INTRODUCTION
In recent years, innovation studies have become a fundamental component of the research programs of almost every business and economics school in the world (Spanjol et al., 2023). These studies have established that innovation plays a leading role in the development of economies and firms, as well as in the economies’ transition to sustainable systems (Hashimy et al., 2021; Kihombo et al., 2021; Herrera & Trujillo-Díaz, 2022).
Thus, it is clear that both firms and the regions where they are located should strive to achieve better innovation outcomes that translate into greater amounts of intangible assets within firms (Cardozo-Torres et al., 2021; Cuellar et al., 2022). However, there are glaring disparities among regions in terms of investment in science, technology, and innovation (STI) (Méndez-Morales et al., 2022), which can be explained by a variety of factors, such as public policies or the propensity of firms to innovate (Méndez-Morales & Yanes-Guerra, 2018; Méndez-Morales & Muñoz, 2019).
This propensity to innovate is high when firms do not encounter barriers to management. However, they usually perceive that there are many obstacles that prevent them from carrying out innovation projects and, therefore, from obtaining innovative outcomes. Among the most common obstacles that firms face when introducing innovations are cost, knowledge, and market barriers (D’Este et al., 2012; Pellegrino, 2018).
Cost barriers are typically related to the lack of resources inside or outside the firm and ultimately prevent it from making high investments in its innovation projects (Méndez-Morales, 2019; Anzola Morales et al., 2019). Knowledge barriers, in turn, are related to the impossibility for firms to hire qualified personnel, the lack of knowledge of market rules, and the lack of information on the innovations to be introduced in the firms’ processes and products (Abubakar et al., 2019; Torres de Oliveira et al., 2021). For their part, market barriers refer to the obstacles faced by firms that, despite having developed innovative products and processes, cannot bring them to the market, thus yielding no return on investment and discouraging innovation (Torres de Oliveira et al., 2021).
Although the study of barriers to innovation is very widespread, it was not possible to find systematic literature reviews on this topic, especially in Spanish. Consequently, the question addressed in this paper is: What are the existing research trends and future research directions for the barriers to innovation? In other words, the objective of this study is to provide a systematic literature review on the barriers that prevent firms from achieving the desired outcomes in their innovation projects.
This paper is organized as follows: The first section provides a definition of the barriers to innovation according to the Oslo Manual to understand them from a traditional point of view. The following section describes the methodology employed to identify the relevant literature. The subsequent section analyzes and discusses the different types of barriers to innovation from various perspectives and groupings. The final section draws the conclusions of the study and proposes future lines of research.
Defining barriers to innovation in the Latin American context
Barriers to innovation according to the Oslo Manual
The Oslo Manual is a methodological document that serves as the basis for designing innovation business surveys in much of the world (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development [OECD] & Eurostat, 2018). This document defines barriers and obstacles to innovation as follows:
An innovation barrier prevents a non-innovative firm from engaging in innovation activities or an innovation-active firm from introducing specific types of innovation. Innovation obstacles increase costs or create technical problems, but are often solvable (OECD & Eurostat, 2018, p. 160).
It follows from the above definition that barriers to innovation are those problems that prevent a firm or group of firms, whether innovative or not, from successfully carrying out their research, development, and innovation (R&D&I) projects. Firms encounter such barriers or constraints as they intend to run their projects. These barriers are typically classified in the literature using a homogeneous system that goes back to the first studies on barriers to innovation (Arundel, 1997; Baldwin & Lin, 2002; Mohnen & Rosa, 2002).
The studies on the barriers to innovation have one thing in common: they use the innovation surveys of the countries under study-which are based on the Oslo Manual-to determine whether there is statistical validity in the relationship between certain characteristics of firms at the micro level and firms’ assessment of these barriers. That is, whether firms’ characteristics correlate with specific groups of barriers or constraints to innovation. These studies produced a large number of papers that, using econometric techniques, tried to prove that barriers, indeed, moved firms away from innovative projects and outcomes, especially in European countries (Abazi-Alili et al., 2016; Blanchard et al., 2013; Galia & Legros, 2004; Iammarino et al., 2009; Silva et al., 2008; Madrid-Guijarro et al., 2009; Méndez-Morales, 2013; Ocampo-Wilches et al., 2020; Segarra-Blasco et al., 2008; Tourigny & Le, 2004).
According to the literature, barriers to innovation can be grouped into three types: cost, knowledge, and market factors. Each type of barrier affects the outcome of innovation in different ways and at different stages of the innovation process (D’Este et al., 2012).
Cost barriers are those that affect the cash flow of organizations, either internally or externally. According to Wrålsen et al. (2021), these cost factors can be defined as challenges to financial viability and lead to investors’ uncertainty when entering the business. Cost barriers typically include poor cash flow, lack of external resources (e.g., banks, partners), high cost of introducing innovations, and low profitability of such innovations. The results of innovation surveys in countries such as Argentina, Colombia, Chile, Paraguay, and Uruguay show that cost barriers have a great impact on firms, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Cost barriers in Latin America
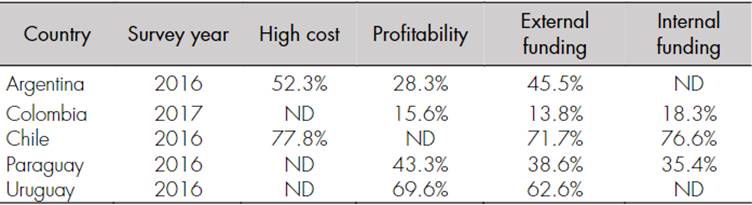
Source: authors’ calculations based on Vargas, Guillard et al. (2022).
The data collected by Vargas, Guillard et al. (2022) vary considerably across countries, in part because of differences in data collection methodologies from region to region. Nevertheless, the data for all countries indicate that cost barriers are major obstacles for firms to innovate.
For their part, knowledge barriers can be defined as the lack of information on the market, competitors, collaborators, technology, and innovation policies and incentives, either among employees or within the firm’s processes, that keep the firm from producing innovation outcomes (D’Este et al., 2012; Roberts et al., 2021). Table 2 shows the proportion of firms in each country that reported that knowledge barriers prevented them from innovating.
Table 2 Knowledge barriers in Latin America
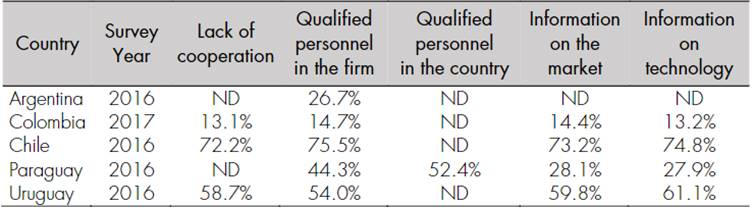
Source: authors’ calculations based on Vargas, Guillard et al. (2022).
Market barriers, in turn, can be defined as those obstacles that prevent firms from bringing their innovations to the market and, therefore, keep firms from achieving their innovation outcomes. These barriers include, among others, inadequate national intellectual property policies, uncertain demand, lack of public policies to foster innovation, a market dominated by large and traditional firms, small market size, and sectoral technological dynamics (D’Este et al., 2012; Sulikashvili et al., 2021). Table 3 shows the behavior of these barriers in Latin America.
Table 3 Market barriers in Latin America
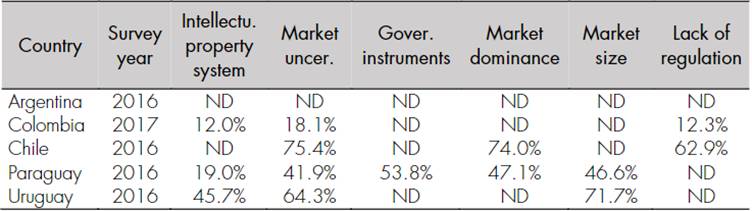
Source: authors’ calculations based on Vargas, Guillard et al. (2022).
Although the use of different measurement methods precludes a direct comparison of the survey results, it is possible to observe that firms in these countries have been affected by the barriers to innovation.
The use of innovation surveys based on the Oslo Manual provides valuable information for the measurement of barriers to innovation. However, not all barriers are addressed in the surveys, as it is impossible to have a complete inventory of the barriers faced by firms in different countries. Consequently, it is essential to take into account that other data collection methods, such as case studies, are also useful to analyze these types of barriers. Similarly, understanding how firms perceive barriers to innovation outside the logic of the Oslo Manual is important to determine how they face them and what strategies they adopt to overcome them.
Thus, the purpose of this study is to contribute to the understanding of how the literature has addressed the barriers to innovation in recent years outside the framework of the Oslo Manual. In addition, it aims to provide a new perspective, different from the traditional approach that typically relies on microdata from innovation surveys to conduct econometric studies.
METHODOLOGY
The systematic literature review was conducted in the Scopus database and included open access peer-reviewed documents published between 2016 and 2021. Initially, different combinations of keywords were used to search for results in the field of business and economics. Subsequently, due to the large number of retrieved documents (634), the search criteria were refined to include only documents published between 2019 and 2021. The search string employed in the systematic literature review is as follows:
TITLE-ABS-KEY (barriers AND innovation OR Research & development OR obstacles) AND (LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA,"BUSI") OR LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA,"ECON")) AND (LIMIT-TO (PUBYEAR,2022) OR LIMIT-TO (PUBYEAR,2021) OR LIMIT-TO (PUBYEAR,2020) OR LIMIT-TO (PUBYEAR,2019) AND (LIMIT-TO (OA,"all").
Using this search key, 370 documents were retrieved. The abstract of each document was carefully reviewed seeking to identify literature on the barriers to innovation that did not necessarily rely on innovation surveys based on the Oslo Manual-which is the typical approach in the existing literature. Table 4 shows the number of documents per year that were found using the proposed search string.
After the abstract review, 26 documents were selected that met the initial criteria: they were published between 2019 and 2021; their main topic was cost, market, knowledge, or other barriers to innovation; and they did not necessarily adopt the Oslo Manual’s approach. Figure 1 summarizes the methodology used to identify relevant publications.
RESULTS
Upon reviewing the selected documents, it was found that 10 articles focus on knowledge barriers, 12 articles address market barriers, and 14 articles discuss cost barriers, as shown in Table 5.
The authors found that the documents reviewed agree with the Oslo Manual-even if they do not necessarily follow the same typology-in that there are three main groups of barriers to innovation: cost, knowledge, and market factors. In addition, the findings of this review were grouped into four categories for comparison: economic approach (developed vs. developing economies); size of the firm (small and medium-sized vs. large firms); business sector (commercial, industrial, or services); and type of effect of the barrier to innovation addressed in the literature. These relationships and findings are summarized in Table 6.
Regarding cost barriers, common problems were identified, such as little interest in funding innovation projects. On the one hand, the education sector in some developing economies proposes innovation tools and projects that can solve problems in the industrial sector; however, the industry remains distant and refuses to fund them (Nsanzumuhire et al., 2021). On the other hand, smart agricultural technologies can potentially reduce environmental impacts. For their part, public-private partnerships have the potential to help the agricultural sector to develop these types of innovative tools, processes, and supplies. However, this progress is hampered by the lack of information and support (Senyolo et al., 2021).
Industrial firms also encounter difficulties in obtaining funding. An example is the pharmaceutical sector, which must constantly introduce innovations in its processes and products. Despite the progress made, it is still a challenge for these firms to raise the necessary funds because adapting facilities, hiring personnel, and carrying out tests are some of the most resource-consuming processes (Fraccascia et al., 2020; Calza et al., 2021). Something similar occurs in the transport industry, where the transition to sustainable energy sources is held back by the high investment required for the service, maintenance, and implementation of the new processes (Björner Brauer & Khan, 2021).
The lack of resources is an even bigger problem in small firms committed to innovation, where the impossibility of allocating internal resources to knowledge management, technology, business strategies, and a healthy work environment hinders innovation (Khan, 2021). Similarly, the absence of initial capital to fund improvement processes or developments aimed at innovation causes fear, especially among small entrepreneurs who invest all their capital in a project. In addition, there is no support from governments for those small firms that want to innovate (Sulikashvili et al., 2021).
With respect to knowledge barriers, an aversion to innovation and new technologies was observed in developed economies. Particularly, manufacturing industries that want to make the transition to sustainable management practices find it complex because it requires readjusting all the processes and, in general, the organizational culture (Roberts et al., 2021). Moreover, the lack of business training and the low efficiency to access and transfer knowledge are major barriers to innovation. Furthermore, some basic processes within firms are still far from making use of innovative technology (Maliqueo Pérez et al., 2021), as someone with the knowledge and tools required is more likely to start their own innovative business (Amini Sedeh et al., 2022).
Similarly, small firms are faced with knowledge barriers when they want to orient their processes towards sustainability but lack the skills and knowledge to do it and receive little orientation (Corazza et al., 2022). These barriers also affect migrants who want to start their businesses, given that this population often does not have the knowledge, let alone the resources, to do so (Pugalia & Cetindamar, 2022). All this translates into an inability to provide efficient and even sustainable services (Viholainen et al., 2021; Greene & van Riel, 2021).
Lastly, market barriers were identified in developed economies with a lack of trust in successful innovation and intellectual property protection (Vargas, Lloria et al., 2022). The market does not always guarantee the effective protection of ideas because procedures are lengthy and cannot prevent the idea from being copied (Hashimy et al., 2021).
Another barrier related to the market was found in commercial and manufacturing firms, in which regulations limit innovation in communication with customers. A concrete example is the prohibition of testing products that have not yet been approved in the pharmaceutical industry. In these cases, the timely participation of users is crucial for the development and introduction of different innovations (Magistretti et al., 2021). It should also be noted that the market is constantly changing and, if firms do not seek to differentiate themselves or evolve over time, they may not be able to achieve success. The challenge lies in continuously engaging the customer, that is, achieving customer loyalty (Chen et al., 2021). In addition, the number of regulations and procedural requirements for new entrepreneurs is extensive, which discourages them from starting their businesses; however, this barrier can be mitigated if governments streamline processes (Braido et al., 2021).
DISCUSSION
In this section, the results of the literature review are classified by topics: a) effects of the barriers to innovation by firm size; b) effects of the barriers to innovation in developed and developing countries; c) effects of the barriers to innovation by economic sector; and d) effects of these barriers on different types of innovations.
Effects of the barriers to innovation in small, medium-sized, and large firms
Barriers to innovation are most common among small and medium-sized firms (SMFs). For example, the risk of losing the invested capital increases uncertainty when it comes to betting on innovation. Moreover, the tools to foster innovation are excessively expensive. These firms also encounter knowledge obstacles, in addition to the lack of skills and limited experience, especially when the business is starting to operate (Sulikashvili et al., 2021). SMFs always face challenges when transitioning to social responsibility and sustainability; however, partnerships can be extremely helpful in overcoming these types of barriers. Furthermore, SMFs report that they are poorly trained to develop products and processes aimed at sustainability (Corazza et al., 2022). A common knowledge barrier among large firms is related to their organizational culture and way of working as a team. In these types of firms, human resources usually have a hierarchical structure with very operational positions that do not adopt innovation strategies (Maliqueo Pérez et al., 2021). These aspects need to be addressed to improve management practices and foster innovation processes (Khan, 2021).
With respect to the challenges faced by entrepreneurs in bringing innovations to the market, the case of immigrant women in the technology industry is particularly noteworthy. They have to overcome the lack of business education and skill training, language differences, little guidance to help them dispel the fear of entrepreneurship, in addition to the limited media coverage showcasing women in technology (De Vita et al., 2014). They also encounter social barriers such as gender discrimination, male-dominated cultures, and limitations to independence and mobility. However, some strategies were identified in the literature review to reduce barriers to innovation among women entrepreneurs: gaining expertise and knowledge on the business and industry, adopting masculine traits, and developing critical entrepreneurial characteristics (Pugalia & Cetindamar, 2022).
Research and development (R&D) barriers can be divided into two main groups: cost barriers and knowledge barriers. On the one hand, cost barriers are related to the high cost of research, development, and exploitation projects for innovation; however, studies highlight that, if the innovation is successful, it will produce internal resources that will lower the barrier. On the other hand, knowledge barriers are mainly associated with qualified personnel to teach, study, explore, and exploit the firm’s innovation processes (Vargas, Lloria et al., 2022).
Effects of the barriers to innovation in developed and developing economies
In developing countries, different barriers prevent the adoption of new technologies and the development and implementation of patents (Cuellar et al., 2022; Méndez-Morales et al., 2022). Studies explain that, at the corporate level, several key organizational technology adoption models include knowledge obstacles, such as risk aversion, which is a critical factor for innovation acceptance. This factor, combined with skepticism towards new technology, can make an innovation a success or a failure (Roberts et al., 2021). Among other knowledge barriers, teaching methods are a key factor in making individuals feel engaged and comfortable with what they are learning. These individuals will ultimately shape the industry in the future (Nsanzumuhire et al., 2021).
The lack of human and financial resources is one of the challenges faced by farmers in adopting climate-smart agricultural technologies in their processes to reduce the impact of climate change in the region (Trujillo-Díaz et al., 2021). Public-private partnerships should consider supporting farmers with caution, taking into account the regulations, which do not offer conducive scenarios to introduce royalty-free seeds to small farmers. The results of the studies suggest that small farmers should develop their expertise and skills to do business and that the private sector should provide them with technical support (Senyolo et al., 2021).
Innovative entrepreneurship (IE) is one of the main drivers of economic development, especially in less developed economies. This includes those businesses that offer new products or services, as well as those that develop new methods to offer existing products or services (Morales-Rubiano et al., 2019).
The knowledge barriers identified in this category include the lack of business education, inefficiencies in accessing and transferring knowledge, shortage of skilled labor, and legal obstacles. In addition, the relationship between IE and perceived entrepreneurial opportunity (PEO) becomes stronger when infrastructure, transport, and communications (customer responsiveness mechanisms) are underdeveloped. Therefore, it was found that entrepreneurial motivation is a great solution to bridge the legal and financial gaps in developing economies (Amini Sedeh et al., 2022).
Developed economies have technologies able to reduce knowledge, financial, and trust barriers. One of these technologies is blockchain, which ensures reliability and optimizes costs and processes (Hashimy et al., 2021). Another example is industrial symbiosis (IS), which is a key factor in the transition from linear to circular economy. However, barriers such as the cost of plant and equipment were also identified, which are exacerbated by the lack of cooperation among industries and the supply-demand fluctuations (Fraccascia et al., 2020).
Effects of the barriers to innovation in industrial, commercial, and service firms
Industrial firms may be the most complex environment to introduce innovations. Internally, it is necessary to adapt facilities, acquire new technologies, and train personnel, which entails great financial risks for investors (Calza et al., 2021). Externally, governmental and cooperative support is required for innovations to have a better chance of success (Björner Brauer & Khan, 2021).
For their part, service firms also require governments to adopt new legislations that support innovation and allow them to improve their service provision. In addition, knowledge barriers such as the lack of global studies on relevant topics delay the adoption of technologies and stifle innovation. Moreover, the lack of information leads to skepticisms about the new ways of storing and ordering data series or customer information (Tijan et al., 2021). To overcome resistance and skepticism, marketing education should be provided to stimulate the understanding of the benefits and motivation towards service innovation (Greene & van Riel, 2021).
In regulated markets and commercial firms, one of the main barriers is regulation, which limits the innovation capacity of businesses. To overcome this obstacle, the literature suggests involving partners from the early stages of the innovation process (Magistretti et al., 2021). Furthermore, diversifying the product portfolio may enhance firms’ performance to a certain degree, although design iteration is necessary throughout the lifecycle. In fact, frequent design iterations can overcome the barriers that innovative firms face when implementing a diverse set of experiences in product development (Chen et al., 2021).
Service firms also encounter market entry barriers. Traditional firms have the trust of customers, which makes it very difficult for new competitors to penetrate the market. In addition, the adoption of new technologies increases uncertainty among customers, who perceive them as a threat to the security of their operations (Braido et al., 2021).
Effects of the barriers on different types of innovations
Different types of innovation have been described in the literature. For example, according to the Oslo Manual, there are product, process, or market innovations. However, a great part of the documents reviewed focuses on two types of innovation that are not considered in the manual: green and social innovations.
Green innovations suggest increasingly more profitable use of alternative technologies running on sustainable fuels, as they aim at reducing pollution (Björner Brauer & Khan, 2021). However, technological and infrastructure barriers remain in this type of innovation. For instance, for the implementation of new advances on fuels -besides facilities adaptations-more accurate and proper supporting technology is needed. There are also cost barriers to invest in new infrastructure or in the adaptation of existing infrastructure. Additionally, governments are required to foster and commit to the internalization of environmental and social externalities (Fraccascia et al., 2020).
Furthermore, when there is still no cutting-edge technology to support the system in the place where such innovations are to take place, costs for importing or adapting technology are higher (Bastas & Liyanage, 2021). For their part, knowledge barriers are quite present as well; the staff’s experience and skills in how new processes work are very poor or nonexistent (Viholainen et al., 2021). Luckily, combined efforts between the purchasing management and operations management research fields could contribute to reducing cost barriers. Regarding governments, they can create subsidies for firms or apply firm-binding regulations (Fraccascia et al., 2020). Finally, barriers can be broken down by creating continuous knowledge, assessing innovations, and favoring knowledge interaction (Gardeazabal et al., 2021).
New circular businesses are also faced with different challenges. To adopt circular models, firms need resources as well as policies and regulations that promote new technologies. However, the most critical obstacle is financial because most customers focus only on the market price rather than on the whole process involved. Firms require investment to carry out improvements; consequently, they have to increase final prices, which poses a risk for investors (Wrålsen et al., 2021). For their part, the automotive sector also wants to move into a circular economy model, not only with electric cars but also with lithium batteries. However, there are shortcomings and gaps in the environmental legislation and in the imposition of fines and restrictions for noncompliance with recycling, considering that a second life of these batteries delays closed-loop recycling (Albertsen et al., 2021).
While no general barriers were identified for the reuse of reclaimed water, there are limitations on the production of drinking water from nonconventional water resources. There is also a need for measures that support integrated resource management and ensure adequate quality and monitoring standards for small-scale collection and treatment systems. Regarding cost barriers, water rate structures are typically designed for urban areas; therefore, smaller service authorities are forced to find ad hoc solutions for local service providers. A possible solution is the implementation of close water-related loops under an innovation agreement prepared to support European governments (Cipolletta et al., 2021).
As for technological innovations with implications in society, blockchain technology has been proposed as a solution to knowledge, market, cost, and other barriers to innovation. This technology also seeks to boost efficiency, lower costs, and ensure immutability and transparency in the exchange of information, while solving problems related to lack of trust, financing, raw materials, domestic and international market limitations, and intellectual property rights (Hashimy et al., 2021). At the same time, it supports the implementation of the electronic government, overcoming obstacles such as lack of information and specialists, the need for training on the use of specific tools, and poor support from management (Saleh et al., 2021).
CONCLUSIONS
Firms around the world are striving to innovate. However, these efforts are frustrated by the existence of barriers to innovation traditionally categorized into three main groups: cost, knowledge, and market factors. In addition, this study demonstrated that there are other types of constraints that affect innovation, such as those related to government decisions and public policies. It was also possible to establish that barriers to innovation in the literature are largely classified according to the original typology proposed in the Oslo Manual.
It was also found that small firms usually have more difficulties in overcoming barriers to innovation because they have fewer mechanisms to deal with them. Likewise, firms in developing countries are exposed to a greater number of barriers, especially related to costs and government regulations.
Firms in all the economic sectors are faced with barriers to innovation; however, they are more difficult to overcome in specific sectors. Finally, it is worth highlighting that cost barriers seem to have a stronger effect than the other types of barriers. In fact, some firms do not even start their innovation projects due to lack of funds.
For future lines of research, it would be useful to understand how other types of barriers lead to reductions in the productivity of firms, that is, whether each of those barriers separately has negative effects on firms and which of those effects is stronger. To this end, case studies or the innovation surveys based on the Frascati and Oslo manuals can be employed. It is also important to understand what government policies lead to a decline in the perception of innovative firms, and whether specific policies implemented in some countries constitute success stories that can be applied in new contexts. On this last point, further research could focus on understanding how tax incentives reduce barriers to innovation, given that, in cases such as Colombia, such incentives seem to generate additional cash flows that can be used to fund new innovation projects (Méndez-Morales & Muñoz, 2019).











 text in
text in 







