating, or reducing the biases induced by the influence of stereotypes and preferences in the design of the instrument or the appreciation of judges. There exist other factors that can affect the ethical use of the results of the tests. They are specificity, neutrality, independence, impartiality, and impersonality. These would be characteristics that, according to the authors' judgment, would lead to determining results closer to the reality of education, far from the idealisms of governments, subject to the approval of international organizations that associate the educational level with the incursion of individuals into a society of productive economy.
Saber Pro and its involvement in higher education
With Decree 1781 of 2003, the Ministry of Education of Colombia-MEN established the obligatory nature of the presentation of the State Quality Exams of Higher Education-ECAES, today called Saber PRO Tests and regulated by Decree 3963 of 2009. Since 2008 MEN undertook actions aimed at the formulation of generic or transversal competencies to all the nuclei of training programs in higher education, which make it possible to monitor the quality of higher education in the country and that can become the articulating element of all educational levels (Timaran-Pereira et al., 2021). The national government has promoted the development of proposals that allow the evaluation of education in Colombia at all levels. The evaluation results will be the reference to determine the plans for improvement and curricular and pedagogical restructuring. Also, applied tests must reach the standards provided by public entities, set in the goals of the generic and specific competencies.
The literature also suggests that the Saber Pro Tests are a strategy implemented by the government to identify the levels of educational quality. In addition, this test establishes improvement plans that contribute to overcoming the difficulties and low percentages evidenced in the development of professional skills that would impact social advancement, industrial and the country economy (Poveda etal., 2021). In this sense, ICFES defines a purpose for these exams, considering a standardization of 151 questions in the Generic Competences module, in addition to the modules of Specific Competences organized by Basic Knowledge
Nuclei (Table 1).
Source: ICFES (2018).
Chaves-Manzano and Ordóñez-López (2020) argue that until the '80s, evaluation was to measure, examine, and test, among some concepts. As time went by, evaluation processes begun to be conceived as an integral process, where not only knowledge is evaluated but students and teachers' aptitudes, attitudes and didactic. All of this regarding the evaluation process promoted with the implementation of the State tests. In this sense, evaluation becomes a process that brings multiple aspects that can determine the measurement of educational processes. Therefore, Moreno et al. (2018) affirm that the quality of professionals in education does not depend solely on improving the results in the Saber tests but also on designing adequate curricula that match the education policies according to the country's needs. The faculties of education play a critical role since they are the calls to propose curricula following the Colombian contexts and scenarios.
Relationship between Educational Quality and Saber Pro Test
The concept of higher education quality is not new. According to Ruben (2018), this concept has looked for excellence in teaching, research, and the projection of activities in society. However, talking about educational quality involves the adjustment of the different scenarios that converge in the robust training processes that respond to the current demands of society. In this way, in the perspective of Rangel (2019), for Colombia, Saber tests are a valuable instrument in decision-making in the educational service and constitute the basis for reorienting processes of improvement in the quality of education.
Ensuring students reach rigorous standards is a crucial goal of equity in education. However, many questions the value of standardized testing, as the opportunity to receive a high-quality education and graduate adequately prepared for university-level academic studies remains inequitable (Jiménez y Boser, 2021). To construct a concept of quality that responds to the reality of education, research on this matter suggests contemplating four elements: Excellence, Resources, Merit, and Added Value and Results (Figure 1), which energize the closest definition of the topic.

Source: Taken from Ahumada et al. (2019), modified Giraldo, Abad y Díaz, (s. f.).
Figure 1 Elements to build the concept of quality
Meanwhile, the dialogue of knowledge around the quality of education and its relationship with saber tests continues. Cifuentes et al. (2018) affirm that evaluation is not only a matter of standardized tests, and the quality is not only the result of them. They are just one of the aspects of the educational system. We should not only see the results of national and international standardized tests but see the system in general and understand that there is a need to advance towards the quality of education with evaluation help. The educational quality approach has transformed into organizational quality, developed in the industrial and business environment. That is, we went from an educative quality concept supported by an unstructured ideal of improvement built on subjective evaluations to quality based on results involving factors of efficiency, productivity, and improvement evaluated through objective measurements over time (Delahoz-Domínguez et al., 2020).
These debates seek to determine the link between educational quality and the results obtained in standardized tests such as Saber Pro. Other studies affirm that it is crucial to point out that evaluation has become a subject of reflection not only from the teaching perspective but also occupies relevant places in institutional discussions and the interests of educational systems. From this approach is assumed that the evaluation becomes the assessment made from certain historical and social permanence in each context (Parra, 2018).
From these statements, the theoretical debate can be concluded by affirming that the administrative and operational processes proposed by a high-quality management model impact the performance of the Saber Pro Tests. It affects students' training since the test only evaluates professional and work context (Delahoz-Domínguez et al., 2020). However, contrary to these ideas Martin Calvo (2018) says that the quality of education is associated with evaluation, and it is understood as the measurement of results. A conception underlying the conviction that the central task of institutions is not education but the training of young people for immediate application performances or skills.
Materials and Methods
The research is part of the mixed non-experimental approach of a descriptive type, since it accounts for the results of the Saber Pro tests students. They are part of the bachelor's program in Basic Education with Emphasis in Mathematics, Humanities and Spanish Language from 2019. It should be noted that the program is part of the study offered in distance learning with virtual support at the Faculty of Distance Learning of the Pedagogical and Technological University of Colombia -UPTC. The analysis also allowed to establish a projection through a comparison between the results 2016 to 2019.
Table 2 describes the selected sample, which had the participation of students enrolled in the ninth and tenth semesters of the program in 2019. The population is heterogeneously composed of young people between 18 and 25; this group has more women than men. They all are from different regions of the country.
The population under study corresponds to 210 students from the Headquarters of Tunja, Duitama, Sogamoso, Chiquinquirá, and Bogotá, who took the exam. Most participants are female students with 80% and the male gender with 20 %.
The test results presented by the students of the bachelor's program are obtained from the databases of the Colombian Institute for the Evaluation of Education-ICFES. The results were used to perform a descriptive analysis of the performances obtained by the group. The result analysis is protected within the informed student's consent. The systematization process was carried out with the information globally provided to the institution by the group that presented the Saber Pro exam in 2019.
Results Discussion
The descriptive statistical analysis of the tests presented by the students from the bachelor's program in Basic Education with Emphasis in Mathematics, Humanities and Spanish Language of the Faculty of Distance Learning of the UPTC corresponds to the year 2019. The analysis is carried out according to two aspects: in one hand, the results of the Generic Competences are presented and analyzed. On the other hand, specific modules in Education results and analysis are presented.
Descriptive analysis of Generic Competences
The generic competencies correspond to Written Communication, Quantitative Reasoning, Critical Reading, Citizen competencies, and English. The analysis process begins with the overall score.
Concerning Figure 1, the program performance is lower than the institutional average that exceeds average. In the same way, it is below the average of the reference group at the level of all the Universities that offer teaching bachelor's degree programs in the country. In this same sense, it is evident that the program average is also below the reference group of the Common Basic Core of Knowledge - NBC.
The five modules of the Generic Competences: Written Communication, Quantitative Reasoning, Critical Reading, Citizen Competences and English of the program in relation to the Institution, Reference Group and NBC Reference as a projection in relation to the positioning the bachelor's degree in Basic Education with emphasis on Mathematics, Humanities and Spanish Language.
Figure 2 shows the comparative results between program, institution, headquarters, and reference group. The written communication module shows that the program results are below the institution and brunches average. Likewise, the reference group is below the average of the program. In quantitative reasoning, the students' performance is above the reference groups but below the institutional and brunch average.
In relation to the critical reading module, the students program performance is below the averages of the reference group, the institutional average and that of the brunches. In the citizen competencies module, the students program performance is below the average of the reference group, the institution, and the brunches. In addition, the English module performance is below the averages of the reference groups, the institutional average, and the brunches.
In Figure 3, students' performance in each of the modules of generic competencies shows: written communication, critical reading, English, quantitative reasoning, and citizen competencies; according to results regarding the general competencies of the bachelor's degree students and that these modules correspond to all undergraduate programs. A commitment from the entire community is required, both directors of the institution, academic unit, program, professors, and students to continue strengthening the modules with the best average. In the same way, teamwork is imperative to enhance the dynamics of the modules of lower indicators so that better results are obtained in all the modules of the generic competencies.
From 2016 to 2019, when the program students took the Saber Pro tests, the average of the institution was above 150, it was a strength for the institution. However, given the average conditions, it is necessary to promote spaces and contexts of motivation to design and strengthen training and qualification through workshops that generate interest for students of the different undergraduate programs. In the same way, Figure 4 shows that the averages obtained by the students are below the average of the reference group during the last four years despite the different strategies were promoted by the Direction, the Curriculum Committee, and the faculty.
Figure 5 shows students' performance in each generic modules, the competencies are observed and compared to the institution results and the reference group. It is evident that the written communication module during these four years is below the institutional average but managed to keep it above the reference group. The quantitative reasoning module is below the institutional average but above the reference group average. The critical reading module is, in these four years of analysis, below the institutional average and below the average of the reference group.

Source: Own elaboration
Figure 5 Comparative generic competences program-institution-reference group 2016-2019
The citizen competences module is also below the averages of the institution and the reference group during the years analyzed. Likewise, with respect to the English module, it is also below the averages of the institution and the reference group during these years. Then it is highlighted that, the modules above are the reference group during these four years correspond to written communication and quantitative reasoning.
Descriptive analysis of the Specific Competencies
The modules that comprise these competencies correspond to the training of Graduates, in this sense, there are three specific competencies for this profession: Teaching, Evaluating, and Training. Thus, the analysis of this part of the Saber Pro Test corresponds to compare the population results with the Program and the reference group.
In Figure 6, the results of the modules of specific competencies of the future teacher are observed. The Evaluate module are better than the Teaching and Training modules. They present results with a minimum percentage difference. Due to the implications of the training of a graduate in Basic Education, it is necessary to strengthen the motivation processes and design strategies to consolidate the interest in preparation in the field of pedagogy in such a way that better results are obtained in this specific test.
In Figure 7, it is evident that the results of the reference group in the modules of specific competencies of the future graduates are above the performances obtained by the program students. Dynamics reflect the different actors of the training and preparation process in the various aspects that concern their future performance as education professionals.
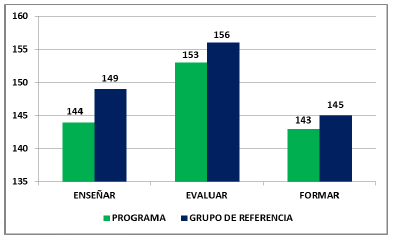
Source: Own elaboration.
Figure 7 Comparative modules of specific competences program and reference group
It is evident the need for the teamwork of both managers, teachers, and students in terms of the pedagogical, disciplinary, and interdisciplinary preparation of students for professional life also the willingness to present the Saber Pro tests.
Finally, in Figure 8, the comparison between the results of the program and the reference group during the last 4 years is presented. There, it is shown that the results of the reference group are above the performance of the students of the program in all the training modules of the future graduate in Basic Education.

Source: Own elaboration
Figure 8 Comparative modules of specific competences program and reference group 2016-2019
It is evident that there is a difference of two percentage points in the three competencies at the program level with respect to the reference group generates. It is important to establish spaces for reflection, which allow to identify the motivation and responsibility that is needed for the presentation of the Saber Pro Test. For the academic program is essential to dynamize strategic plans that awaken the interest of future graduates. The continuous training within the pedagogical, interdisciplinary, and disciplinary field, that is not necessarily measured with the results of a standardized test for a heterogeneous population, could be in the projection of compliance with a degree requirement.
That is, the presentation of the exam, without a minimum of approval, constitutes the requirement for graduation, which is why the projection of post-formal training or students' professional performance should be supported by a satisfactory score in this test without being a reference of measurement for the continuity of their studies.
Final Considerations
In the analysis of the results of the generic competence modules in 2019, of the bachelor's degree in Basic Education with emphasis on Mathematics, Humanities, and Spanish Language students, the Written Communication module stands out as the best average can be considered as a strength to be enhanced. However, the Citizen Competences module, as the one with the lowest score on the measurement scale exposes the weaknesses of the training of graduates in the contents that are evaluated.
In the case of specific competencies with the highest average is Evaluate, and with only one percentage point of difference are the Teaching and Training modules. Concerning the reference group, it maintains the same differential line. Therefore, results should allow an in-depth analysis within the program to generate improvement plans in addition to those already existing. The preparation for the presentation of the Saber Pro is encouraged, especially in what has to do with the specific competences which concern education of future professionals.
The preparation process and the results derived from the Saber Pro tests are co-responsibility between the educational institution and its directors, the program, the teachers, and the students. However, for students, it does not generate a concern of possible commitment since the degree requirement is reached with proof of attendance at the two sessions that comprise the test. Consequently, there is no difference in presentation resulting from the results achieved.
The current regulations of the Ministry of National Education of Colombia, state that there are incentives for the best results. However, these are not significantly representative for students. Meanwhile, they are taken into account by the program and the university to make visible the strength of the academic offer.





















